
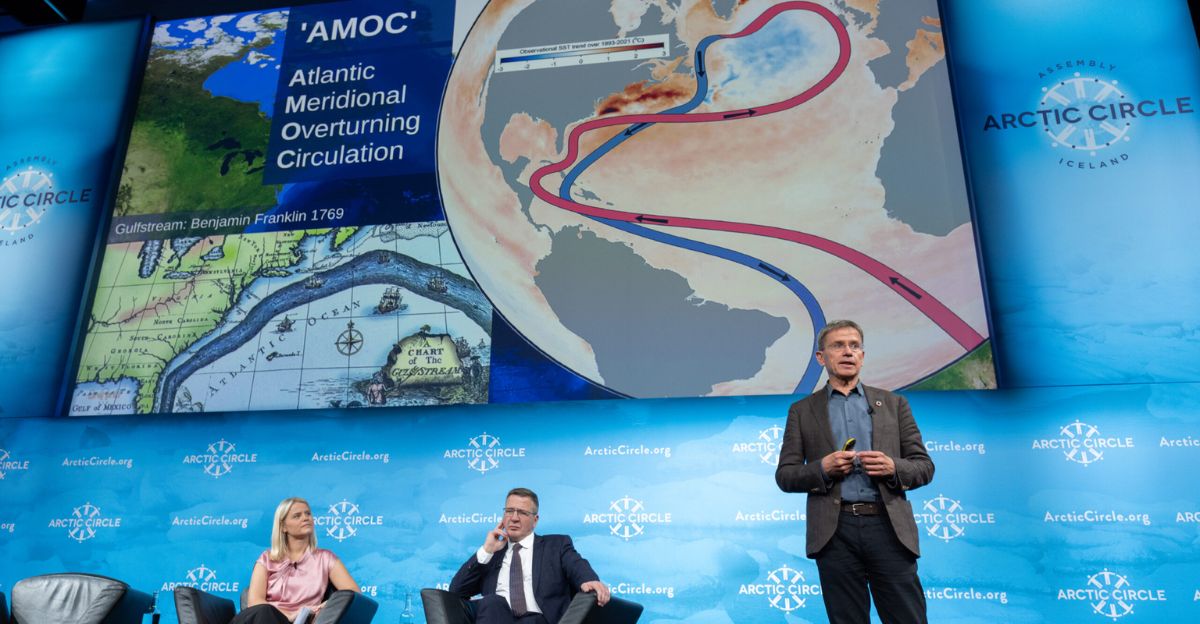
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), a crucial ocean current system, is experiencing unprecedented decline, signaling a potential planetary emergency. Research spanning over four decades has revealed a measurable weakening of this ancient current, raising alarms among climate scientists globally.
A 2023 study by Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution definitively confirms these changes. The implications extend far beyond marine ecosystems, affecting European winters and coastal cities in the United States.
Coastal Flooding Crisis
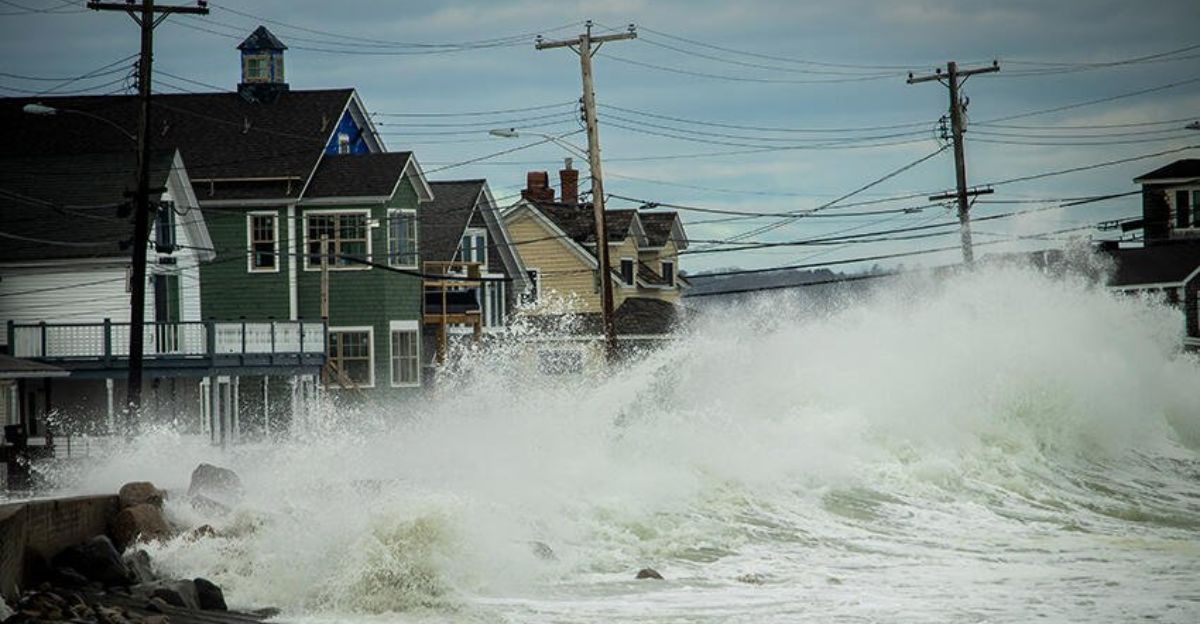

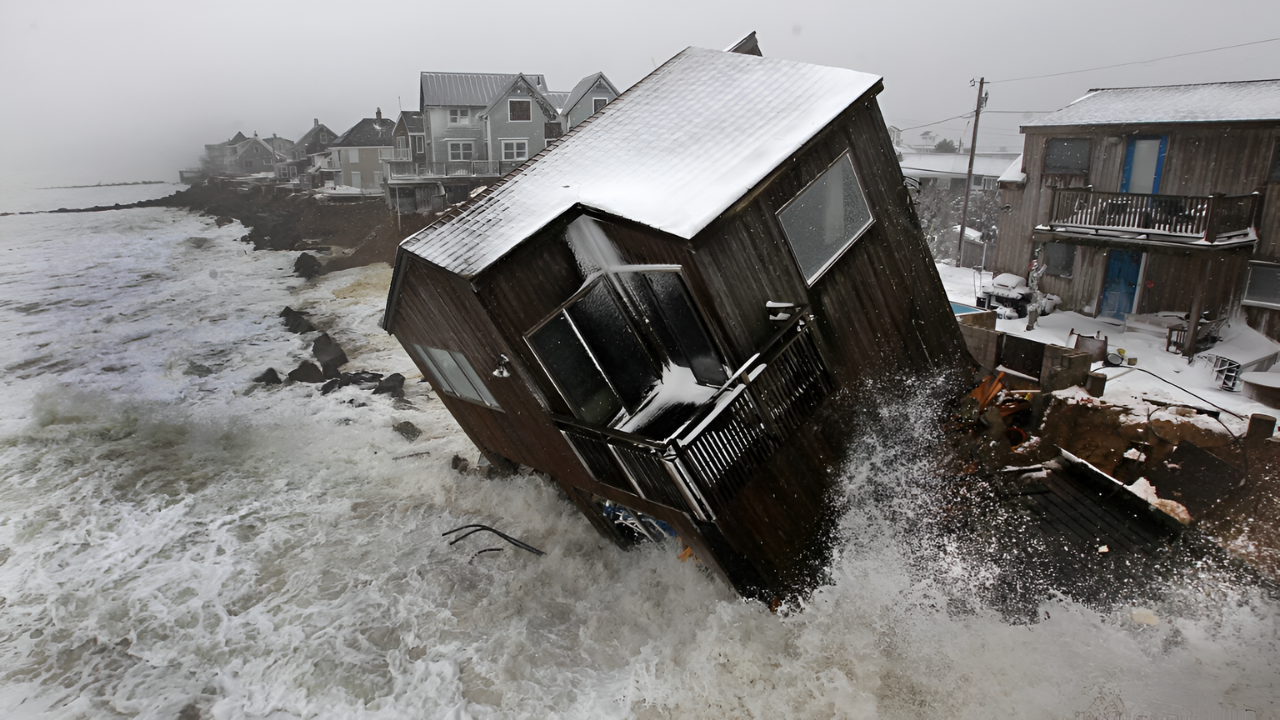
The deterioration of the Gulf Stream is already manifesting in intensified coastal flooding across the U.S. Northeast. In a shocking analysis between 2005 and 2022, researchers found that up to 50% of flooding events in this region could be attributed to the weakening ocean current.
This isn’t a distant threat; the impacts are immediate, reshaping life in major cities like New York, Boston, and Norfolk. These communities, which were once prepared for gradual sea-level rises, now grapple with accelerated timelines, prompting urgent discussions on infrastructure resilience and urban planning.
The AMOC’s Historical Significance
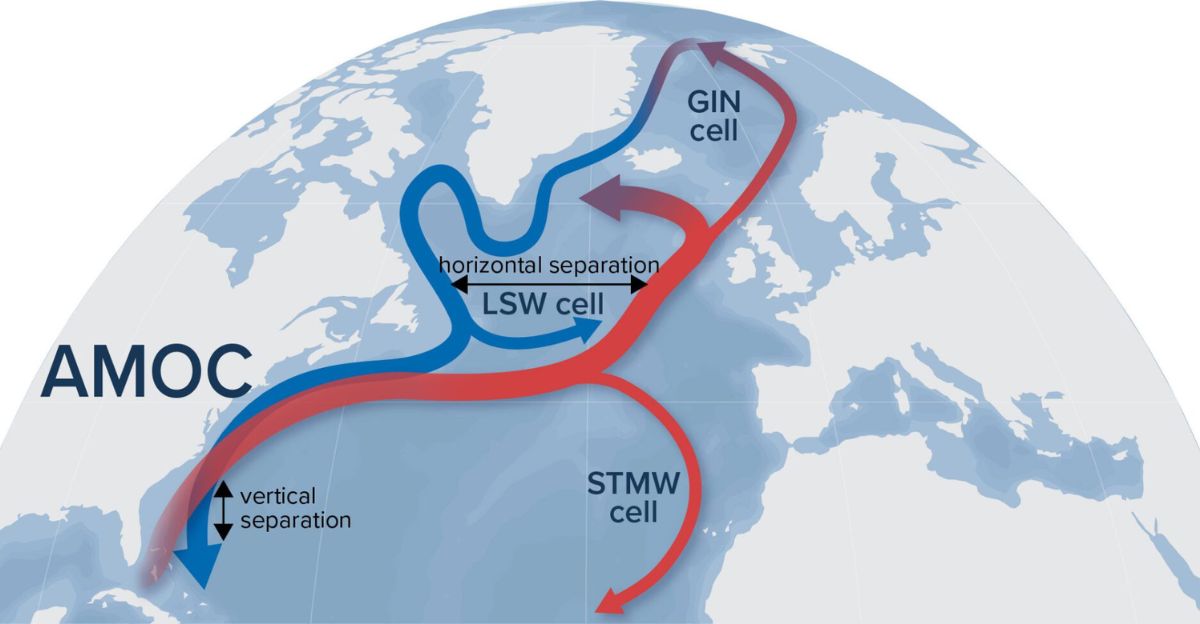
For approximately 1,600 years, the AMOC, often referred to as the ocean’s “conveyor belt,” has maintained a stable role in regulating climate. By transporting warm tropical waters northward, it has moderated climates in Europe and North America.
Historical records suggest that earlier Norse settlements in Greenland thrived due to this warmth. Researchers now stress that this stability is under threat, with potential consequences that could alter climate and coastal dynamics. The AMOC’s importance, once taken for granted, is now at the forefront of climate discourse.
The Subtle Signals of Change

Oceanographers have speculated about the AMOC’s weakening for decades, but it wasn’t until the 1980s that they began to gather concrete evidence of its weakening. Subtle changes in measurements evolved into disturbing trends by the 2010s, when satellite data confirmed a slowdown of the system.
Concurrently, Greenland’s ice sheet is melting at an accelerated rate, contributing freshwater to the Atlantic, which disrupts critical salt gradients necessary for the AMOC’s function. This combination of factors raises alarming questions about future stability.
Definitive Evidence

In 2023, Woods Hole released groundbreaking evidence: the Gulf Stream transport through the Florida Straits has decreased by 4% over the past four decades, with 99% statistical certainty. This is more than a hypothesis; it’s a direct observation indicating a significant, measurable change in a system integral to the global climate.
Scientists have described this finding as alarming, suggesting that we may have passed a critical tipping point. This evidence calls for immediate action and further investigative efforts to understand better what the collapse of the Gulf Stream would mean for the planet.
The Northeast Coast’s Vulnerability
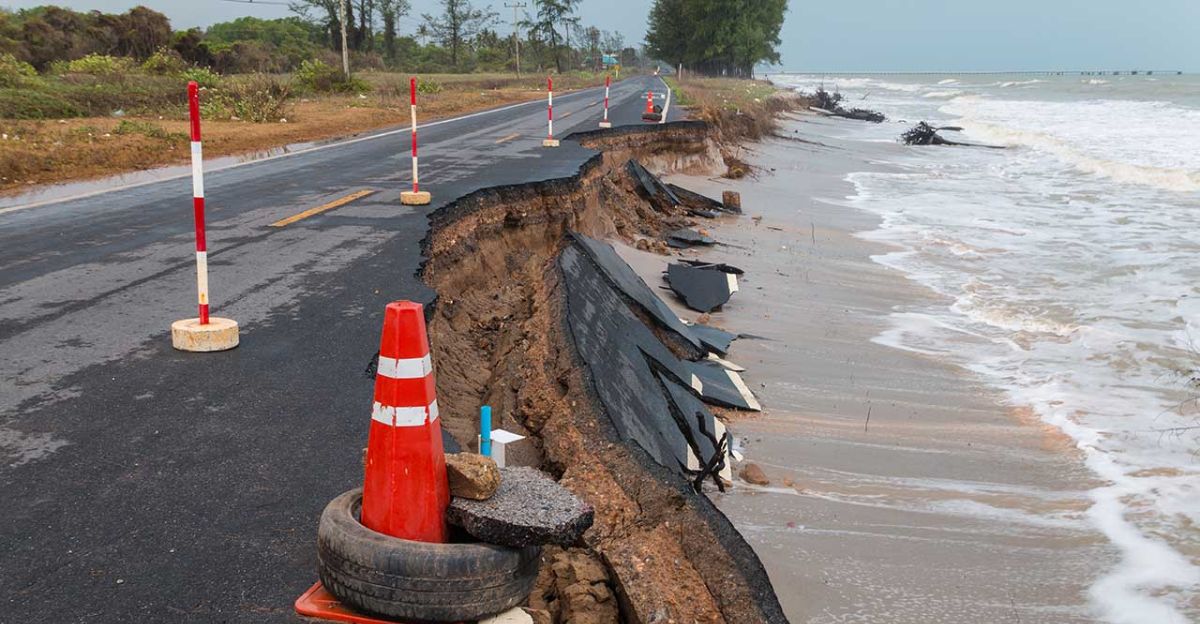

The U.S. Northeast is experiencing sea-level rise at a pace three to four times faster than the global average. Tide gauges in cities like Boston and New York demonstrate annual increases that are becoming increasingly difficult to ignore.
Norfolk, Virginia, has begun constructing new infrastructure with raised foundations, indicating the urgency of adapting to changing coastal conditions. This region is literally sinking into the sea, a phenomenon known as coastal subsidence, or “coastal squeeze.” City planners scramble to implement adaptive measures that can sustain urban life amidst this evolving climate crisis.
A Scientist’s Dire Warning

Liping Zhang, a climate scientist at NOAA’s Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory, expresses urgent concerns about the potential collapse of the AMOC. “If the AMOC were to fail, it would significantly heighten the frequency of flooding along the U.S. coastline, even without severe storms,” he warns.
His studies indicate that AMOC-driven sea-level rise has led to an increase of up to eight additional flood days per year since 2005. Coastal mayors and infrastructure officials are now looking to science for guidance and solutions, as the stakes continue to escalate.
Political Response to an Emerging Crisis

The potential impacts of a weakened AMOC are severe enough to prompt a shift in policy among global leaders. The European Union has begun re-evaluating its climate adaptation strategies, particularly in light of potential cooling temperatures resulting from AMOC disruption.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has raised its warnings, indicating that the AMOC is “very likely” to weaken further. This coordinated effort highlights the pressing need for international collaboration and proactive climate policies in response to an increasingly complex global challenge.
The Financial Imperative

With 2025 expectations on the line, the economic implications of rising sea levels are alarming. Coastal communities must plan for infrastructure upgrades, which could cost billions of dollars. As cities grapple with the economic realities of climate change, local governments and residents are beginning to feel the pinch of climate adaptation costs.
The financial stakes are high, with the potential for property values to plummet in impacted areas. Adapting requires substantial investment in resilient infrastructure that can withstand rising seas and increasing flood risks.
Global Repercussions
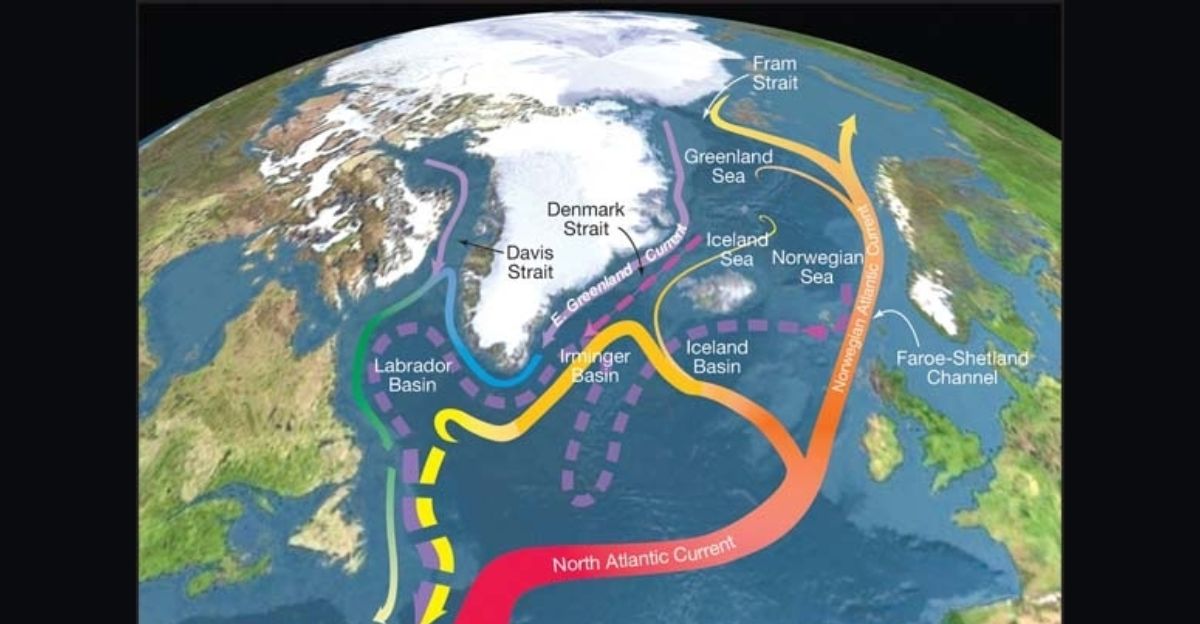
As we assess the possibility of an AMOC shutdown, the potential for profound cooling in Northern Europe looms large, even amidst global warming trends. Experts are drawing connections between the weakening current and potential regional weather shifts that could encompass everything from agricultural viability to energy demand.
This situation not only threatens coastal U.S. cities but also has far-reaching implications for global climate patterns. The interconnectedness of climate systems underscores the urgency of proactive response measures.
Engaging the Public for Change

Communities across the U.S. East Coast are beginning to engage in the climate conversation, focusing on local resilience strategies. Public awareness campaigns aim to educate residents about the impacts of climate change on flooding, infrastructure, and natural ecosystems.
Activism is on the rise, with community leaders organizing events to push for policy changes. The movement towards sustainable practices is gaining traction, prompting individuals to reconsider their roles in mitigating climate challenges. Collectively, these efforts emphasize the importance of community engagement in combating climate change.
The Role of Technology in Monitoring

Technological advancements are playing a critical role in monitoring ocean currents and climate change. Researchers are deploying sophisticated satellite systems and buoy arrays that provide real-time data on the health of ocean systems. This data enables scientists to assess the status of the AMOC, thereby improving predictive models for climate impact assessments.
Technology innovation not only enhances scientific understanding but also helps inform policymakers and the public. As climate change accelerates, these tools will be vital in guiding responsible decision-making.
The Human Cost of Inaction

As the crisis unfolds, it is essential to consider the real human cost of inaction. Communities at the front lines of rising sea levels face displacement, economic instability, and loss of cultural heritage. The stories of individuals impacted by flooding serve as powerful reminders of the stakes involved.
For instance, interviews with residents of vulnerable coastal towns highlight personal narratives that illustrate the emotional toll of environmental displacement. These individual experiences motivate broader societal engagement in climate resilience efforts.
Norfolk, Virginia

Norfolk serves as a pivotal case study in the impacts of climate change on urban life. This coastal city, already grappling with accelerated sea-level rise, is implementing projects to adapt to future conditions. Local initiatives focus on elevating infrastructure and hardening coastlines to minimize flooding risks.
The commitment from community leaders, citizens, and scientists highlights the collaborative efforts required to navigate this crisis. As Norfolk leads in proactive response, it sets an example for other vulnerable cities across the U.S.
Regional Climate Impacts

According to researchers, the repercussions of an AMOC disruption extend beyond immediate sea-level rise. Changes could lead to intensified storms and altered weather patterns worldwide. The disruption of the Gulf Stream may have unpredictable consequences, particularly for regions that depend on stable climate conditions.
Agricultural sectors, energy production, and even public health may all see disruption as ecological balance becomes strained. The interconnected nature of our climate systems illustrates the critical importance of understanding and adapting to these changes.
The Importance of Policy Innovation

In light of growing threats, innovative policy frameworks are crucial for addressing climate change effectively. Governments must prioritize sustainable practices, invest in renewable energy sources, and develop incentives for communities to engage in climate adaptation strategies.
Collaborative efforts between governmental bodies, scientists, and communities can yield adaptability and resilience against climate impacts. Policies should focus on preventive measures and rapid response capabilities, ensuring that communities are not only reactive but also proactive to safeguard their futures.
Preparing for the Future

Preparing for potential AMOC collapse means prioritizing both infrastructure and community resilience. Education, awareness, and planning must be combined to ensure that citizens understand their role in climate adaptation and adaptation planning.
Local governments are increasingly investing in data-driven decision-making processes that integrate scientific research into community planning efforts. As the reality of climate-driven changes unfolds, the onus is on citizens and local officials to work hand-in-hand in building adaptive strategies that prioritize safety and sustainability.
The Role of Education in Climate Awareness

Education is a critical component in raising awareness about the urgency of climate change. Schools and community programs are taking initiatives to inform youth and adults alike about the emerging challenges.
Workshops, seminars, and local events focused on climate science educate citizens about the implications of a weakening Gulf Stream and related phenomena. By fostering strong connections between communities and scientific communities, educational efforts can inspire collective action and engagement in climate resilience strategies.
Bridging the Science-Policy Gap

Closing the divide between scientific knowledge and policy application is essential in mitigating climate impacts. Scientists must communicate their findings in accessible formats, making it easier for policymakers and the public to understand the significance of conditions like the weakening of the AMOC.
Collaborative partnerships between the scientific community and governmental agencies enhance the translation of research into actionable policies. This approach fosters a conducive environment for science-based policy initiatives that can guide effective climate action.
A Call to Action

As we navigate the implications of the Gulf Stream’s decline, collective action is imperative. Communities must unite with pressure on policymakers to adopt proactive measures that protect vulnerable populations. The time for dialogue is over; actions must follow.
Engaging citizens in climate conversations, advocating for sustainable practices, and investing in resilient infrastructure are crucial steps. Together, we can confront the challenges posed by climate change and work towards safeguarding our future against the backdrop of a shifting climate landscape.
Sources:
Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution New Study Definitively Confirms Gulf Stream Weakening September 2023
CNN A Crucial System of Ocean Currents Is Slowing It’s Already Affecting Coastal Flooding May 2025
Nature Communications The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation at Risk of Collapse 2023
NOAA Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory AMOC-Driven Flooding Impact Study 2025
Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Possible North Atlantic Overturning Circulation Shutdown January 2025
IPCC Sixth Assessment Report Ocean and Cryosphere 2021–2023