
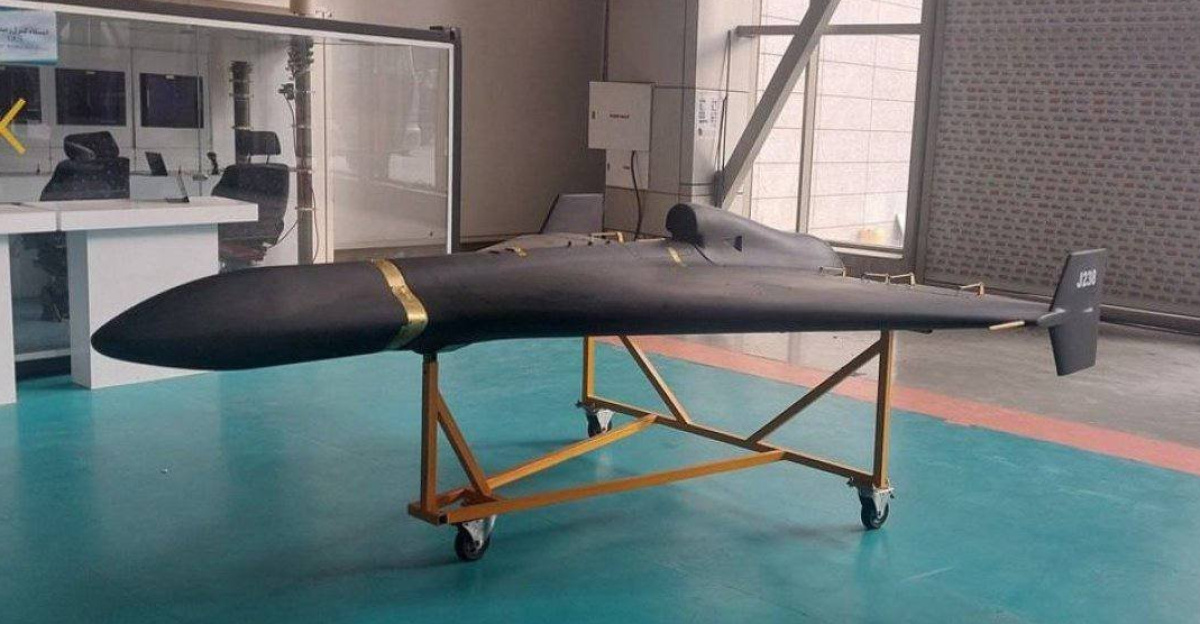
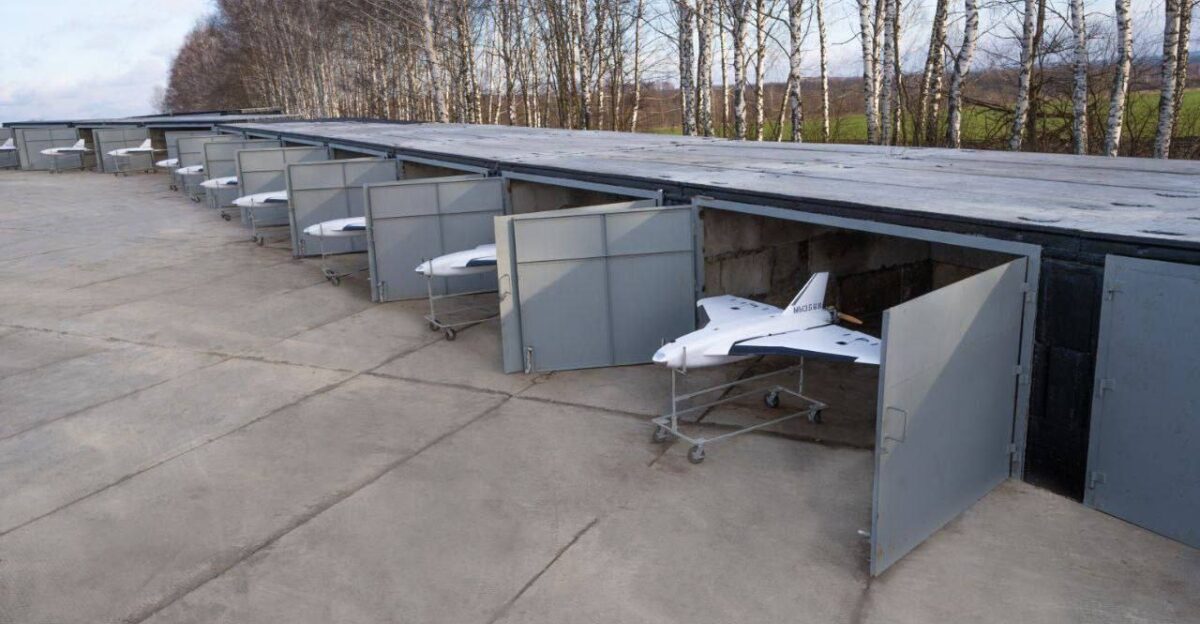
Russia’s air arsenal has grown teeth. After months of relentless drone bombardment using propeller-driven Geran-2 attack drones which move at roughly 115 mph Moscow deployed a new generation capable of nearly double that velocity. By early December 2025, Ukraine’s military detected 138 of these jet-powered systems penetrating its airspace.
The speed jump posed an existential question for Ukrainian air defenses already stretched thin by waves of cheaper, slower attackers. Intercepting these faster threats required technology that didn’t yet exist in operational form. The clock was ticking.
The Growing Gap in Defense
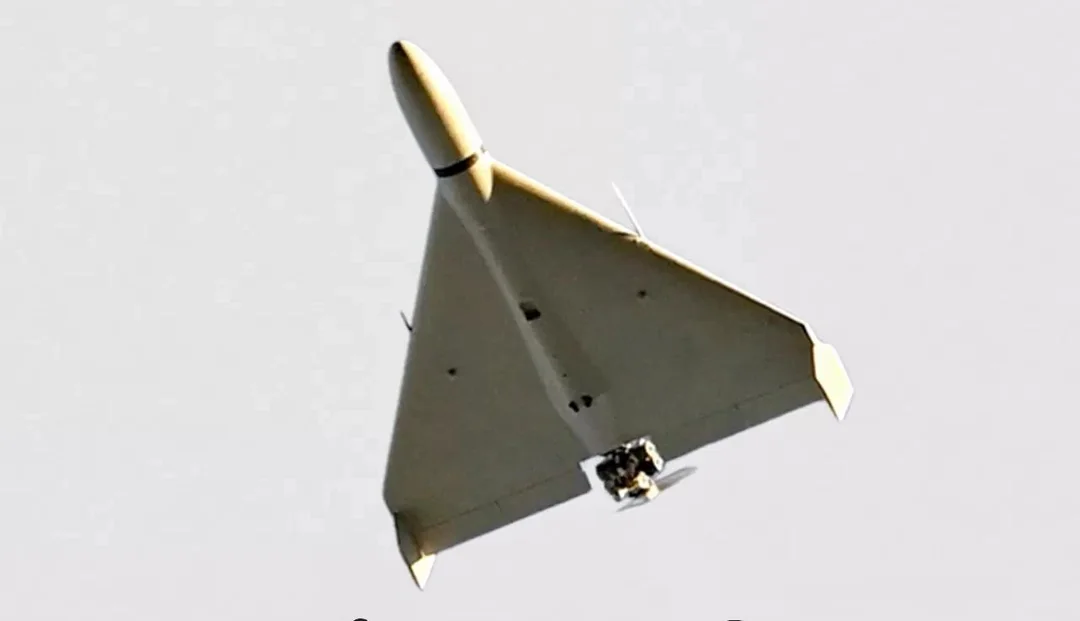

Ukraine’s existing air defense arsenal traditional missiles, machine gun crews, and earlier-generation interceptor drones faced a mounting gap against Russia’s accelerating threat. The Geran-2’s slower speed had allowed defenders time to detect, lock, and fire. But the new Geran-3, powered by a turbojet engine, compressed that window to near-impossibility.
Military analysts warned that without a counter-technology, major Ukrainian cities like Kyiv and Kharkiv could face a new vulnerability. The pressure mounted as Russian strikes intensified, with documented waves striking urban centers. Desperation breeds innovation and Ukrainian engineers knew failure wasn’t an option.
Innovative Homegrown Solutions
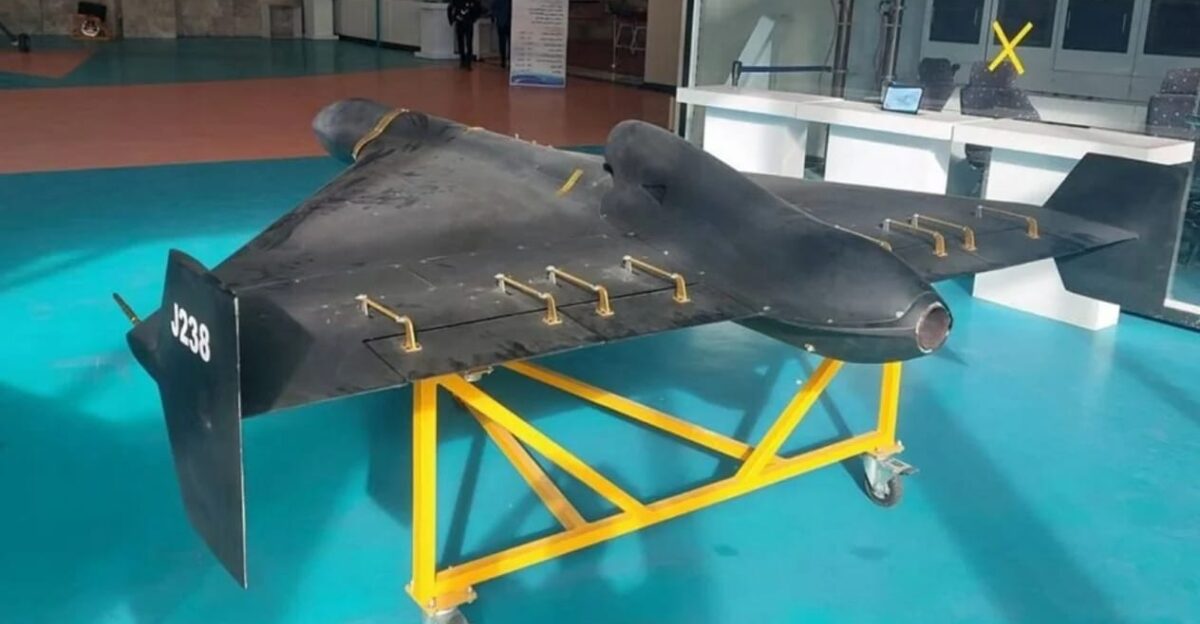

Long before Russia deployed the Geran-3, Ukrainian technologists were building their own interceptor drone ecosystem. By mid-2025, volunteer organizations and defense companies notably Wild Hornets, a Ukrainian startup had developed working prototypes designed to hunt and destroy incoming threats autonomously.
These weren’t imported solutions. They were built locally, tested under combat conditions, and refined in real-time. Pavlo Palisa, a prominent figure in Ukraine’s defense sector, emphasized in September 2025 that Kyiv had already developed interceptor drones “capable of fighting the Shaheds with jet engines.” The message was clear: Ukraine wasn’t waiting passively for a Russian advantage to metastasize.
Introducing the Sting Interceptor
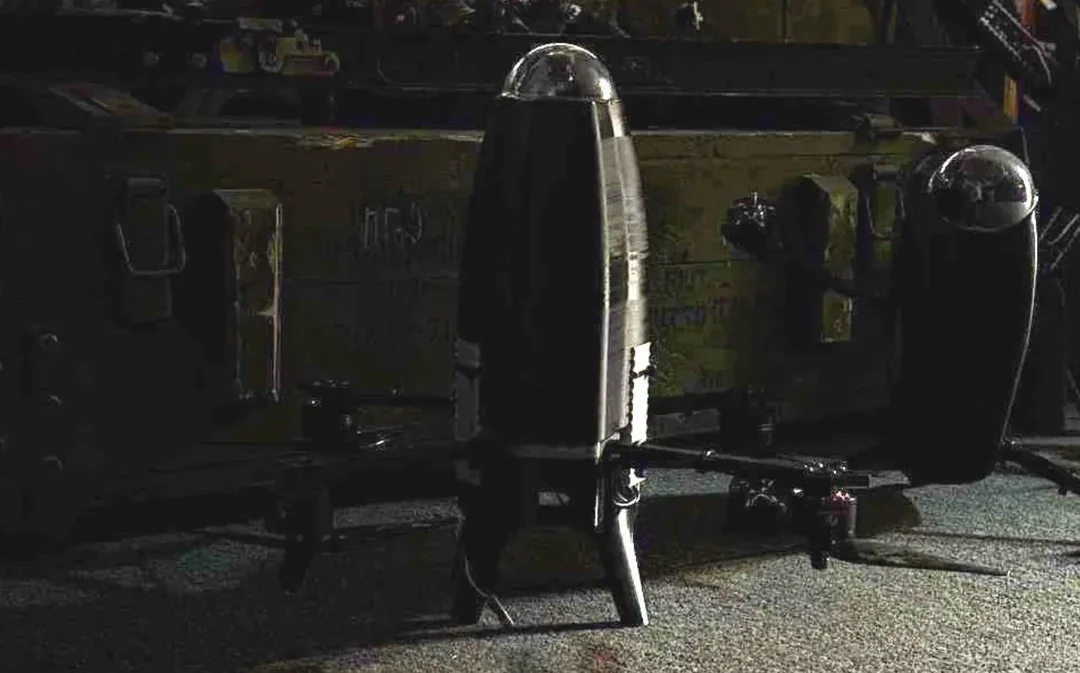

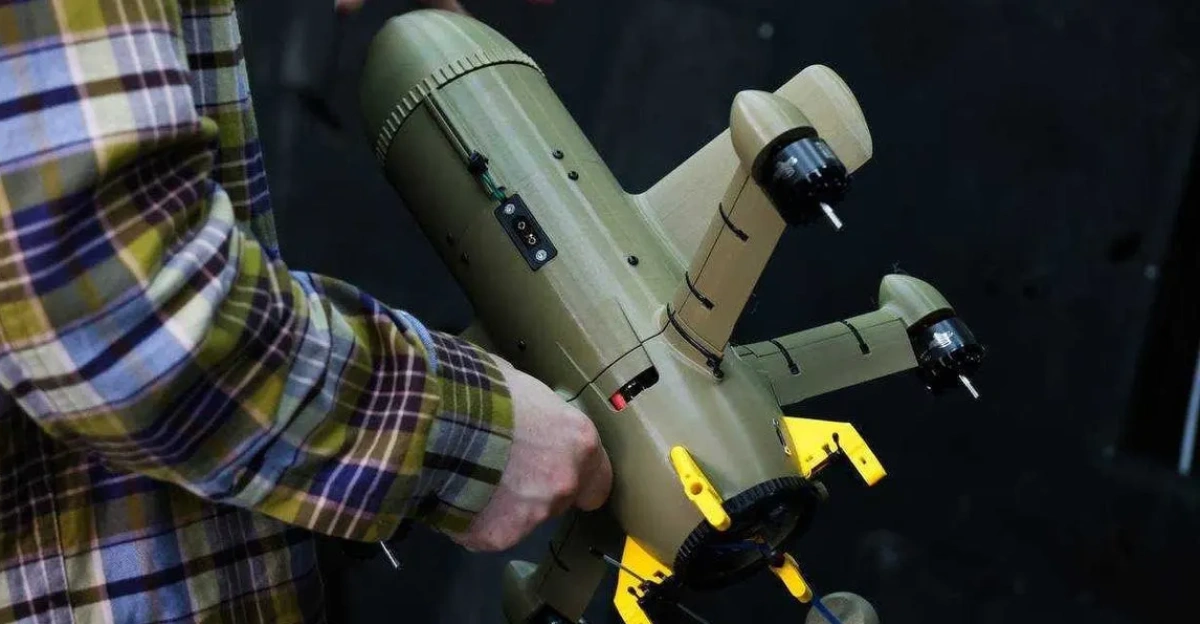
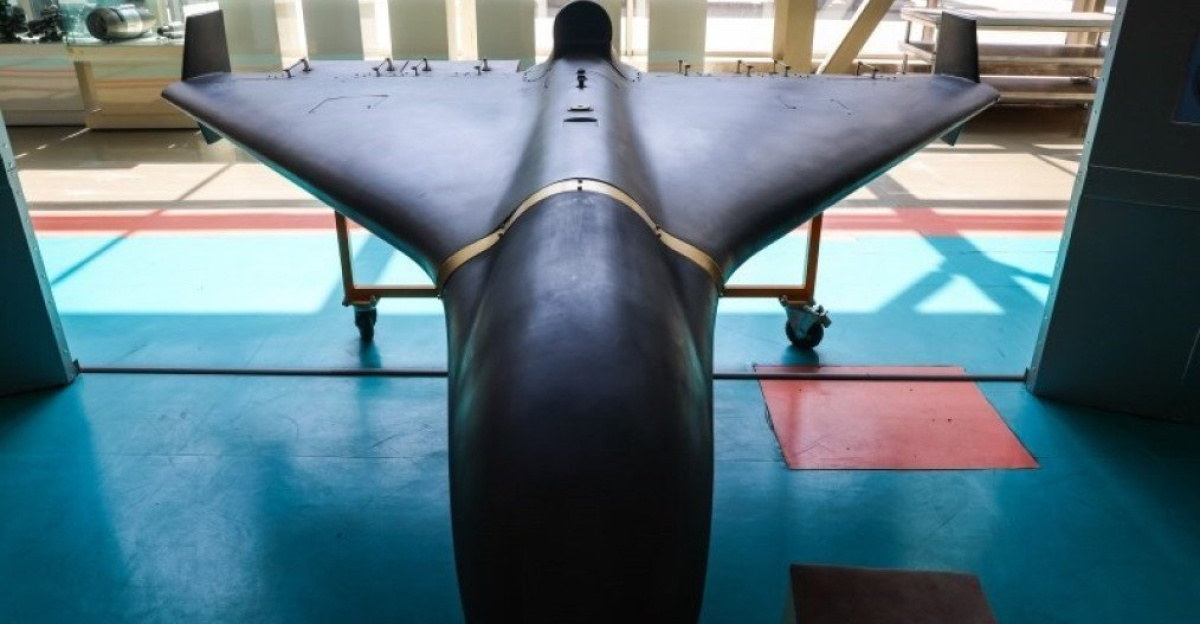
Wild Hornets’ flagship interceptor called the Sting began circulating in Ukrainian air defense units in late 2025. Standing out for its unique four-rotor design and autonomous targeting capability, the Sting flew at approximately 215 mph, powered by electric motors. Its unit cost ranged from $2,000 to $6,000, a fraction of the $20,000 price tag for a Geran-2 and likely far cheaper than Russia’s new jet-powered variant.
The specifications raised a critical question that military observers had been wrestling with: Could a 215-mph interceptor reliably catch a 230-mph attacker? The math appeared to leave no margin for error. Yet Ukrainian developers expressed confidence in their innovative approaches.
First Blood: The Breakthrough

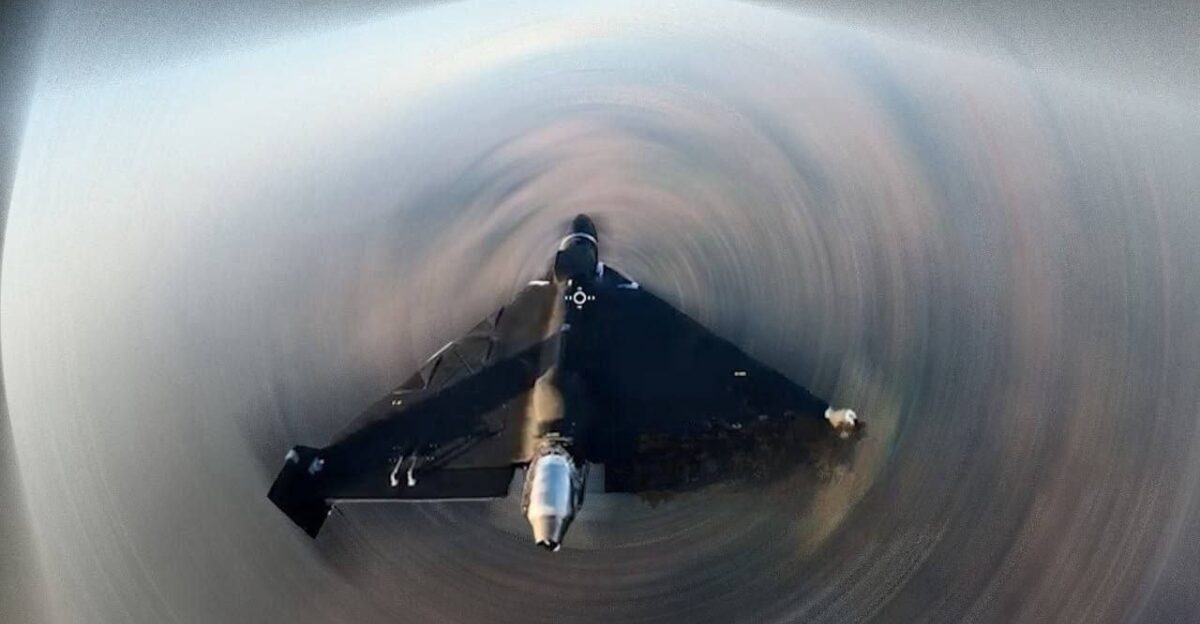
On November 30 and December 1, 2025, Ukraine achieved a significant milestone by confirming its first successful interception of a jet-powered Geran-3 with the Sting interceptor. This historic moment was announced by Serhii Sternenko, a leader in a volunteer drone organization collaborating with Wild Hornets.
He characterized it as “a bit of a historic achievement.” Captured video footage demonstrated the Sting’s tactical capabilities as it outmaneuvered and destroyed a Geran-3 by leveraging speed-matching and strategic positioning. With many of the 138 deployed Geran-3s reported destroyed, this development marked a pivotal shift in the ongoing air defense struggle.
A Moment of Relief

The success against the Geran-3 brought a momentary sense of relief to the Ukrainian military and civilian populations. The ability to counteract such a sophisticated threat reinforced the morale of air defense units that had prepared for overwhelming odds. Strategists, initially concerned about a widening technological divide, expressed cautious optimism about achieving a sense of parity.
For civilians in cities under threat, the operational success symbolized defensive capabilities that could evolve alongside Russian innovations, shifting the narrative from one of vulnerability to one of resilience and determination, serving as a beacon of hope amid the ongoing conflict.
The Strategic Implications

The successful interception of the Geran-3 not only boosted morale but also sent ripples through military strategy discussions. Analysts began reassessing the balance of power in the air, recognizing that Kyiv’s innovation could change the dynamics of future engagements.
This development suggests that Ukraine may now possess the tools to adapt swiftly to new threats, a vital capability given the rapid pace of technological advancements in unmanned drones. The increased confidence in Ukraine’s air defense systems could potentially deter future drone assaults from Russia, reshaping the operational landscape of aerial warfare in the region.
Coalition Support and Mutual Development

International support played a crucial role in bolstering Ukraine’s drone development initiatives. Collaborations with allied nations provided not just funding but also access to advanced defense technologies. Such partnerships enabled Ukraine to refine the Sting and other interceptors, improving their effectiveness against the Geran-3.
This cooperative effort reflected a unified stance against aggression while emphasizing the importance of innovation in defense strategy. As foreign military advisors worked alongside Ukrainian tech experts, the emphasis on shared knowledge and resource optimization paved the way for substantial advancements in counter-drone capabilities.
Continuous Improvement
Acknowledging the rapid shifts in battlefield technology, Ukrainian engineers are committed to continually improving the Sting interceptor. Feedback from frontline use was integral to its iterative development, allowing for enhancements in speed, targeting accuracy, and operational durability.
Every successful interception brought invaluable data that informed future upgrades and battle strategies. The process of adaptation underscored a broader trend wherein frontline realities directly shaped technological advancements, ensuring that Ukraine remained responsive to the evolving tactics employed by Russian forces.
A Resilient Future
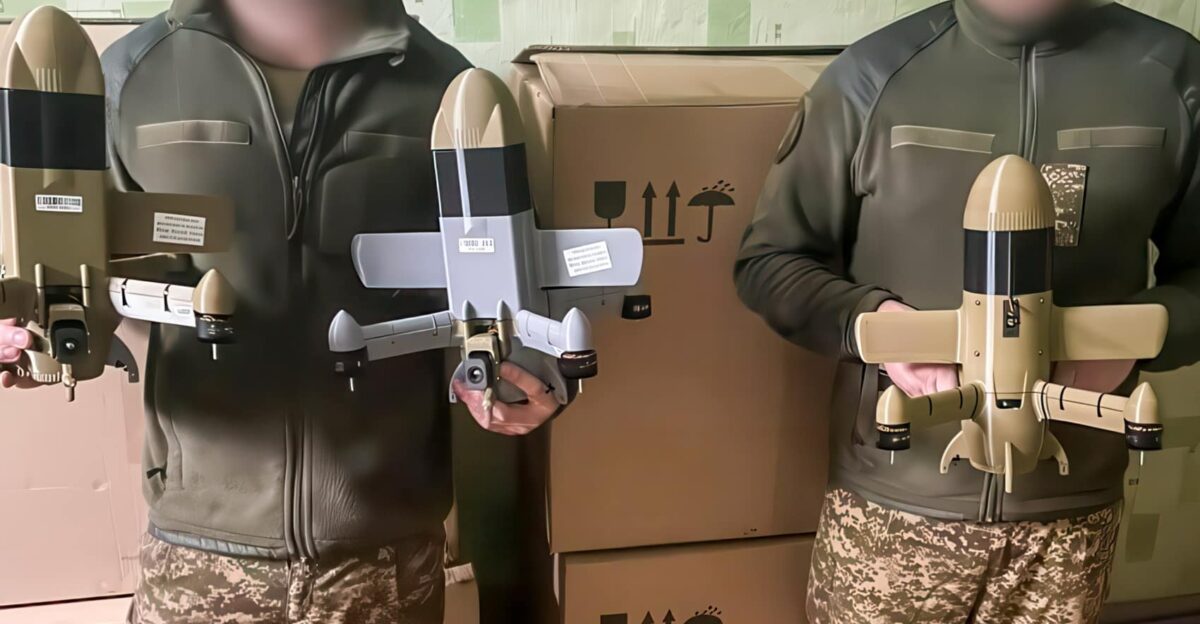

The successful deployment of the Sting against the Geran-3 not only marked a tactical victory but also illustrated Ukraine’s resilience in the face of relentless pressure. Ukrainian officials noted that such innovations could lead to a shift in momentum in air warfare. They reflected a commitment to continuous evolution, driven by necessity and ingenuity.
This spirit of defiance was palpable, as military leaders emphasized the importance of adapting quickly and efficiently. As Ukraine prepared for future challenges, the Sting’s success highlighted a critical narrative: that innovation is often born from adversity, paving the way for a safer sky over Ukraine.
Civilian Impact and Community Response
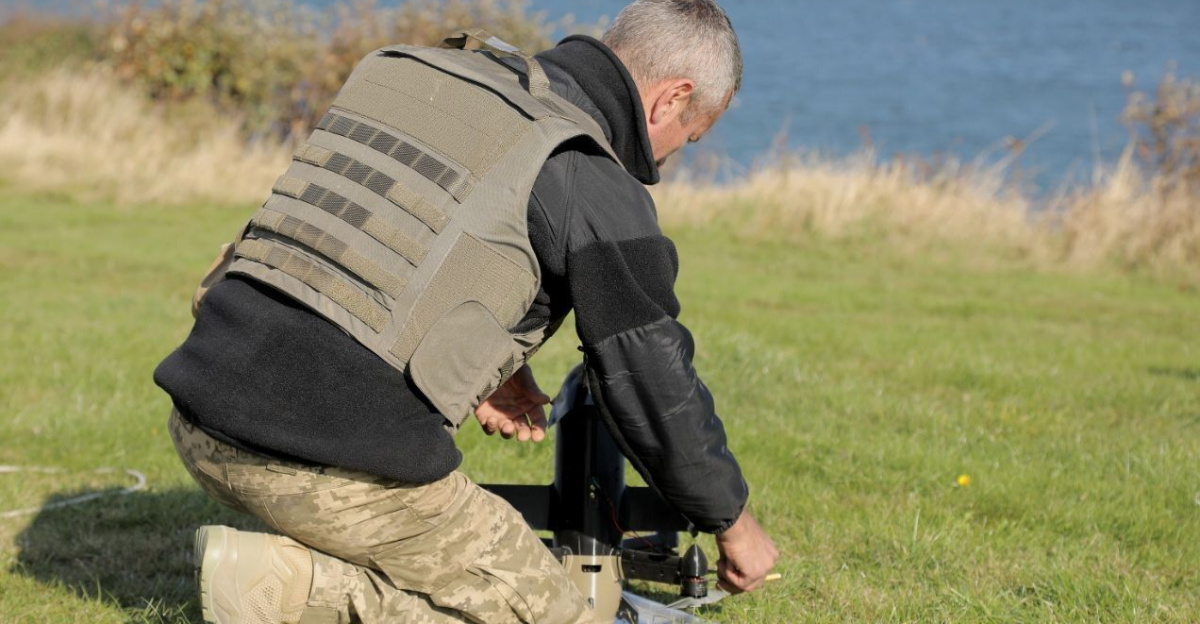

The successful interception of Russian drones by the Sting provided a surge of hope amongst civilians living under the shadow of impending aerial threats. Many citizens expressed feelings of relief and gratitude for the technological advancements protecting their communities.
Grassroots support for defense initiatives has grown, fostering a strong sense of community spirit amongst Ukrainians determined to defend their homeland. These advancements cultivated a sense of shared purpose, serving as a reminder that technological progress can bring communities together against common adversaries and strengthen national resolve.
Broader Lessons for Modern Warfare

The narrative surrounding Ukraine’s development and deployment of interceptor drones serves as a cautionary tale for militaries worldwide. The rapid evolution of drone warfare necessitates that nations become proactive in addressing emerging threats.
Ukraine’s experience underscores the importance of adapting technology to counter enemy capabilities while simultaneously fostering domestic innovation. Military analysts argue that this case highlights a critical evolution in asymmetric warfare, where less powerful states can harness creativity, local industry, and community support to counter technically superior foes, redefining modern combat strategies.
Comparative Cost and Effectiveness

When examining the cost-effectiveness of the Sting versus its adversaries, the financial advantage becomes stark. The Sting costs between $2,000 and $6,000, while the estimated cost of a Geran-3 remains above $20,000. This disparity allows Ukraine to deploy more interceptors without sacrificing quality or capability.
Given that the Sting has proven effective at intercepting faster drones, this financial model supports sustained defense efforts without overextending resources. Military experts note that maintaining a high volume of inexpensive interceptors provides a strategic edge, enabling a flexible response to potentially overwhelming numbers of enemy drones.
Future Developments and Tactical Advances

As the conflict continues, military strategists anticipate further adaptations in drone warfare tactics on both sides. Ukraine’s successful interception of the Geran-3 signals a broader readiness to adopt innovative defense strategies.
Research into enhancing the Sting’s performance is ongoing to improve autonomy and resistance to electronic warfare tactics that Russia may deploy. Continued investment in research and development will be vital not just for maintaining the current balance but for potentially gaining the upper hand in future confrontations as technology evolves at an accelerating pace.
A New Chapter in Air Warfare

The first confirmed interceptions of jet drones by Ukraine mark a defining moment in the modern battlefield narrative. This development not only underscores the innovative tenacity of Ukrainian engineers and military strategists but also highlights the importance of collaboration in contemporary warfare.
As geopolitical tensions continue to evolve, nations worldwide will likely look to Ukraine’s experience as a blueprint for leveraging homegrown technology and cooperative defense strategies in the face of rapidly escalating threats. The Sting and its capabilities are not just tools of war; they represent hope and resilience in an age of unprecedented aerial conflict.
Sources:
Business Insider, Ukraine’s Interceptor Drones and Russia’s New Geran-3 Jet-Powered Drones
Pravda Ukraine, Ukrainian Sting Interceptor Drones Destroy Jet-Powered Shahed
United24Media, Ukraine’s Interceptor Drone Downs Russia’s Jet-Powered Shahed for the First Time
Militarnyi, Ukrainian Interceptor Drone Downs Jet-Powered Shahed
Ukraine Arms Monitor, Sting Interceptor Drone by Wild Hornets