
NASA’s Perseverance rover has made an astonishing discovery on Mars that has left scientists baffled. After five years investigating the Red Planet, the rover identified a rock with an unusual “sculpted” shape, standing tall amid the surrounding terrain. This 31-inch specimen, named Phippsaksla, has sparked intrigue with its unique geometry and unusual composition, leading scientists to question how such an anomaly ended up in Jezero Crater.
As teams race to unveil the mysteries of this discovery, the likelihood that it is an interstellar visitor has researchers questioning our understanding of Mars’s geological history and cosmic interactions.
The Oddity Deepens
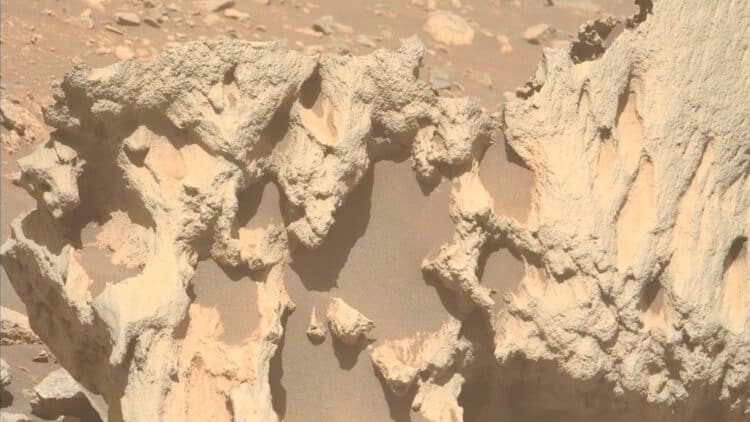

What sets Phippsaksla apart is not just its striking external features; it’s also the glimmers of exotic materials that lie within. Spectroscopic analysis indicates that the rock contains high levels of iron and nickel, elements rarely found concentrated in typical Martian rocks.
If confirmed, Phippsaksla would mark Perseverance’s first definitive meteorite discovery, despite extensive searches across the Jezero Crater basin. This could dramatically reshape our knowledge of Martian bombardment history and reveal a potential connection between Mars and the broader cosmos. Scientists are now working diligently to validate these findings, marking an exciting chapter in planetary exploration.
Jezero’s Cosmic History
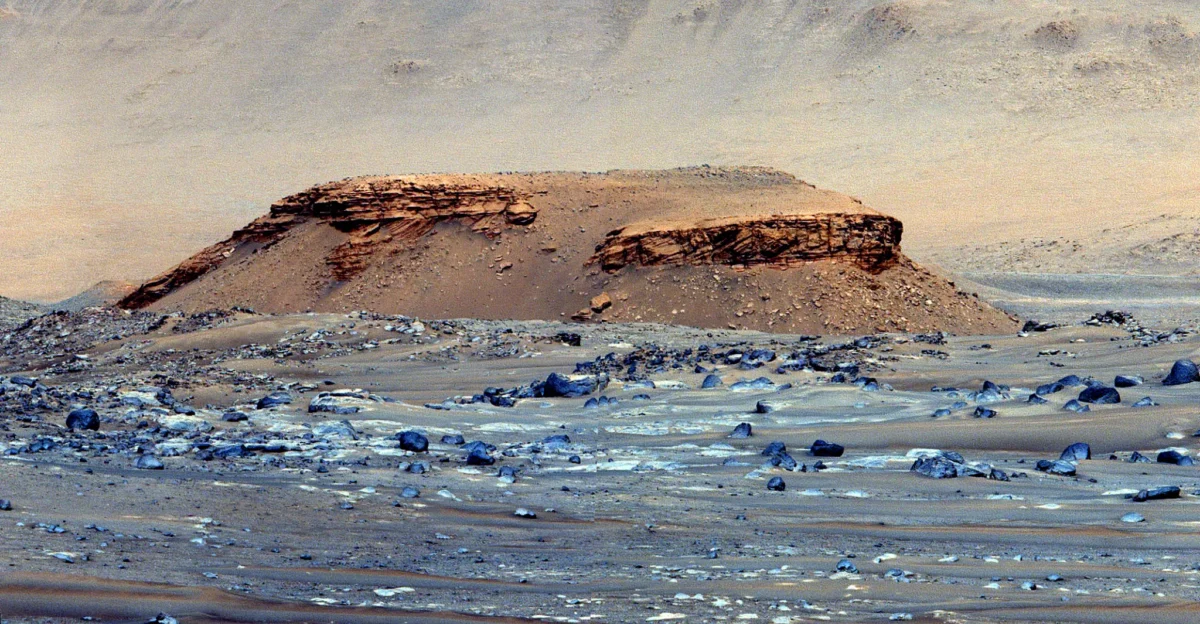

Jezero Crater, a former river delta, is historically rich, spanning nearly 28 miles and dating back approximately 3.8 billion years. This impact basin has been a witness to Mars’s turbulent past, serving as a collector of meteorites throughout its existence.
Dust accumulations and geological formations within the crater tell tales of ancient violence caused by meteor impacts. The presence of water and the interaction with space debris make Jezero an ideal site for scientific inquiry, contributing to our understanding of Mars’s development and the solar system’s evolution over billions of years.
The Search Intensifies
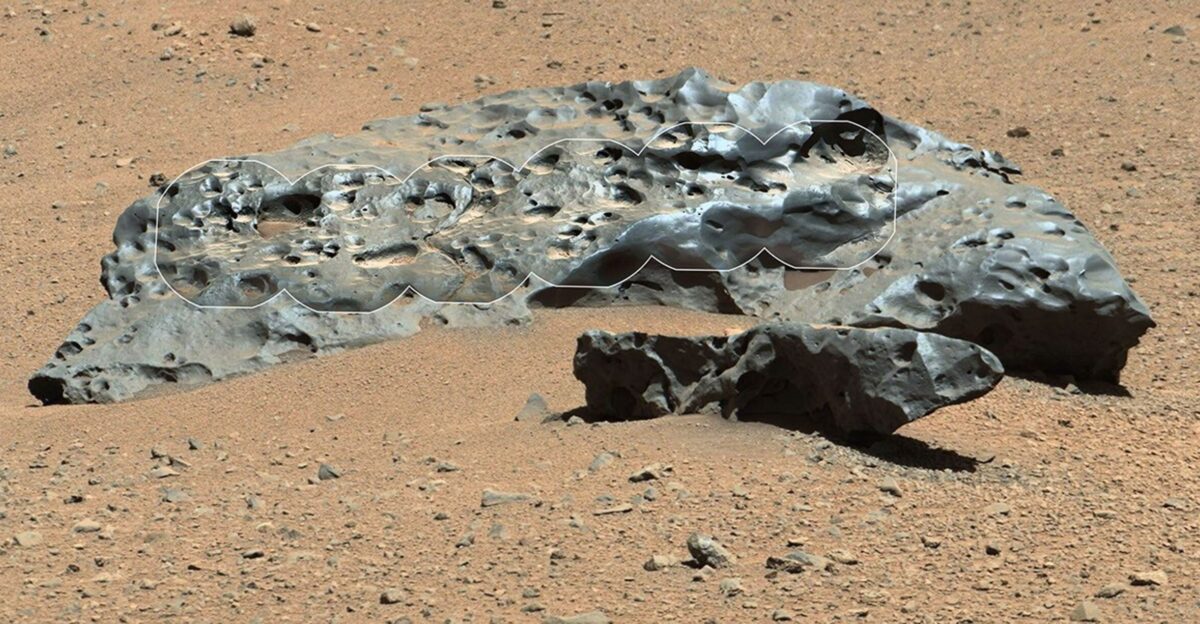

Preceding missions by rovers like Curiosity and Spirit have unearthed iron-nickel meteorites, confirming the possibility of such discoveries on Martian soil. Despite this, Perseverance, which launched in 2020, had yet to confirm a meteorite until now. Scientists applied sophisticated detection methodologies, blending high-resolution imaging with advanced chemical spectroscopy.
Each analysis not only uncloaked new geological features but also forged closer ties to Mars’s cosmic history. The evolution of detection techniques has underscored the ongoing challenge and excitement of exploring the Red Planet as we piece together its story.
The Discovery Unveiled
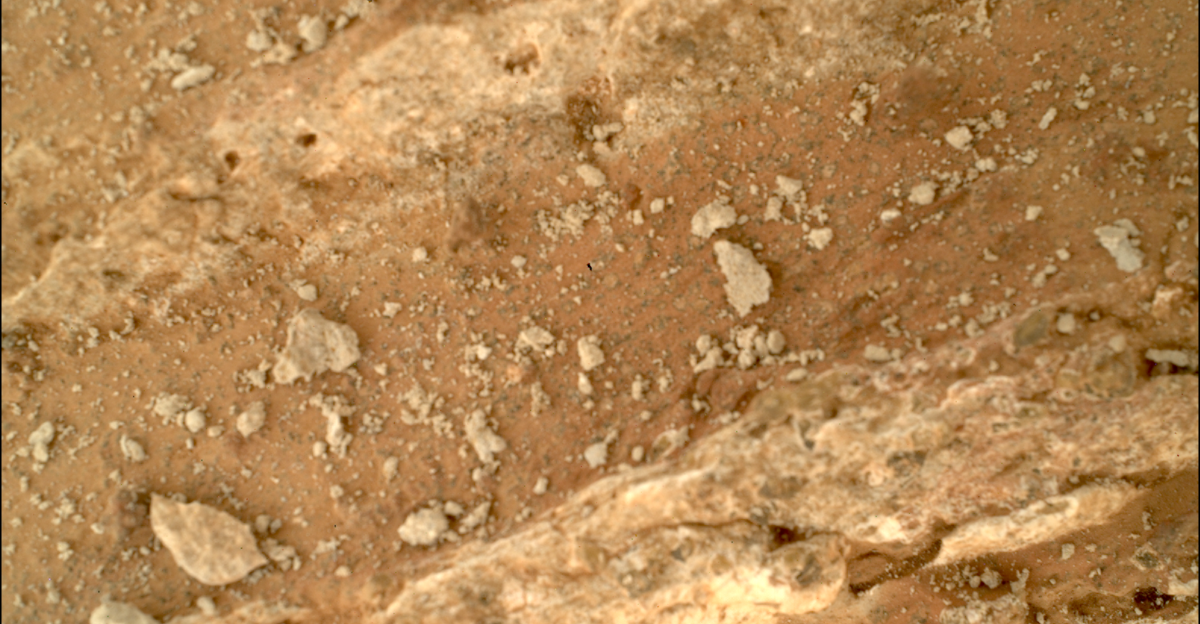

The pivotal moment occurred on September 2, 2025 (Sol 1612 of Perseverance’s mission), when the rover’s cameras detected an anomaly in the Vernodden region of Jezero Crater. The rock, later named Phippsaksla after a location in Svalbard, dramatically contrasted with its flat, fragmented neighbors. The rover’s SuperCam immediately targeted this distinct object.
Preliminary compositional analysis showed elevated iron and nickel concentrations, consistent with what scientists expected from a meteorite. This moment marks a long-awaited scientific breakthrough after years of seeking robust evidence of extraterrestrial materials on Mars.
Why Vernodden Matters
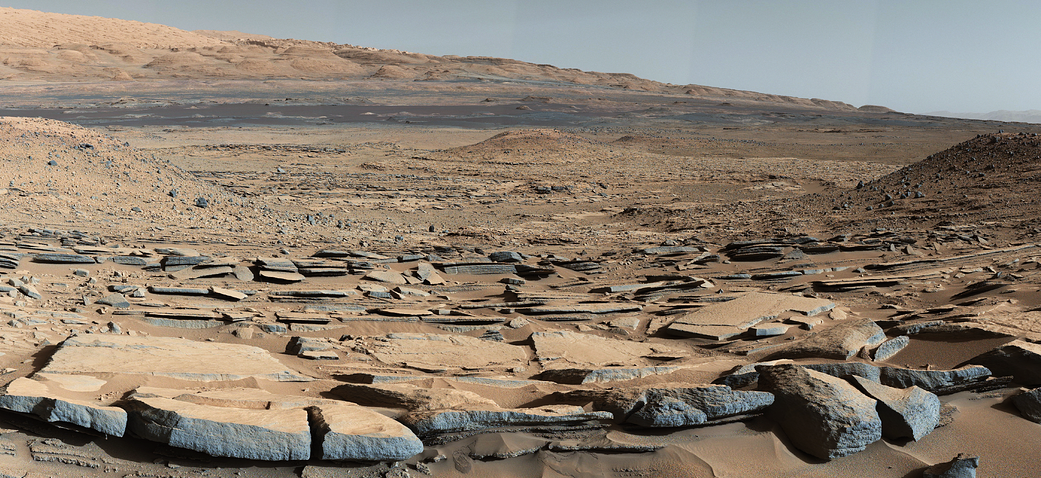

The Vernodden site offers a significant glimpse into Mars’s geological history, as it represents a transition zone between ancient geological layers. The unique composition and erosion of rocks at this location facilitate the exposure of buried meteorites. Perseverance was initially tasked with studying aqueous minerals indicative of past water, a potential harbinger of habitability.
The unexpected identification of Phippsaksla during operations intended for water research highlights the multifaceted roles planetary rovers serve in deepening our understanding of extraterrestrial terrains while also pursuing key scientific objectives.
A Scientist’s Reaction

Candice Bedford, a Research Scientist at Purdue University leading the meteorite analysis, reflected on this unexpected phenomenon: “It has been somewhat unexpected that Perseverance had not seen iron-nickel meteorites within Jezero crater.” Drawing comparisons to past discoveries made by Curiosity, including the notable “Lebanon” meteorite in 2014, she emphasized the need for further laboratory testing.
While her optimism about Phippsaksla’s classification as a genuine meteorite is palpable, Bedford’s remarks remind the scientific community of the rigorous validation process necessary before conclusions can be drawn with confidence.
SuperCam’s Role

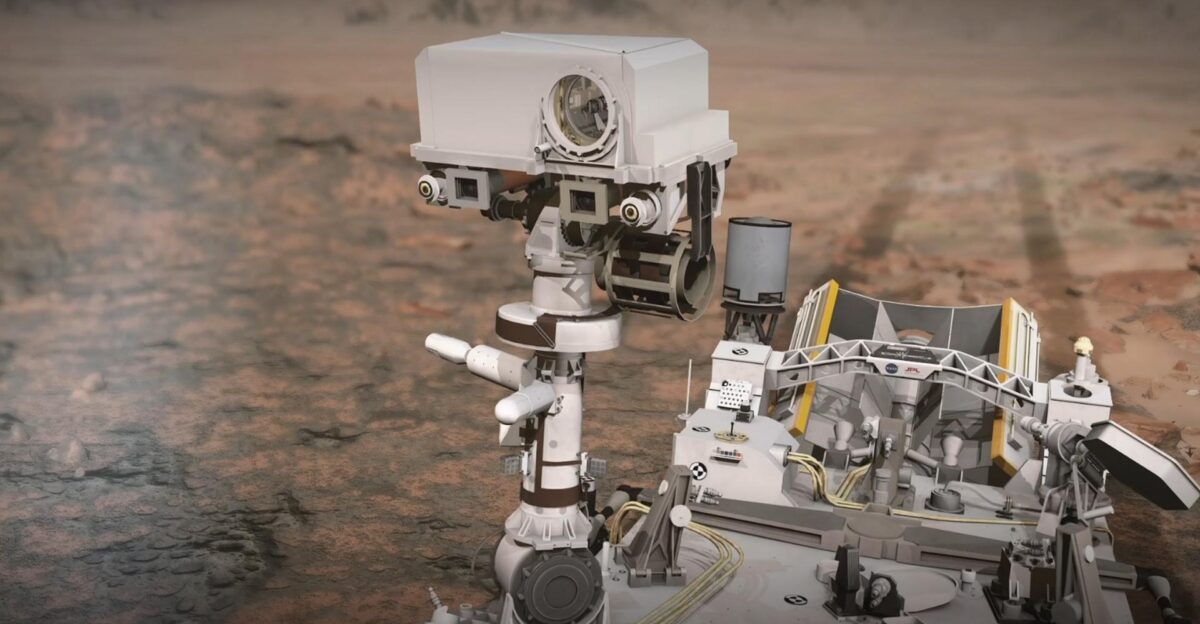
The evolution of scientific instrumentation has significantly enhanced data acquisition on Mars. SuperCam, a laser-based analytical device mounted on the Perseverance rover’s mast, played a crucial role in analyzing Phippsaksla’s composition. This innovative tool fires an infrared laser at targets up to seven meters away, then analyzes the resulting plasma to identify the elemental makeup.
SuperCam detected notably high concentrations of iron and nickel in Phippsaksla, marking it as an anomaly among Martian rocks. The compelling data sparked a surge in scientific interest, prompting further investigation into the history of Martian meteorites.
Solar System Context
Understanding the origins of meteorites provides essential context for the significance of Phippsaksla. Iron-nickel meteorites are remnants left over from the cores of large asteroids formed during the solar system’s infancy around 4.5 billion years ago. Collision events within the asteroid belt can fragment these bodies, sending pieces across interplanetary space.
Mars, strategically located between the asteroid belt and the inner solar system, acts as a collector for these fragments. Phippsaksla’s journey likely spanned millions of miles through space before impacting Mars, where it remained hidden until Perseverance’s discovery.
The Cacao Connection
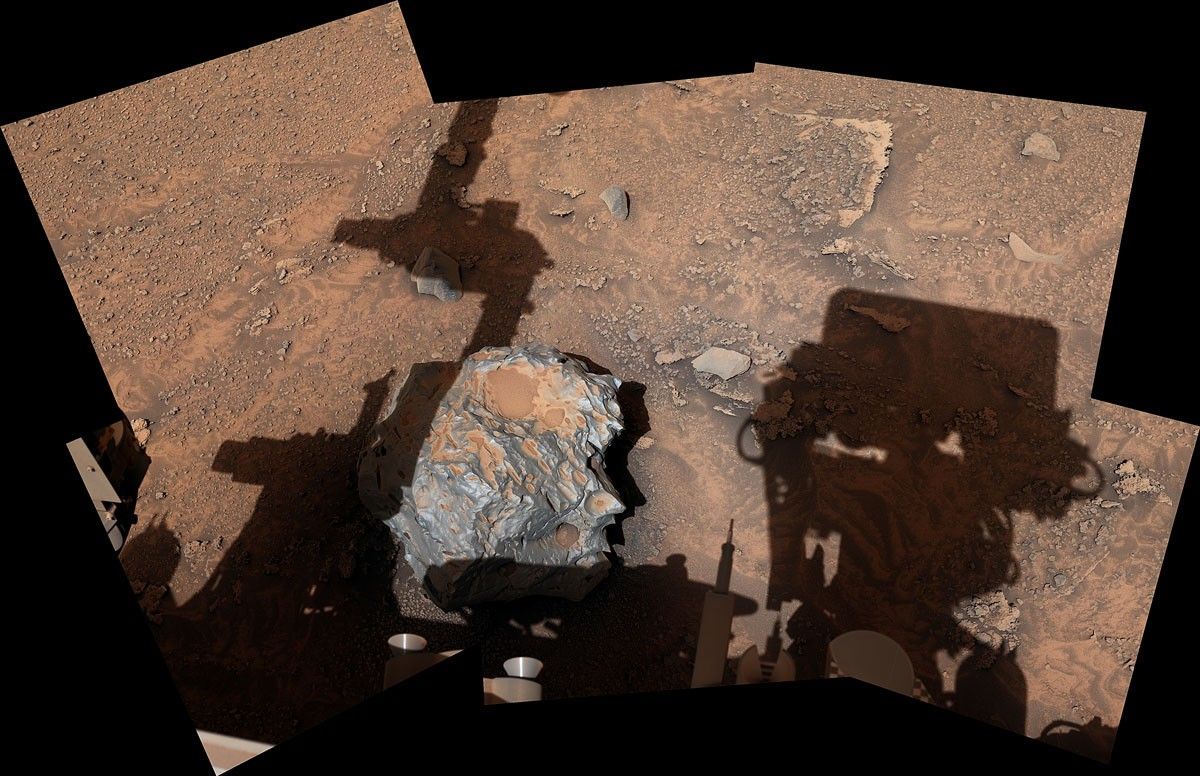

This discovery opens the door for reevaluating past findings. Cacao, another significant Martian meteorite identified by Curiosity in 2023, shares a potential lineage with Phippsaksla. As researchers analyze similarities in composition and morphology, the implications of these findings could reveal broader interstellar connections.
Each meteorite recovered not only enriches our scientific catalogs but also fosters intriguing inquiries about the history of our solar system. Phippsaksla’s identification as a meteorite could offer fresh perspectives on Mars’s dynamic past and its role as a cosmic archive.
Future Missions

With Perseverance’s recent findings, the focus is now on future exploration missions aimed at uncovering more secrets about the solar system’s history. The upcoming Mars Sample Return program aims to retrieve Martian materials and bring them back to Earth for detailed analysis in terrestrial laboratories.
These efforts could confirm the presence of carbon-rich compounds and signs of ancient microbial life, adding depth to our understanding of the planet’s habitability. Each discovery on Mars enhances the case for continued investment in planetary exploration, holding promises for extraordinary insights into our cosmic neighbors.
Challenges of Mars Exploration

Despite the excitement surrounding discoveries like Phippsaksla, challenges persist in Mars exploration. Perseverance has to navigate a harsh environment filled with dust storms, temperature fluctuations, and rocky terrains. These obstacles may hinder data collection and mission objectives.
Additionally, the power supply for the rover, reliant on solar energy, is subject to fluctuations based on environmental conditions. Adapting to these challenges is crucial for the success of future discoveries while ensuring that the rover continues to operate effectively to answer key scientific questions.
The Royal Mars Landscape

Exploration in Jezero Crater is not limited to meteorite detection. The crater’s geological features provide a unique opportunity to study sedimentary processes and ancient environments that may have supported life. From examining river deltas to analyzing layer deposits, every aspect of the Martian surface contributes to understanding its climatic history.
The multidisciplinary approach employed by the Perseverance team enhances our understanding of Mars’s geological evolution, combining insights from geology, astrobiology, and climate science to provide a holistic perspective on the Red Planet’s past.
The Implications of Discoveries
Each discovery on Mars, particularly those like Phippsaksla, serves crucial scientific purposes, from redefining planetary histories to informing future explorations. Scientific findings inspire global collaborative efforts to adapt and innovate in planetary sciences. Phippsaksla’s unique characteristics may prompt a reevaluation of current theories related to planetary formation.
Collaboration among multiple space agencies and academic institutions can accelerate our understanding of not just Mars, but the entire solar system and fosters a sense of shared purpose in uncovering insights that inform both scientific curiosity and societal applications.
Dr. Bedford’s Vision

Dr. Candice Bedford envisions the findings not just as isolated events, but as transformative opportunities to reshape our scientific understanding of Mars. “Understanding how we can observe terrestrial processes through Martian rocks enriches not only our planetary science but also geological studies on Earth,” she emphasizes.
Her perspective highlights the interconnectedness of planetary exploration and its broader implications on terrestrial environments. Each stone examined on Mars may reflect broader cosmic narratives, suggesting a shared heritage among planets that has a significant impact on understanding life’s potential beyond our home.
Engaging the Public

The excitement generated by discoveries like Phippsaksla involves engaging a broader audience through science communication. NASA’s efforts to disseminate findings and cultivate public interest are vital for fostering appreciation and support for planetary sciences.
Knowledge-sharing platforms enhance public understanding of Mars exploration through visually captivating storytelling and interactive media. Engaging the public in ongoing missions helps stimulate curiosity, inspiring the next generation of scientists, engineers, and explorers dedicated to unraveling the mysteries of the solar system.
Climate Considerations
Mars’s climate presents an additional layer of complexity influencing exploration efforts and data interpretation. Understanding past climates assists in reconstructing potential habitable environments on Mars. NASA’s research aims to draw parallels between Martian and terrestrial climatic patterns, revealing insights about both planetary histories and future habitability.
This comparative analysis can shed light on aspects of climate change on Earth, offering critical lessons learned from our planetary neighbor’s transitions over billions of years that could enhance our approaches to addressing current global challenges.
Science and Policy

Investments in space research and planetary exploration reflect national and international priorities in science, technology, and innovation. Policymakers play a crucial role in supporting research initiatives that lead to groundbreaking discoveries. The synergy between scientific discovery and strategic funding can propel forward-thinking exploration of celestial bodies.
By backing programs like Mars exploration, nations can address profound questions about existence, growth, and the potential for life beyond Earth. Collaborative international research expands horizons while fostering partnerships crucial to achieving ambitious exploration goals.
Perseverance’s Impact

The legacy of the Perseverance rover will be measured not just in its findings but also in the essential insights it provides about Mars’s potential to harbor life. Its ongoing mission encourages the exploration of life-sustaining conditions across extraterrestrial environments.
As it continues to work through the unique geological landscapes of Mars, Perseverance is laying the groundwork for future expeditions and enhancing human understanding of our place in the universe. The valuable data collected serves as a stepping stone for humanity’s ongoing quest to explore beyond our home planet.
The Cosmic Journey Continues

The discovery of the Phippsaksla rock illustrates the profound potential of Mars exploration not only to identify past climatic conditions but to inform our ongoing quest for knowledge about life beyond Earth. As scientists continue to delve into this unexpected gem and others like it, they reinforce the idea that each rock has a story to tell.
The ongoing efforts of the Perseverance mission promise to reveal additional insights and mysteries, continually extending the narrative of humanity’s adventures into the cosmos and the enduring search for understanding beyond our planet.
Sources:
NASA Science Blog, “A Stranger in Our Midst?”, November 13, 2025
NASA Perseverance Mission Updates, Mission Status Reports, November 2025
NASA Mars Exploration Program, Jezero Crater Geology, 2024–2025
Space.com, “NASA’s Perseverance Rover Discovers First Meteorite on Mars After 5 Years”, November 25, 2025
NASA Mars 2020 Mission Official Blog, Perseverance Rover Discoveries, October 1–November 13, 2025
Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, Meteorite Database and Analysis, 2025