
Recent genetic breakthroughs are changing what we thought we knew about our origins. Scientists examining ancient DNA have discovered traces of a mysterious group that once bred with early humans…who they were? Still unknown.
This discovery adds a new twist to the story of human evolution. Who were these mysterious ancestors? Where did they span?
And how did their DNA become part of ours? The answers aren’t simple. In fact, they challenge all that we thought we knew about how humans came into existence. This article explores what researchers have encountered and what they still don’t know.
What is Ancient DNA?

Ancient DNA is genetic material retrieved from living beings’ bones, fossils, or preserved remains. It allows scientists to reconstruct the history of evolution.
Unlike modern DNA, ancient DNA is often in pieces and decayed, making it difficult to analyze fully. But when successful, it can reveal facts about disease, migration, and even relationships between long-extinct species.
Early Clues from Neanderthals

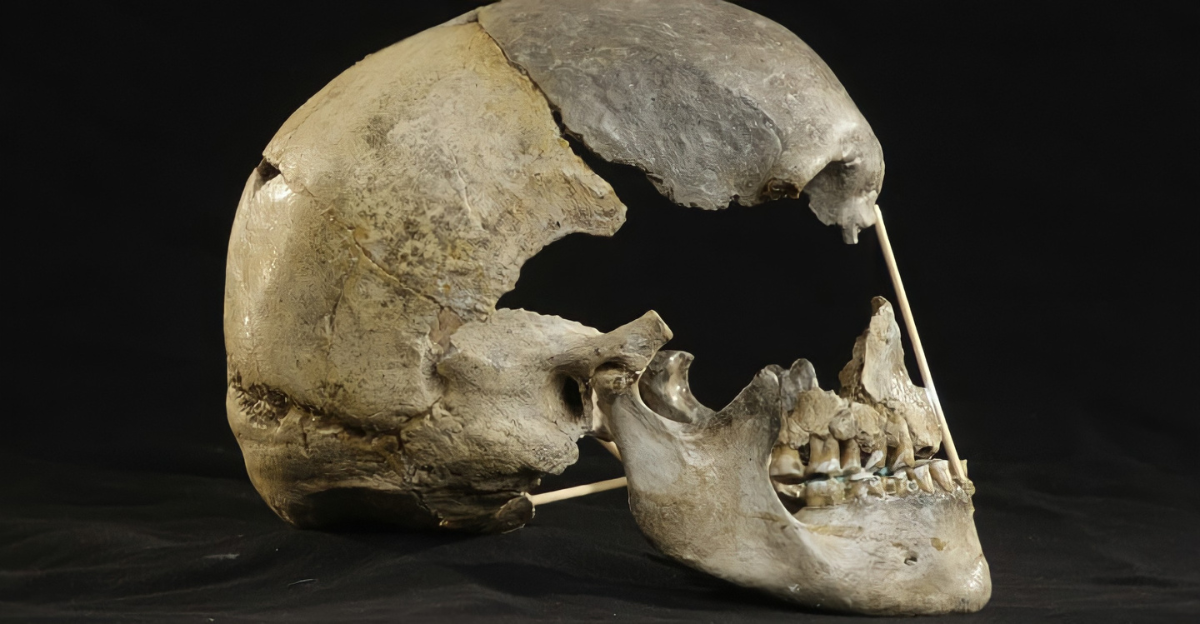
The first breakthrough in ancient DNA came from Neanderthal specimens. It indicated that modern humans outside Africa carry about 1–2% Neanderthal DNA.
This meant that early Homo sapiens interbred with other hominins. It was the first clear confirmation that our ancestors didn’t just replace other groups; they integrated with them.
The Denisovan Puzzle
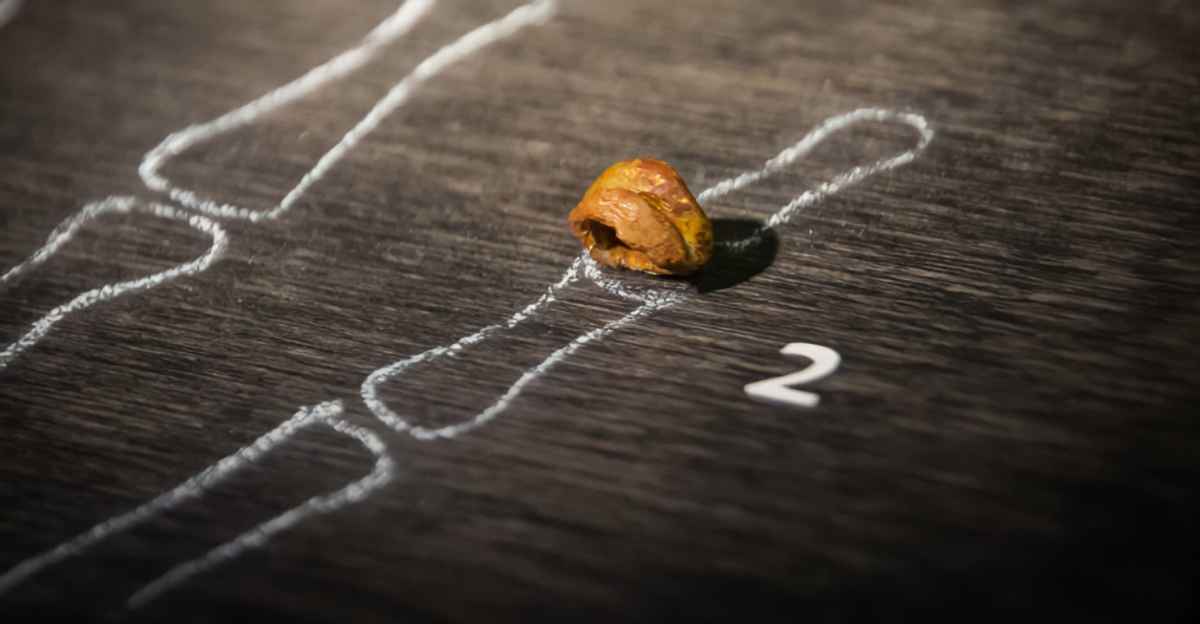

Next came the Denisovans, a group located only through DNA from a finger bone in Siberia. Modern peoples in Asia and Oceania carry notable Denisovan ancestry.
Again, this showed that early humans interbred with yet another group. But these weren’t the only contributors to our DNA.
Introducing the “Ghost” Lineage
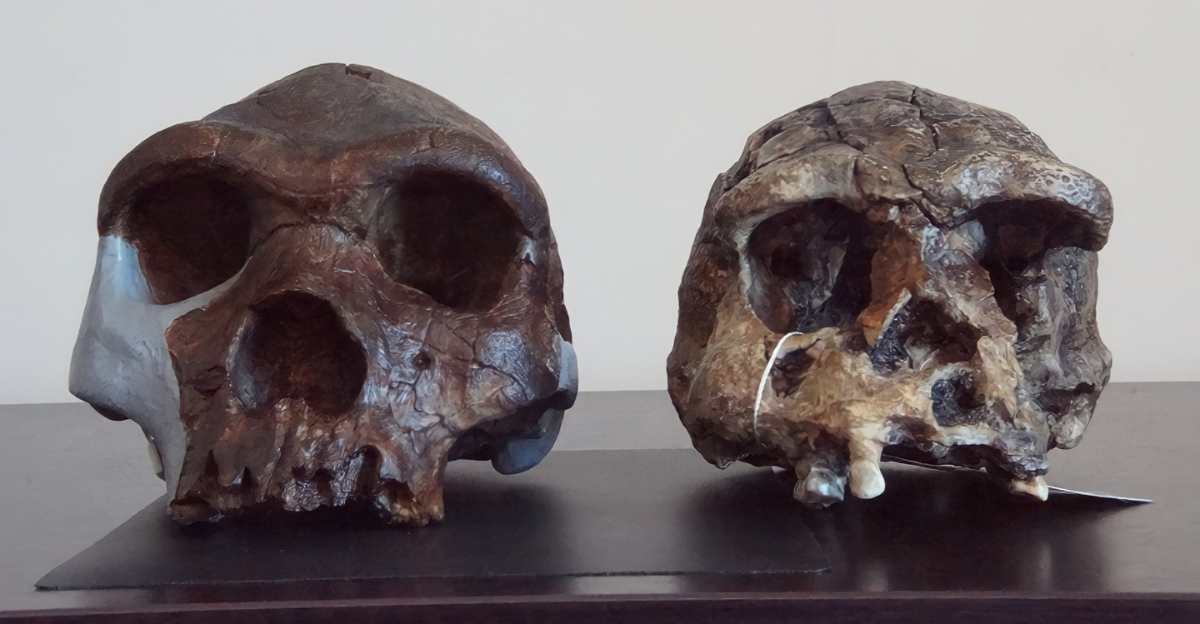

In some groups, especially in West Africa, scientists found DNA that didn’t match any known hominin: Denisovan, Neanderthal, or modern human.
It’s named “ghost DNA” because it suggests a missing ancestor. No artifacts. No bones. Just an unexplained genetic code passed on over thousands of years.
A Hidden Legacy in West Africa
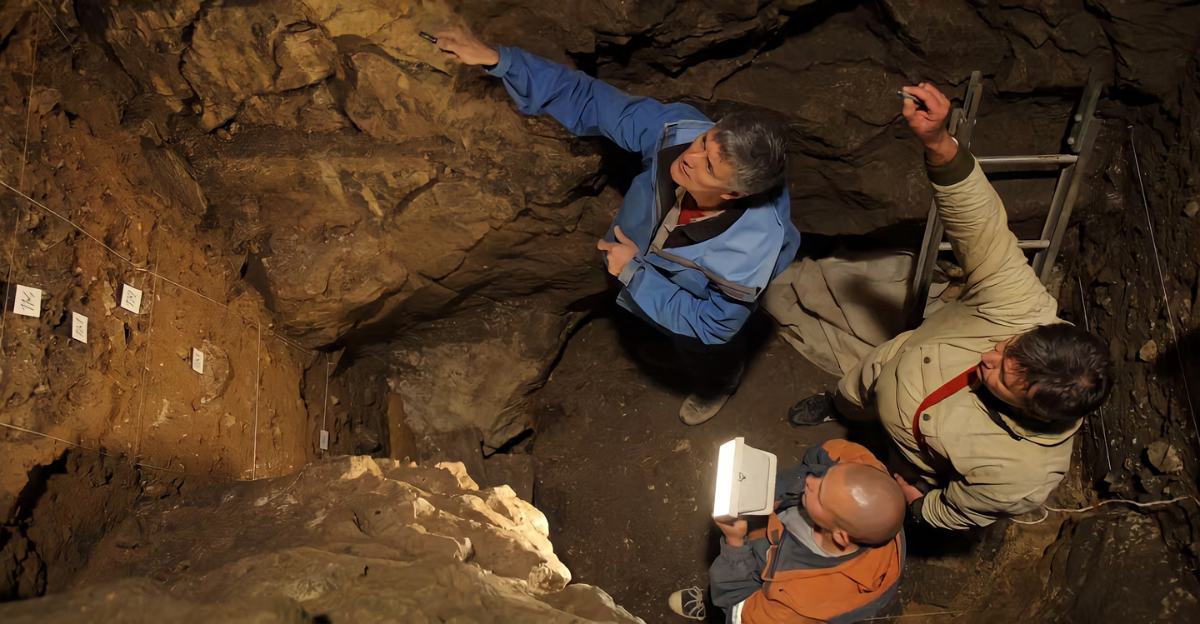

Studies propose up to 19% of some West African genomes originate from this unknown hominin. The evidence indicates interbreeding happened approximately 50,000 years ago.
It wasn’t a rare event, it shaped entire populations. Yet the identity of this group stays completely unknown.
Not a One-Time Event

Interbreeding didn’t just happen sporadically. It most probably occurred on occasions across different regions.
The new data reveals that ancient humans mixed with other hominins more frequently and more widely than previously thought. Human evolution didn’t happen in a vacuum but was deeply interconnected.
Why It Matters

This complexifies our understanding of human history and origins. We used to see evolution as a clear timeline.
Now, it looks more like a spiderweb. Different groups branched off, assembled again, and traded genes. It’s not a straight line. It’s a complex and messy process.
Searching Without Fossils
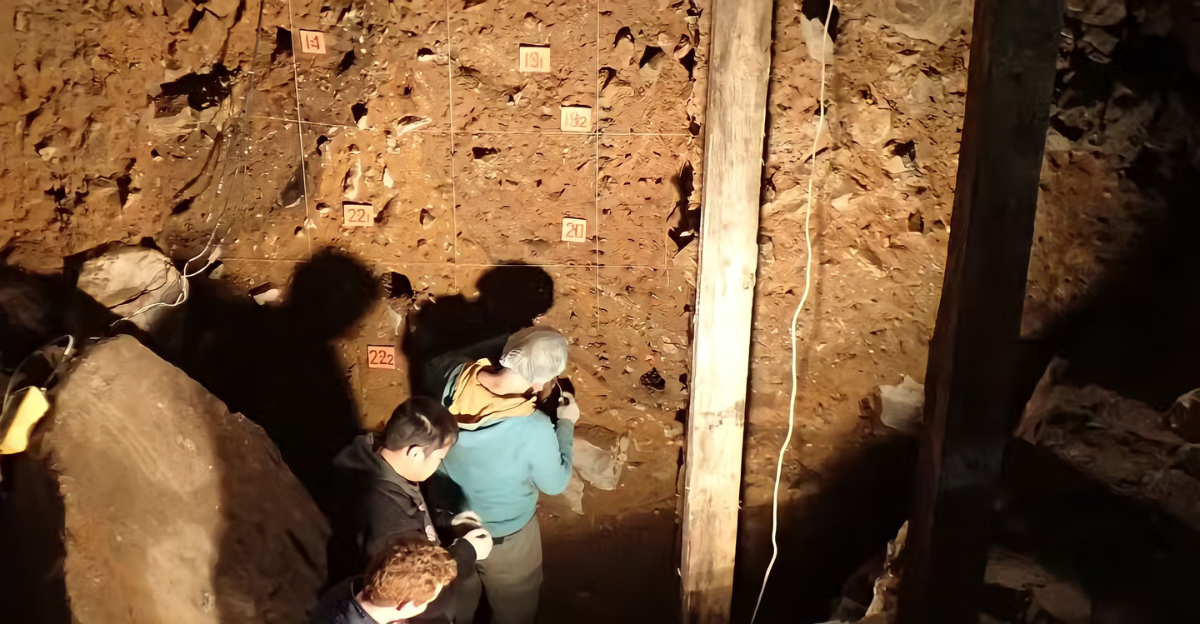

No fossil proof of this unidentified group has been found, unlike Neanderthals or Denisovans. Researchers are relying exclusively on genetic markers.
This makes it more difficult to learn about their appearance, behavior, or where they lived. Their identity remains a mystery.
Other Clues Around the World

Hints of unknown lineages aren’t limited to Africa. Genetic studies in South America, Southeast Asia, and the Pacific have located unusual DNA patterns too. Similar interbreeding events could have happened in multiple regions with other now-extinct hominins.
The Green Sahara Connection

About 7,000 years ago, the Sahara was lushly green and full of life. Genetic specimens from this period suggest the existence of an unidentified population. This group could form part of the unknown lineage contributing to human genetics in parts of Africa.
Lost Peoples of South America

In Colombia, researchers uncovered genetic traces of a group that disappeared roughly 2,000 years ago. Their DNA lives on in some modern Indigenous populations, even though their language and customs no longer exist. It shows how common it is for lineages to disappear while their genes live on.
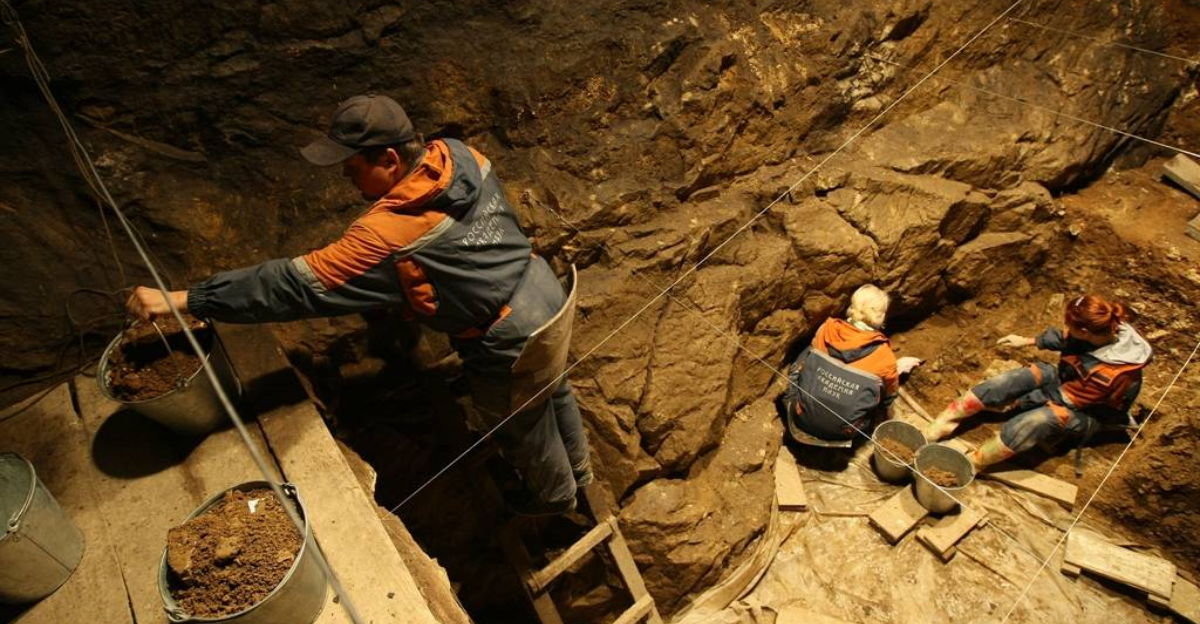
Tools Behind the Discovery

High-powered DNA sequencing, enhanced computing, and better contamination control are making these discoveries possible.
Even tiny fragments of DNA can now be investigated for ancestral clues. The tools are new, but the story they’re uncovering is ancient.
The Challenges of Ancient DNA

Despite the tech, ancient DNA work is challenging. DNA lessens over time, particularly in hot or wet climates. It’s easy to mix up ancient and modern DNA.
And without fossils, many questions are left unanswered. It’s like discovering a page from a book with no title or author.
Why We May Never Know

This unknown hominin may have left no trace except in our genes. Environment, burial practices, or lack of conservation could explain the absence of fossils. But their effect on our DNA is real. We may never know how they appeared, but we know they existed.
Rethinking Evolution
These discoveries force scientists to update human evolution models. Instead of clear-cut stages, the story includes detours, crossovers, and disappeared paths.
Evolution wasn’t about one group replacing another. It was about groups connecting, merging, and adapting together.
What This Tells Us About Ourselves

The ghost DNA story reminds us that humans have always mixed and moved. Migration, connection, and change have made us who we are. Our genetic diversity comes not from seclusion but from repeated contact and exchange with others.
Could There Be More?
Yes. As DNA technology improves, we may find more unknown ancestors. Each new genome added to the global database helps get a clearer picture. There could be numerous undiscovered lineages whose DNA still flows through us.
How This Affects Modern Health
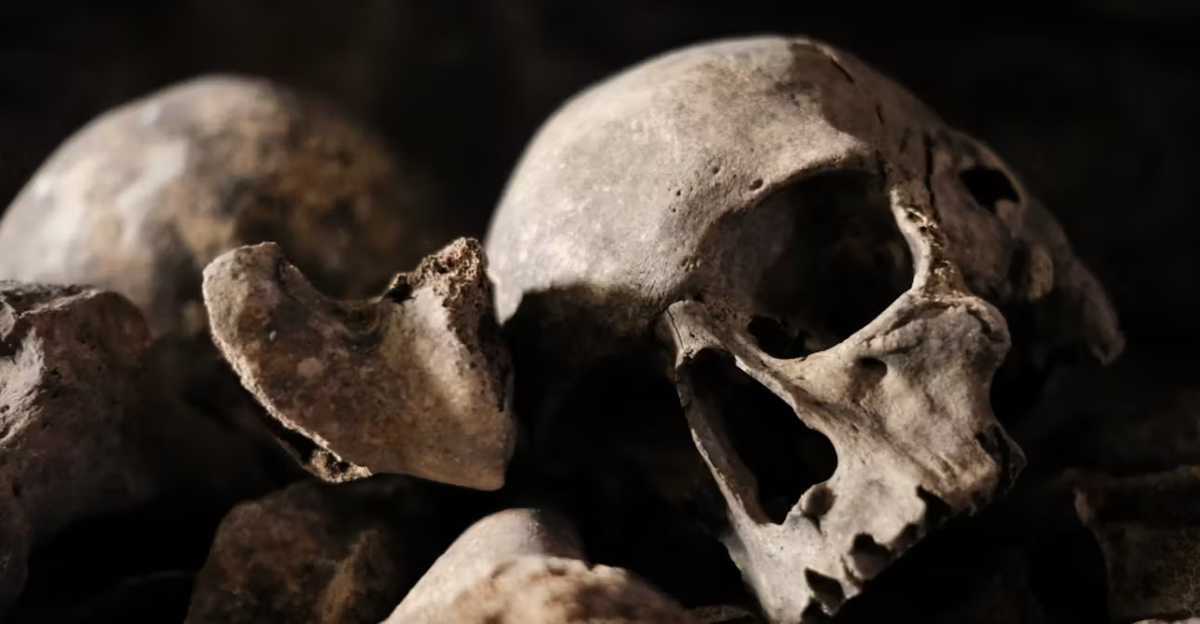

Some inherited genes from ancient hominins may affect immune response, disease risk, or altitude tolerance.
Understanding where these genes came from can help scientists study health, evolution, and adaptation in new ways.
What’s Next in the Search
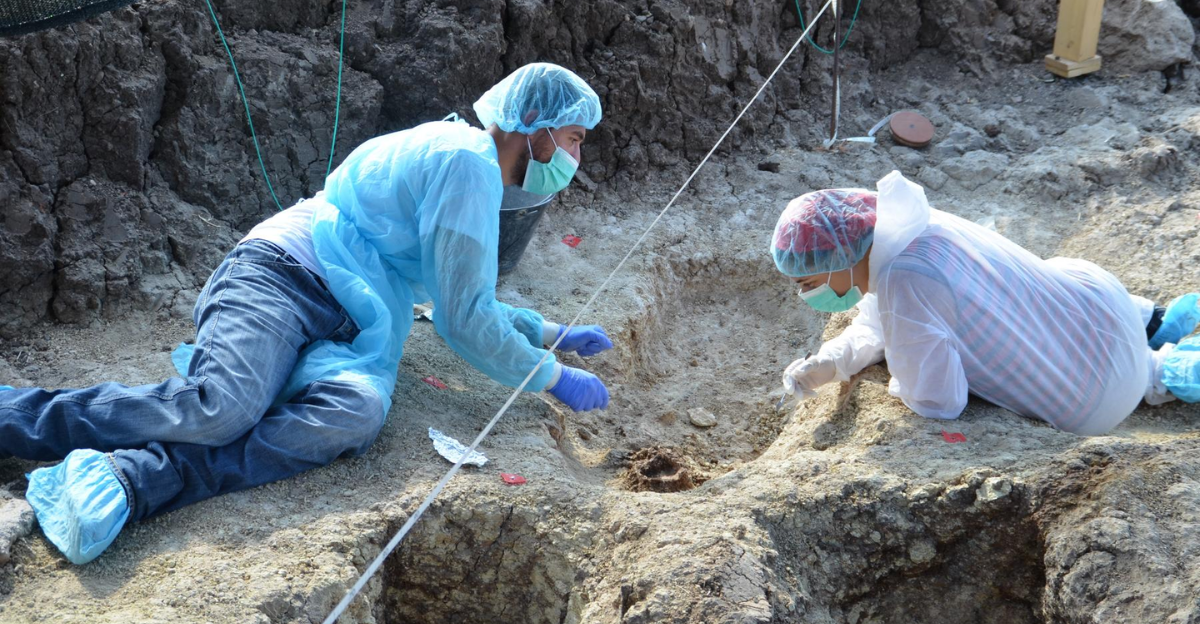

Future research will concentrate on locating fossils that match the ghost lineage and sequencing more ancient genomes from understudied regions.
Teams will combine archaeology, climate science, and genetics to piece together this missing chapter of our story.
We’re Not Done Evolving

The story of human evolution is far from complete. Each finding, like the ghost DNA, adds to a growing panorama of how humans came to be. It reminds us that evolution is still a living process unfolding today.