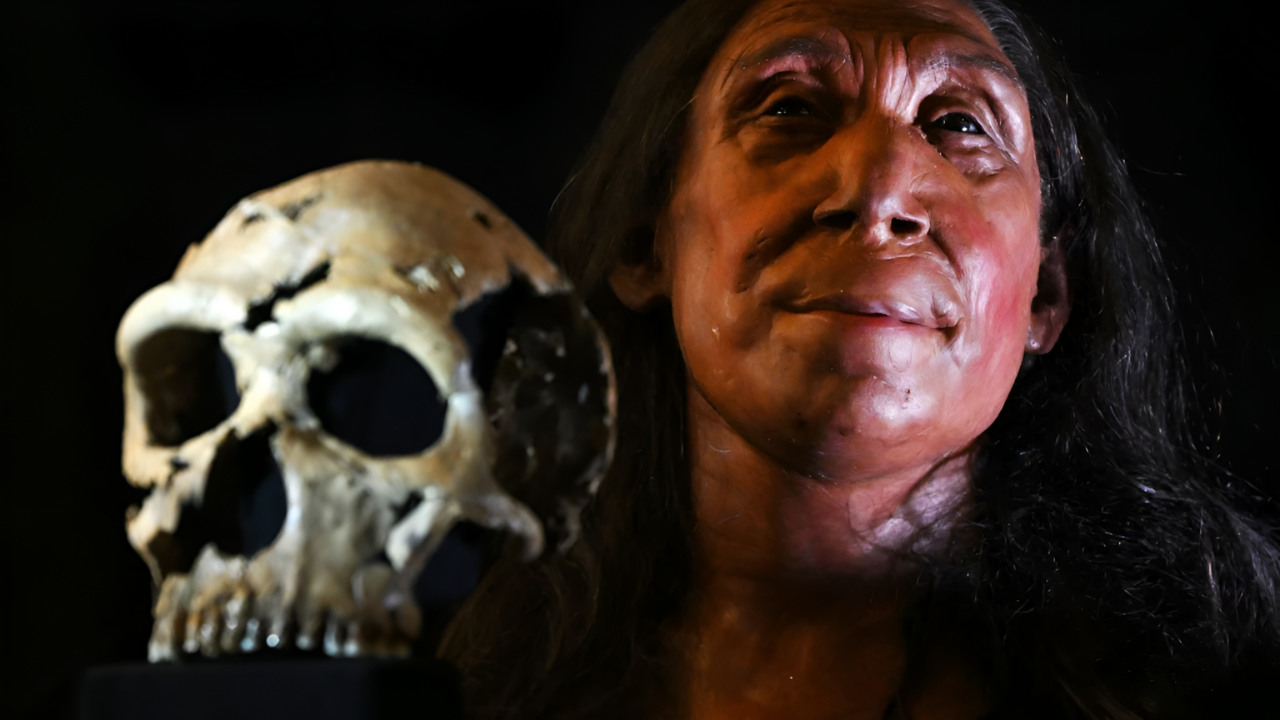

Imagine walking into a museum, staring at a fossil that has gathered dust for decades, and realizing it belongs to a ghost. For fifteen years, scientists knew the mysterious “Denisovans” existed only through DNA found in a Siberian cave—a shadow without a body. Now, the shadow finally has a face.
Anthropologists have unveiled Homo juluensis, also known as “big head” man, a previously unknown species that inhabited Eastern Asia for approximately 250,000 years. They didn’t just survive; they thrived, hiding in plain sight until this very moment.
A Quarter-Million-Year Dynasty

This wasn’t a fleeting footprint in history; it was a dynasty. Homo juluensis held their ground from approximately 300,000 years ago until just 50,000 years ago. Picture a species resilient enough to endure the crushing grip of multiple ice ages, maintaining a stronghold in Eastern Asia for a span of time that dwarfs recorded human history.
Their sheer persistence challenges every simplified map of human migration we’ve ever drawn, proving a distinct, powerful population claimed the East long before modern humans arrived.
The Denisovan Enigma Solved

Since 2010, the Denisovans have been the great “missing persons” case of anthropology. Identified solely by genetic traces from a pinky bone, they lacked a formal species name because no one could match the DNA to a skull. Homo juluensis breaks that silence.
According to the research team, this new classification finally gives the Denisovans a taxonomic home, linking those genetic ghosts to actual fossilized remains. The phantom lineage that haunted our genetic data finally has a skeleton to match its story.
Hiding in the Drawers

The most shocking part of this discovery is where it happened: not in a remote excavation trench, but in the quiet drawers of museums. The breakthrough struck while researchers were devising a new system to organize confusing fossil evidence that had perplexed scientists for decades.
By connecting the dots between “misfit” bones from sites like Penghu and Xuchang, they realized these weren’t random oddities. They were pieces of a single, massive puzzle representing a lost chapter of humanity we had overlooked.
The Experts Were Blindside

Even the hunters were surprised by what they trapped. Christopher J. Bae of the University of Hawai’i, who led the research with the Chinese Academy of Sciences, admitted they never saw this coming. “Although we started this project several years ago, we did not expect being able to propose a new hominin species,” Bae revealed in November 2024.
They went in looking for better organization and came out with a new ancestor, proving that even experts can still be stunned by the past.
A Frankenstein of Features
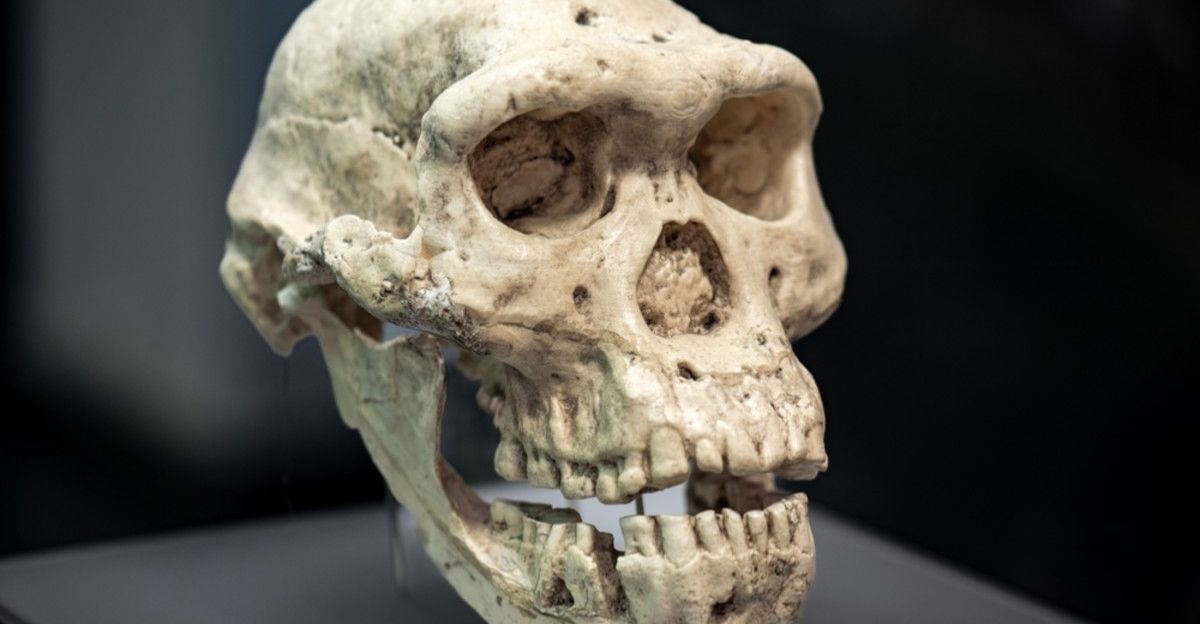
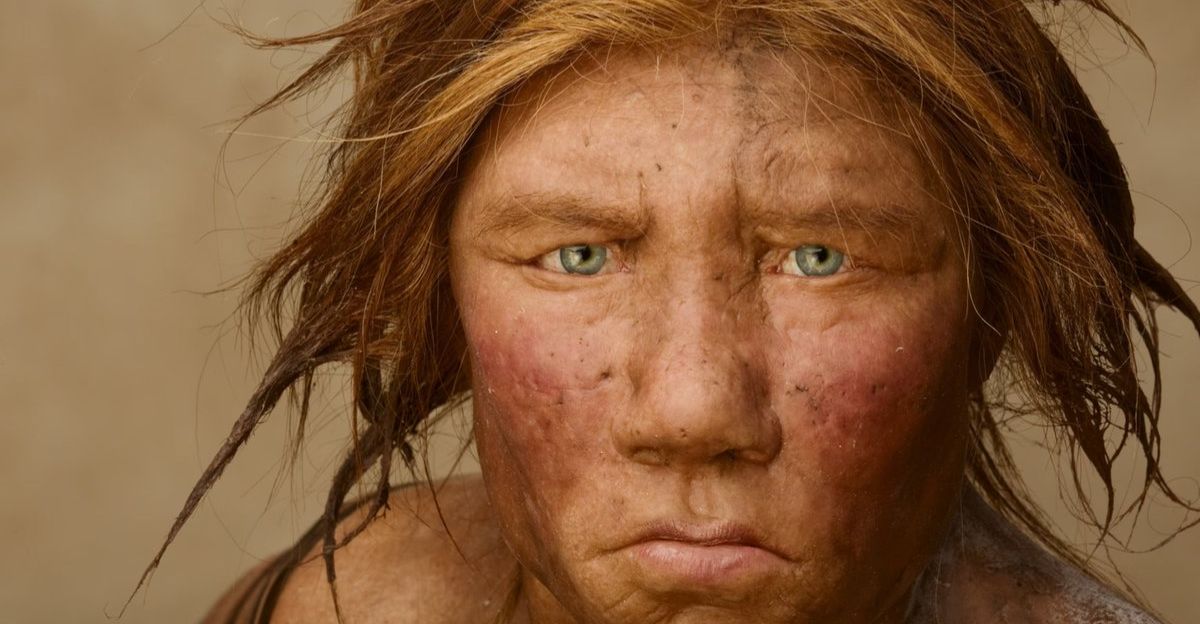
Why did it take so long to see them? Homo juluensis was a biological riddle. The researchers describe the fossils as a “mosaic,” a confusing blend of the ancient and the modern. They possessed the heavy, thick brows of the primitive Homo erectus, yet their teeth mirrored the nuanced features of Homo sapiens.
This strange combination acted like camouflage, tricking scientists into thinking they were looking at two different lineages rather than one unified, distinct species that bridged two worlds.
The Mystery of the ‘Big Heads’
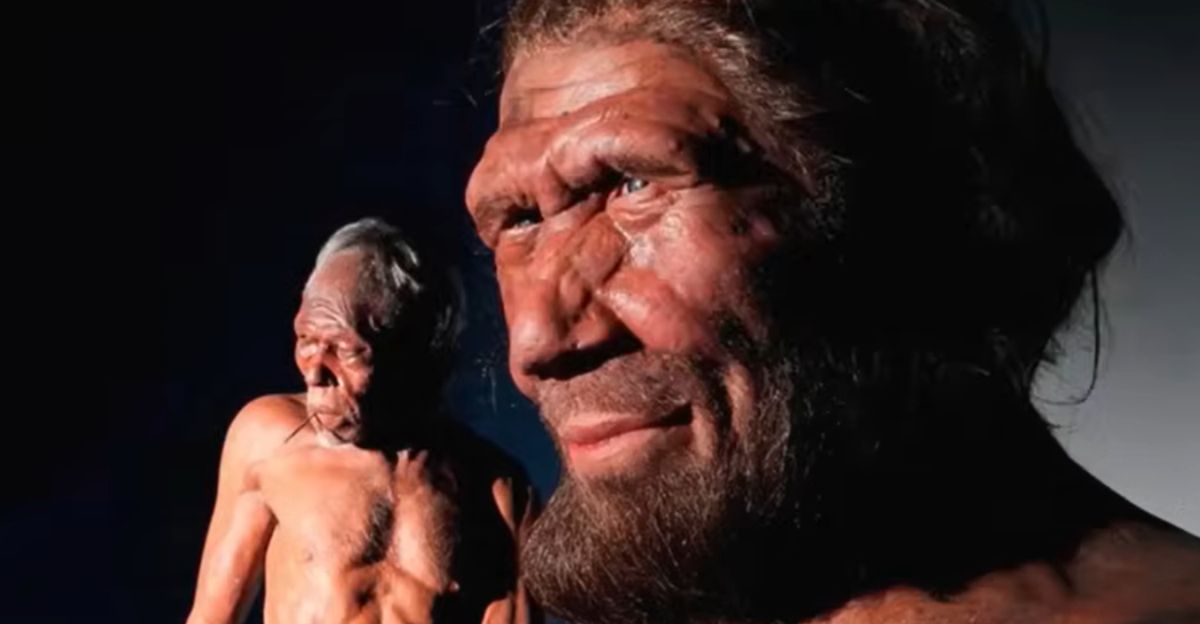

The name juluensis comes from the Mandarin “ju” (big) and “lu” (head), and the moniker is well-earned. These ancient humans carried crania that were massive, breaking records for skull size among Asian hominins. But why the giant heads?
While a large cranium often suggests high intelligence, the biological cost of such a heavy structure is immense. It implies a unique evolutionary path, suggesting these “big heads” were a physically imposing, dominant presence on the ancient Asian landscape.
Lords of the Wild Steppe
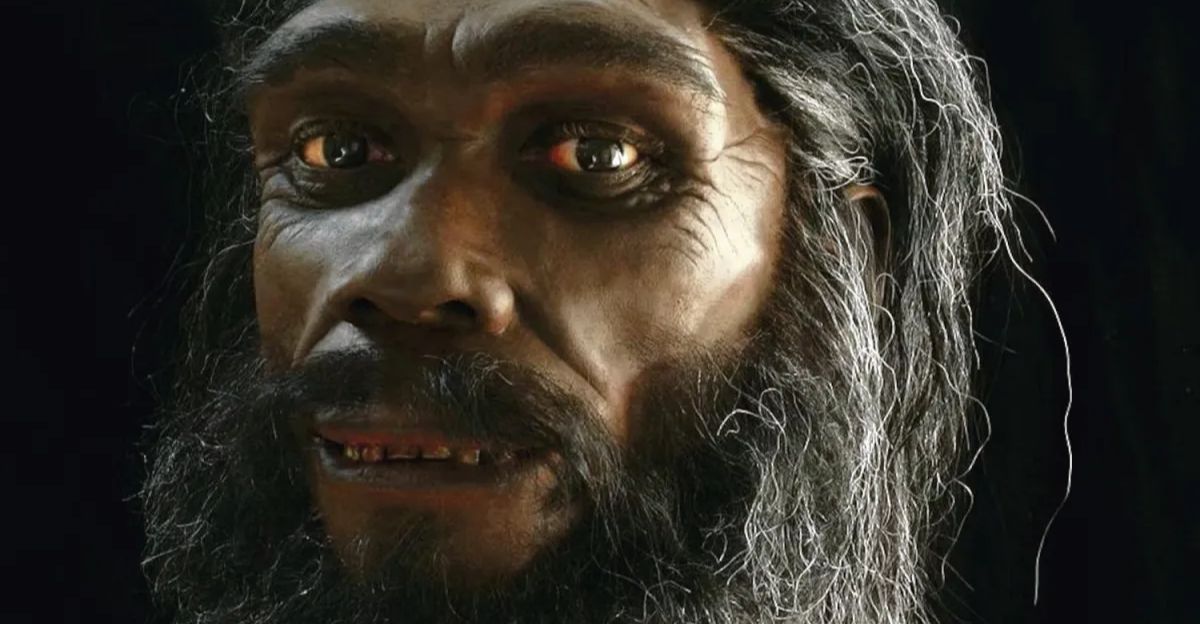

Forget the image of a cowering caveman; these were apex masters of their domain. The archaeological evidence suggests Homo juluensis were sophisticated hunters who tracked and took down wild horses on the open steppe. According to the study, surviving in such a rugged environment required complex planning and social cooperation.
They weren’t just scraping by on the margins of existence; they were the undisputed lords of their ecological niche, processing resources and commanding the food chain for thousands of generations.
Conquering the Ice Age

The timeline of Homo juluensis puts them directly in the crosshairs of brutal climate shifts. To endure the biting freeze of the Pleistocene winters, they had to be innovators. The research indicates they fashioned stone tools and processed animal hides, likely wrapping themselves in furs to survive the cold.
This wasn’t a matter of brute instinct; it was a matter of technological adaptation. They stood against the ice and won, proving they possessed the cognitive spark to manipulate their world just like their Neanderthal cousins.
A Crowded Family Reunion

This discovery shatters the lonely “ladder” model of evolution where one species politely replaces another. The Earth was actually a crowded, chaotic stage. For eons, Homo juluensis coexisted with Homo erectus, Neanderthals, and eventually, early Homo sapiens on the same planet.
Imagine a world where different human species—some giants, some slender, some stocky—crossed paths. It suggests a complex web of rivalry and coexistence that anthropologists are only just beginning to untangle.
Solving the Xujiayao Riddle

For years, fossils from the Xujiayao site were the “problem children” of paleontology—bones that refused to fit in any box. They weren’t quite Erectus, but they definitely weren’t Sapiens. By grouping these stubborn fossils with findings from Penghu and Xiahe, the researchers cracked a decades-old cold case.
The “confusing” traits weren’t mistakes; they were the standard features of Homo juluensis. The puzzle pieces didn’t fit the old picture because they belonged to a picture we hadn’t seen yet.
Rewriting the ‘Out of Africa’ Map

The “Out of Africa” theory just got a massive complication. When modern humans finally pushed out of Africa to populate the globe, they didn’t step into an empty wilderness. They entered an Asia that had been successfully held by Homo juluensis for hundreds of thousands of years.
This suggests the great human migration wasn’t a simple colonization of vacant land, but a high-stakes navigation through territories already ruled by other intelligent, tool-wielding humans.
The Bloodline Connection

With the Denisovan link established, the plot thickens around our own DNA. We already know Denisovans interbred with modern humans. Now that we have a body—Homo juluensis—to match that DNA, the scenario becomes vivid. It’s highly plausible these “big head” humans didn’t just vanish; they may have contributed to the gene pool of modern populations.
The fossils provide the physical evidence that our ancestors likely met, mated, and merged with this newly named species.
The vanishing Act

Despite their massive brains and 250,000-year reign, Homo juluensis disappeared from the fossil record around 50,000 years ago. This extinction is geologically recent—a mere heartbeat in time. What killed them?
The timing is suspiciously close to the arrival of Homo sapiens and major climate shifts. The exact cause remains the villain in this story, a lingering mystery that asks how such a dominant, well-adapted species could simply blink out of existence.
Order from Chaos
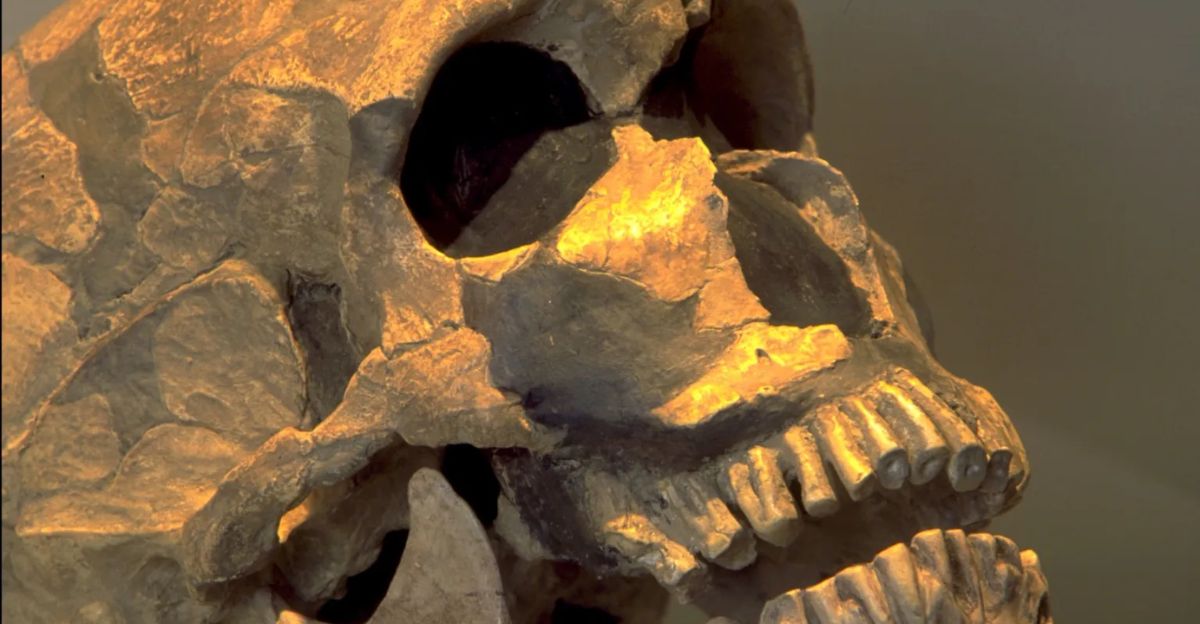

The proposal of Homo juluensis is being hailed as the first comprehensive cleanup of the Asian fossil record. For decades, these bones were tossed into the “miscellaneous” bin, treated as confusing outliers. This study boldly argues that Eastern Asia was, in fact, a significant and distinct center of evolution.
The researchers have effectively taken these forgotten fossils and given them a flag, moving them from the footnotes of history into their own headline chapter.
Science or Speculation?

Is it a done deal? Not quite. The scientific process is a gauntlet, and the researchers themselves are urging caution. Christopher Bae notes that while the evidence is compelling, fully confirming the taxonomy requires more analysis before the community “busts out the ‘Welcome to the Family’ banners.”
The sheer coherence of the data across so many sites creates a magnetic pull, convincing many that Homo juluensis is indeed the missing identity we’ve been searching for.
An Empire of Bones
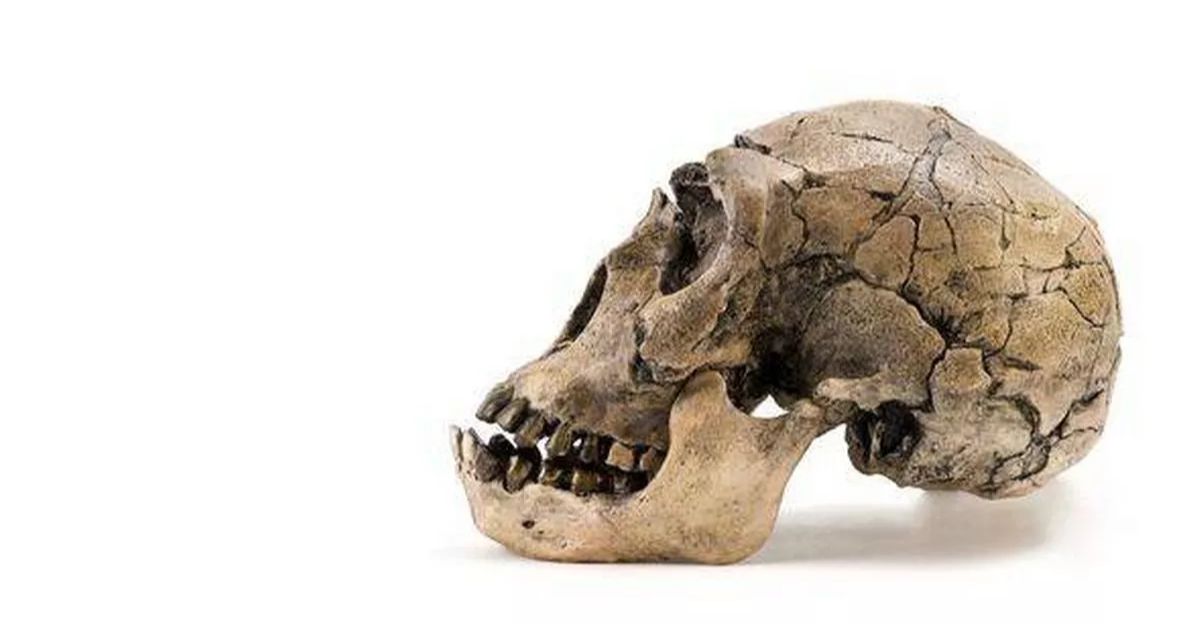
This wasn’t a small tribe hiding in a valley. The geographic spread of the fossils—stretching from the high plateaus of Xiahe to the islands near Penghu—suggests a vast empire. Homo juluensis roamed a massive territory, adapting to diverse climates and landscapes.
This widespread distribution confirms they weren’t a local anomaly; they were a successful, continental power. They didn’t just live in Asia; they occupied it, creating a legacy that spanned thousands of miles.
The Rosetta Stone Jawbone
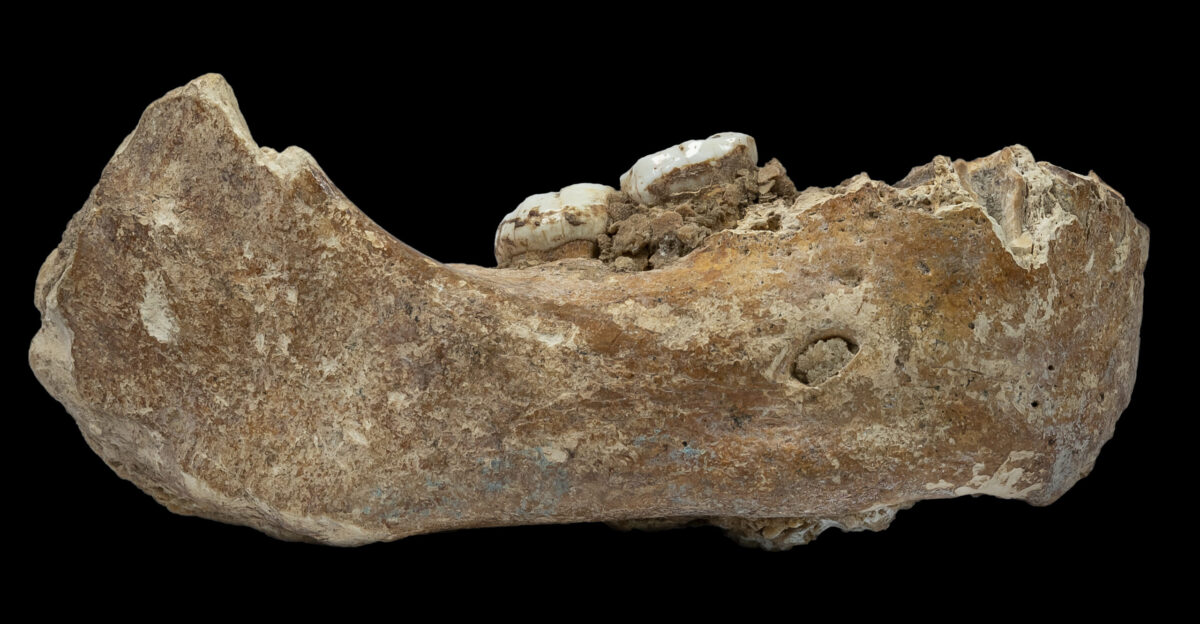

The key that unlocked this door was the Xiahe mandible. Previously identified as Denisovan through protein analysis, its physical shape turned out to be the perfect match for the Homo juluensis profile.
This jawbone acts as the “Rosetta Stone” of the discovery, finally bridging the gap between invisible molecular biology and solid rock. It is the tangible link that proves the proteins in the test tube belong to the “big heads” in the ground.
A New Vision of the Past

We have to rewrite the textbooks. The last 300,000 years were not a solo journey for Homo sapiens. We must now imagine a dynamic, perilous world where different types of humans—some with massive heads, some stocky, others lithe—coexisted on the same Earth.
The past was far more diverse than we dared to dream. It wasn’t a straight line of progress; it was a branching, twisting bush of life where we are just the last ones standing.
What Remains Hidden?

This discovery leaves us with a haunting question: If a species with a 250,000-year history was hiding in our museums until 2024, what else is waiting in the dark? Homo juluensis is a stark reminder that our knowledge is fragile.
As researchers apply new vision to old bones, it seems, as the experts suggest, that it is “only a matter of time” before the human family grows again. The next great discovery might already be on a shelf, waiting for someone to turn on the light.
Sources:
- Nature Communications, November 2024 – Homo juluensis species proposal and fossil analysis
- PaleoAnthropology Journal, November 2024 – Taxonomic classification and Denisovan connection
- Chinese Academy of Sciences – Archaeological excavation data from Penghu, Xiahe, and Xuchang sites
- University of Hawai’i Department of Anthropology – Lead researcher Christopher J. Bae’s published findings
- Protein sequencing analysis – Xiahe mandible identification linking Denisovan genetics to physical fossils
- Pleistocene fossil record – Multi-site archaeological context from Eastern Asia hominin sites