
General Motors has indefinitely frozen its $2.6 billion Ultium Cells EV battery megafactory in Spring Hill, Tennessee. The joint venture with LG Energy Solution, announced October 29, 2025, marks GM’s largest EV manufacturing pullback.
The freeze follows the September 30, 2025 elimination of the federal $7,500 EV tax credit. Over 3,420 workers across four states are affected in the fastest policy-to-layoff cascade in modern auto history. The next slide reveals why GM halted production so abruptly.
Slower EV Adoption Sparks Factory Freeze

GM cited “slower near-term EV adoption” and an “evolving regulatory environment” as core reasons for the freeze. The Q3 2025 $1.6 billion special charge reflects declining EV plant value and layoff costs.
Production at Spring Hill will halt in January 2026 and may resume mid-2026. No guarantees have been provided for workers facing an 18-month wait. Could this extended pause reshape GM’s EV strategy entirely?
Human Toll: Thousands Face Uncertainty

Across four states, GM laid off 1,750 workers permanently and furloughed 1,670 temporarily. Detroit’s Factory Zero lost 1,200 jobs, Warren Ultium plant 550 indefinite and 850 temporary, and Spring Hill Ultium 710 temporary workers.
Salaried positions, IT, and stamping plant workers add 620 more layoffs. Annual wage losses total $125–250 million, impacting 10,000–15,000 family members. How communities cope with this disruption will become evident next.
Corporate Moves: GM and LG Adjust

Spring Hill will suspend production from January to mid-2026. Detroit’s Factory Zero reopened January 5, 2026, with a single shift, cutting half its workforce. Spring Hill vehicle assembly implemented extended downtime, furloughing 700 of 1,400 shift workers since September.
Both GM and LG are reevaluating strategies amid the sharpest EV demand contraction since modern industry emergence. Supplier responses illustrate the broader ripple effect.
Suppliers and Competitors Feel Pressure

Dana Thermal permanently closed Auburn Hills, cutting 200 jobs. IAC shut two Michigan plants, eliminating 250 roles. Volkswagen furloughed 160 workers in Chattanooga. Rivian cut 600 employees in October.
Ford scaled back EV targets, warning that tax credit elimination could reduce demand by 20–30%. These shifts hint at broader regional and competitive impacts in the EV sector.
Global Supply Chains Face Disruption
GM’s pullback affects suppliers in South Korea, Japan, China, Canada, and Mexico. Reduced orders for cathodes, separators, and battery systems ripple through the network.
Visa challenges following the September 4, 2025 ICE raid at Hyundai-LG Ellabell, Georgia, affected technical workers. Some have returned as of November, but workforce stability remains fragile. What happens to the U.S. “Battery Belt” next?
The “Battery Belt” Becomes Layoff Alley

Tennessee, Michigan, and Ohio face the heaviest job losses. Spring Hill sees 1,410 affected positions. Detroit loses 1,200 permanent roles. Warren, Ohio, sees 1,400 layoffs.
Economic impact on Spring Hill alone reaches $50–100 million in lost wages, affecting schools, restaurants, housing, and retail. Will local economies recover quickly or face prolonged downturns?
UAW Demands Worker Protections

The UAW seeks full pay and benefits, warning that “temporary” layoffs often become permanent. Furloughed workers may receive only partial wages, challenging mortgage and bill payments.
Union leaders also advocate trade policies to safeguard manufacturing. Policymakers remain split: some see the tax credit as market distortion; others argue its elimination undermines climate goals and green jobs. How policy choices ripple through communities is next.
Regional Economies Face Downturn

Spring Hill relies heavily on GM employment, with reduced tax revenue and declining property values looming. Michigan’s automotive corridor faces fresh unemployment spikes in Detroit and Warren.
Estimated $125–250 million in annual wage loss threatens local consumer spending, small businesses, and housing markets. Timing worsens the impact: furloughs begin January 2026, leaving workers with uncertain holiday income. Local retailers adjust strategies in response.
Dealerships Pivot Strategies Quickly

Without the $7,500 federal incentive, EV pricing effectively increased $57,500 overnight for consumers. Dealers pivot to hybrids and gasoline vehicles, offering incentives to clear existing inventory.
Industry analysts project slower EV adoption until battery costs drop sufficiently, potentially delaying widespread EV adoption by 3–5 years. Customer cancellations highlight the shifting demand landscape and dealer adaptation challenges.
Restaurants and Local Businesses Brace

Businesses near affected plants anticipate sharp revenue declines. Spring Hill restaurants report 20–30% revenue drops during peak holiday season due to reduced foot traffic.
Owners cut staff and inventory, exploring small business bridge loans and retraining initiatives. Similar patterns emerge in Warren, Ohio, and Detroit. How broader manufacturing sectors respond next will affect the entire regional economy.
Manufacturing Sector Ripple Effects

Plastics, aluminum, and electronics suppliers experience reduced orders. Midwest manufacturers face stranded assets and overcapacity following the 2021–2024 EV investment wave.
200,000–400,000 EV annual production capacity affected at Spring Hill and Warren translates to $300–600 million in lost battery production value. Tier 2 and Tier 3 suppliers also feel cascading effects.
Global Consumer Market Feels Shock

U.S. EV policy reversal reduces international demand certainty. European automakers face added pressure, and Chinese manufacturers redirect focus to Southeast Asia and Latin America.
Without robust U.S. demand, global EV prices may remain high, slowing adoption. Traditional automakers in India and Brazil may benefit as EV scale advantages shift away from U.S. markets.
EV Slowdown Threatens Climate Goals

Reduced EV production delays U.S. transportation decarbonization targets. Slower adoption keeps gasoline vehicles on roads longer, worsening urban air quality.
Analysts warn this threatens 2030 goals of 50% EV or plug-in hybrid sales. Delayed EV adoption disproportionately affects low-income and minority populations already exposed to poor air quality. Environmental setbacks now loom large.
Policy Debate Intensifies

GM’s freeze reignites discussion on government incentives in industrial policy. Tax credit supporters argue market correction; critics highlight abandoned workers and ceded EV leadership.
Cultural and political divides deepen as midterm elections approach. Key swing states—Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania—face direct automotive job impacts. The following slide highlights who benefits amid the disruption.
Unexpected Winners Emerge

Hybrid vehicle manufacturers, especially Toyota, see renewed demand. Gasoline component suppliers and used car dealers gain stability.
Oil and gas industries benefit as electrification slows. Regions less dependent on EV manufacturing remain stable. Internationally, China’s domestic EV market strengthens, potentially extending its global EV technology lead while U.S. production stalls.
Market Volatility Follows GM Pullback
GM’s $1.6 billion special charge caused stock declines of 2–4% on October 29, 2025. Toyota gained 3% for hybrid-focused strategy.
Bond markets reflect debt concerns as GM carries $130+ billion in liabilities. Private equity eyes distressed supplier facilities. Q1 2026 earnings may reveal longer-term investor confidence in EV equities.
Consumer Guidance Amid Uncertainty

Short-term buyers may find 2025 EV inventory discounts, partially offsetting subsidy loss. Long-term buyers should monitor 8–10% annual battery cost declines to regain competitiveness by 2027–2028.
Hybrid alternatives offer a middle path. Verify warranty coverage and production continuity. Total cost of ownership—including electricity, maintenance, and resale—is key in navigating the shifting EV landscape.
Looking Ahead: GM’s Next Moves
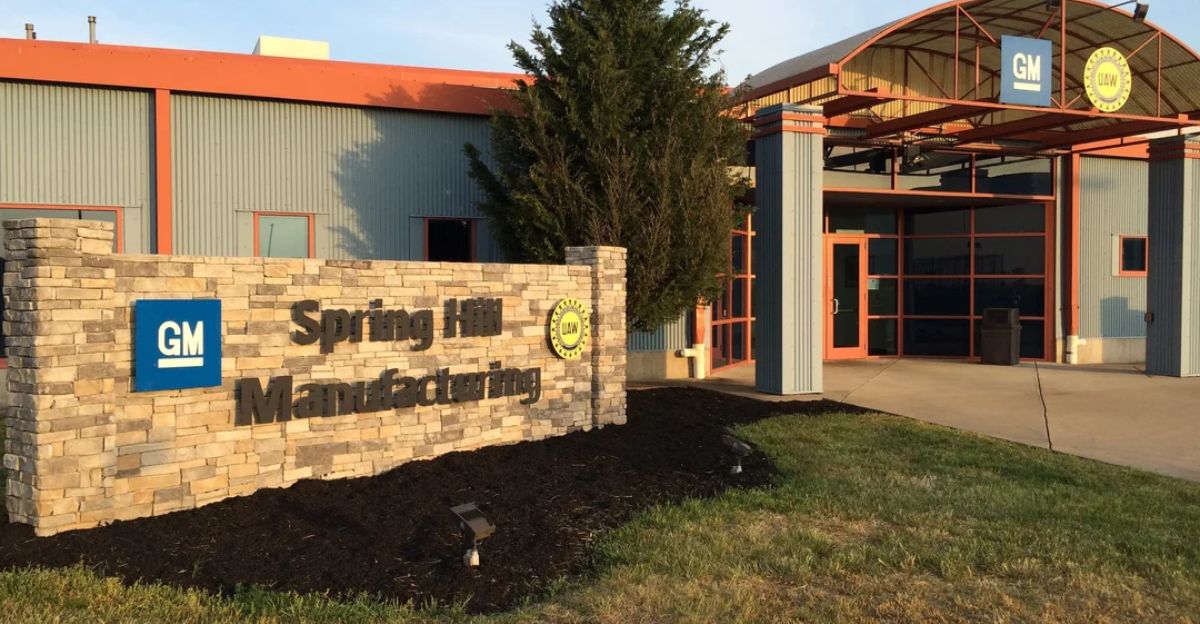

GM plans to revisit Spring Hill mid-2026, though timelines remain uncertain. Temporary shutdowns may become permanent, threatening technical expertise retention.
Optimistic forecasts see recovery as battery costs decline; pessimistic scenarios suggest a U.S. EV stall of 5+ years. GM’s strategy will influence industry direction, including hybrid focus, federal lobbying, and international EV expansion.
Pivotal Moment Reshapes Industry

GM’s indefinite megafactory freeze and 3,420+ layoffs mark a historic inflection for U.S. manufacturing. Four weeks from tax credit elimination to layoffs highlight policy-dependent business fragility.
Communities, wages, and global supply chains are disrupted. The $2.6 billion Spring Hill investment illustrates both promise and peril of government-driven industrial transformation. The next decade will reveal whether this is a temporary setback or permanent shift.