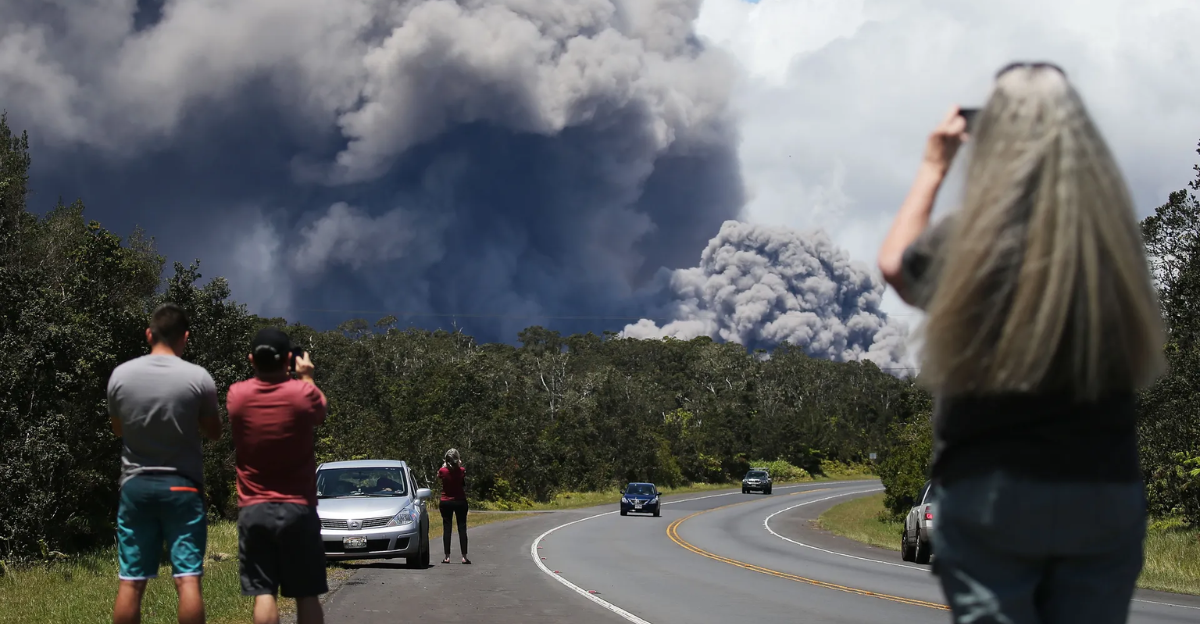

Hawaii’s Kilauea volcano is stirring with rare intensity, threatening its most dramatic eruption in nearly four decades. Tremors ripple across the Big Island, and scientists at the U.S. Geological Survey’s Hawaiian Volcano Observatory warn that Episode 33 could begin “today or tomorrow.”
Lava fountains may rival historic surges, offering a spectacle few witness firsthand. After days of subtle crater shifts and heightened gas emissions, the stage is set for a rare event that could reshape the summit and remind everyone that Hawaii’s landscape is still alive.
Tremors and Tilt Signal Volcano Ready to Explode
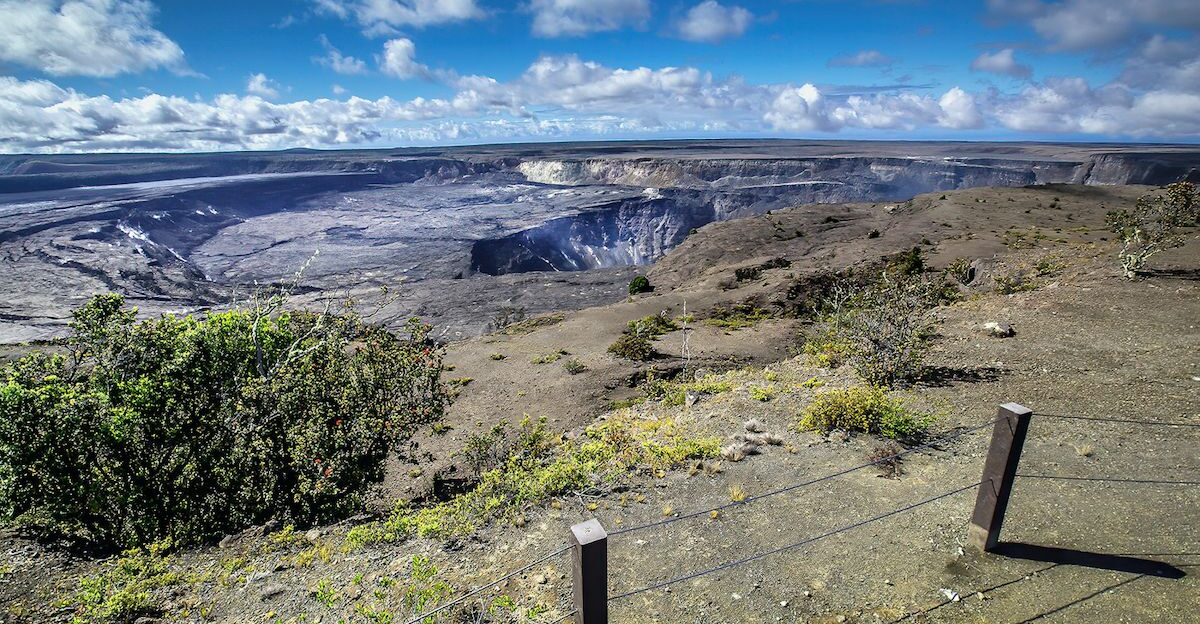

Tiltmeters at Uēkahuna recorded roughly 22.5 microradians of inflation since the last episode ended, while gas-piston cycles have intensified. Even minor lava overflows hint at rising pressure beneath the surface. A USGS spokesperson explained that these patterns often precede dramatic fountaining, signaling Kilauea is quietly gearing up.
Scientists describe monitoring the volcano as tracking a heartbeat, where every tremor and spurt of gas is a clue to what might come next. These subtle changes offer both a warning and a glimpse into the volcano’s growing energy.
Overnight Lava Surges Hint at Imminent Eruption
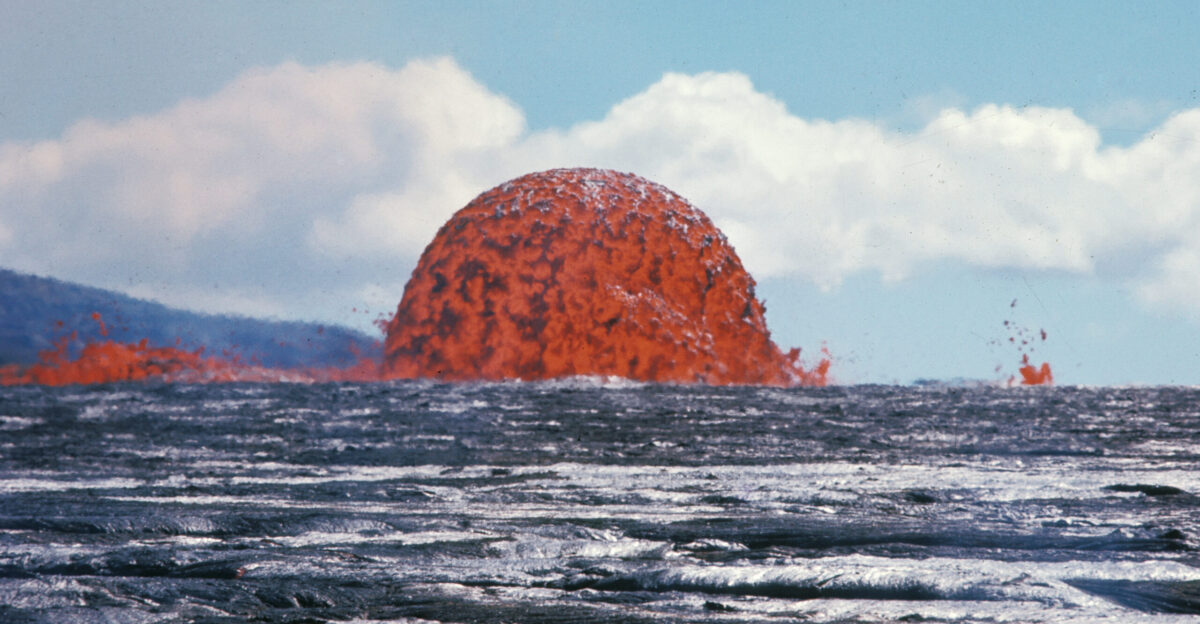

Overnight, dome fountains reached 20 feet, signaling magma movement beneath the summit. Gas-piston cycles produced brief lava surges, while ground tilt readings hinted at mounting pressure. Scientists say this buildup—the calm before a potential storm—is both fascinating and instructive.
Observers call it one of the most compelling parts of Kilauea’s behavior: a moment when nature is quietly gathering strength, offering a rare window to witness the forces driving an imminent eruption.
Gas-Piston Bursts Send Molten Rock Skyward
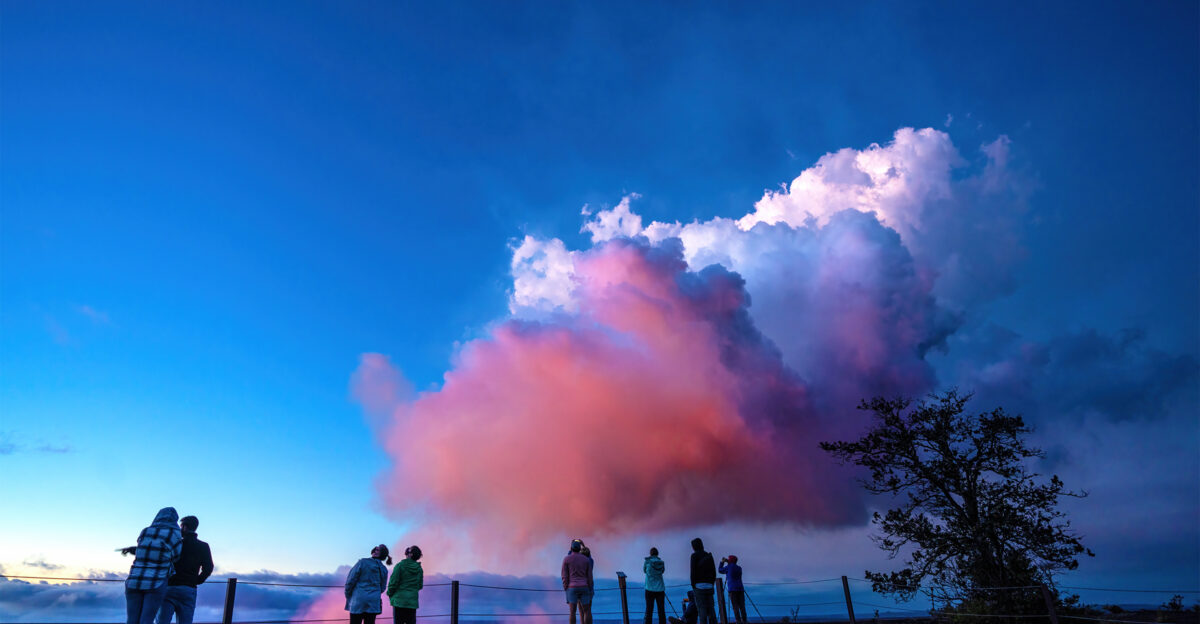

Now, molten rock rises 30 feet above the crater with rhythmic gas pulses every ten minutes. Lava spills across the western floor, then drains back, forming ephemeral rivers of molten rock. Scientists describe these patterns as a living record of underground pressure, a prelude to a potential historic eruption.
Watching the cycles unfold highlights Kilauea’s dynamic system, revealing how energy and magma move in mesmerizing and informative patterns.
Kilauea on WATCH as Air Quality Risks Rise
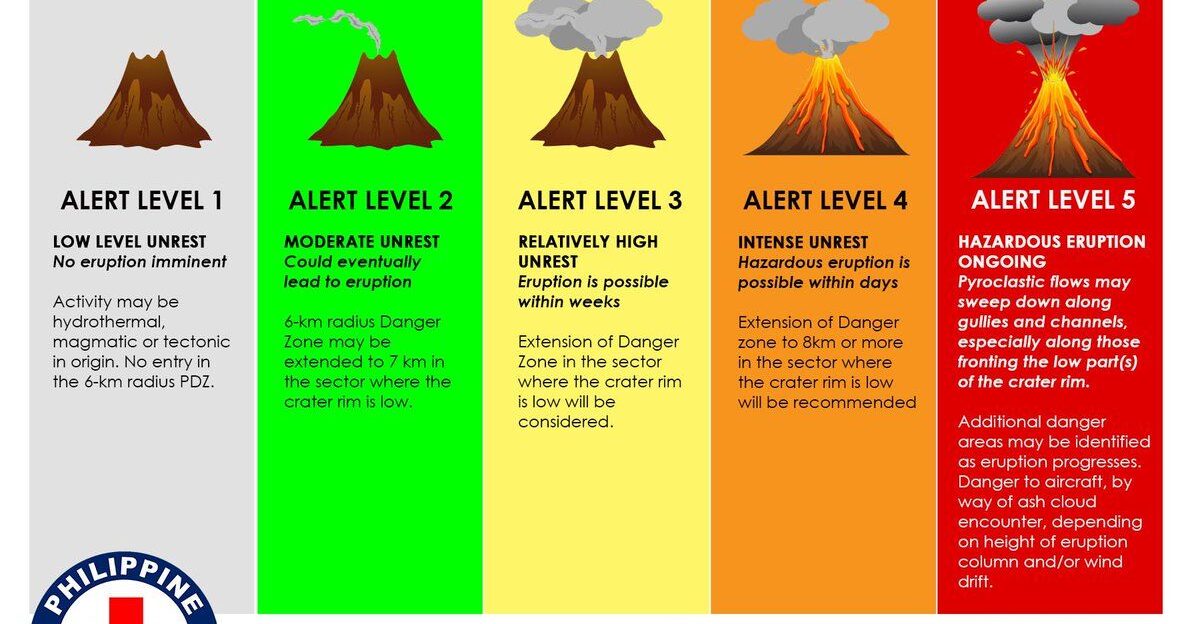
The volcano remains at “WATCH” on the official alert scale, with the aviation color code set to ORANGE. Sulfur dioxide emissions have climbed sharply, affecting air quality near the summit. Daily emissions can spike to 1,500 tonnes, a reminder that dangers extend beyond lava. USGS officials stress observing from a safe distance and wearing protective gear if near the crater.
Even in anticipation, Kilauea demonstrates how geological forces can reach far beyond the eye, impacting air, health, and safety across the surrounding landscape.
Pele’s Hair Blankets Summit, Poses Hidden Hazards
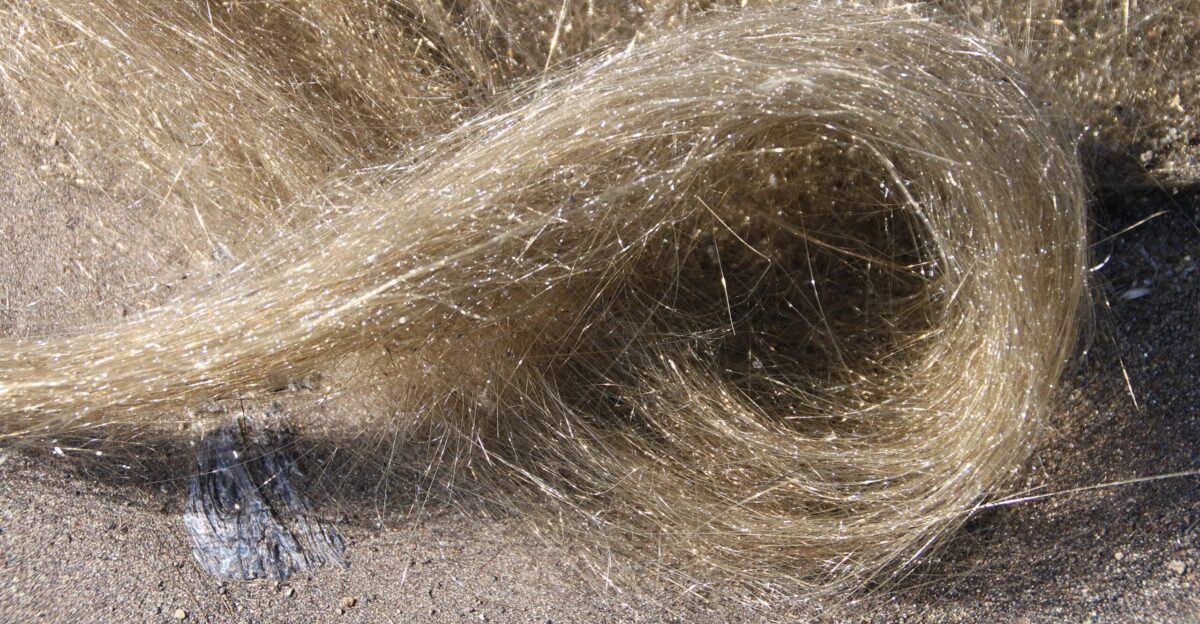

Fine strands of volcanic glass known as Pele’s hair now cover the summit, forming delicate filaments that the wind carries. These sharp strands can irritate eyes and lungs and linger for weeks beyond the crater. Experts warn that airborne debris adds an invisible layer of danger.
Park officials emphasize protective gear, safe distances, and avoidance of exposed skin.
Even when molten rock remains contained, Kilauea illustrates how volcanic hazards extend into the air, reminding visitors that beauty often comes with hidden risks.
Historic Eruptions Offer Clues to Kilauea’s Next Moves
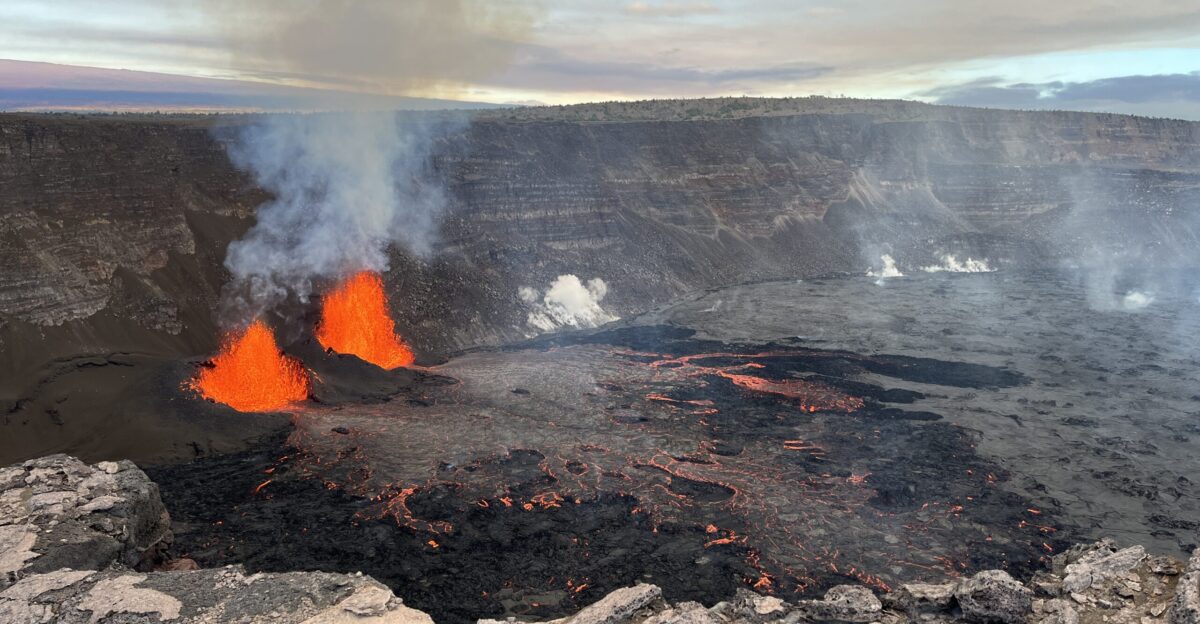

Kilauea’s last major fountaining began in 1983 and continued intermittently until 2018, reshaping communities and the island’s terrain. Lava flows destroyed hundreds of homes and altered coastlines, leaving enduring scars.
Today’s activity mirrors past patterns: vent inflation, episodic gas surges, and rising lava fountains. Geologists note that while behavior remains consistent, current magma supply and vent structure may produce even more dramatic displays, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and safety planning as the volcano evolves.
Hawaii Volcano Among 54 Global Eruptions This Year
Kilauea is part of a global surge in volcanic activity. In 2025, 54 eruptions were documented worldwide, many along the Pacific Ring of Fire, which spans 25,000 miles and hosts over 450 active volcanoes. Kilauea stands out for both its scale and proximity to populated areas.
Experts say it provides a real-time view of eruption dynamics, gas emissions, and vent evolution, offering insights relevant to global volcanic hazards and highlighting how Hawaii’s activity fits into a larger planetary pattern.
Spectacular Lava Shows Draw Crowds and Scientists

Kilauea’s eruptions turn the summit into a natural stage, attracting scientists, photographers, and curious visitors. Volunteers and park rangers witness lava fountains illuminating the night sky. One volunteer described the experience as “sitting in the front row for nature’s most extraordinary show,” capturing the mix of awe and caution.
Observers note the event blends scientific observation with the thrill of witnessing elemental forces that have shaped Hawaii for centuries, providing a rare intersection of education and spectacle.
Jet-Engine Roar Echoes Across Volcanic Caldera
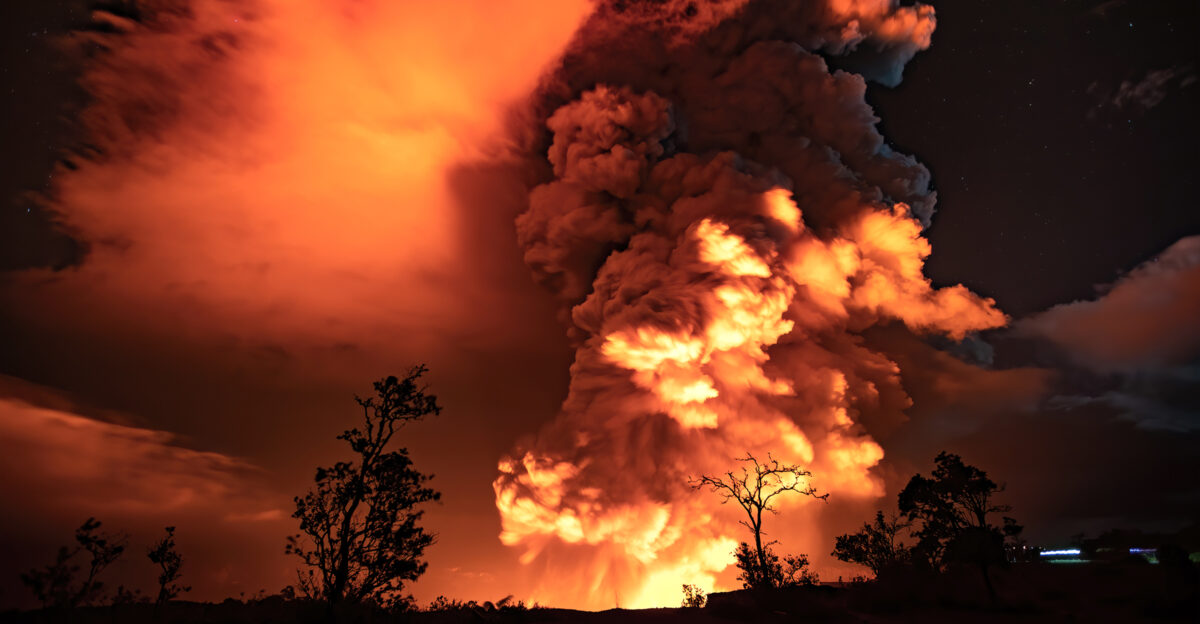

Eyewitnesses compare the eruption’s sound to a roaring jet engine echoing across the caldera. Gas expansion, lava ejection, and vent collapse produce low-frequency rumbles felt and heard. Residents describe the combination of visual and auditory signals as a reminder of Earth’s elemental power.
Scientists note that these acoustic cues complement seismic measurements, offering additional insight into eruption intensity and vent stability. Visitors gain a visceral sense of nature’s force that transcends charts and graphs.
Volcanologists Track Every Tremor in Real Time
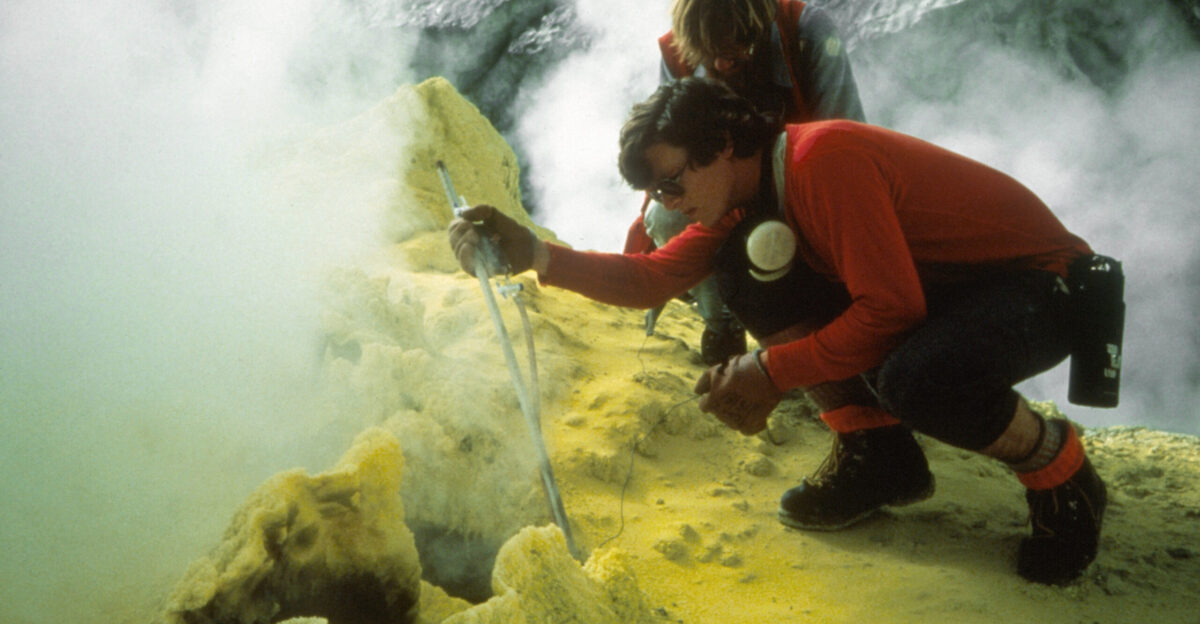

Seismic arrays and ground deformation sensors allow to track Kilauea’s every movement. “It’s like observing a giant animal and trying to anticipate its next move,” one USGS scientist said. Vigilance enables timely alerts, hazard map updates, and coordinated emergency responses.
Combining technology, field expertise, and interpretation ensures even unpredictable volcanic behavior is monitored effectively, providing residents and visitors with crucial information to stay safe while the summit evolves in real time.
Current Activity Mostly Contained, but Risks Loom
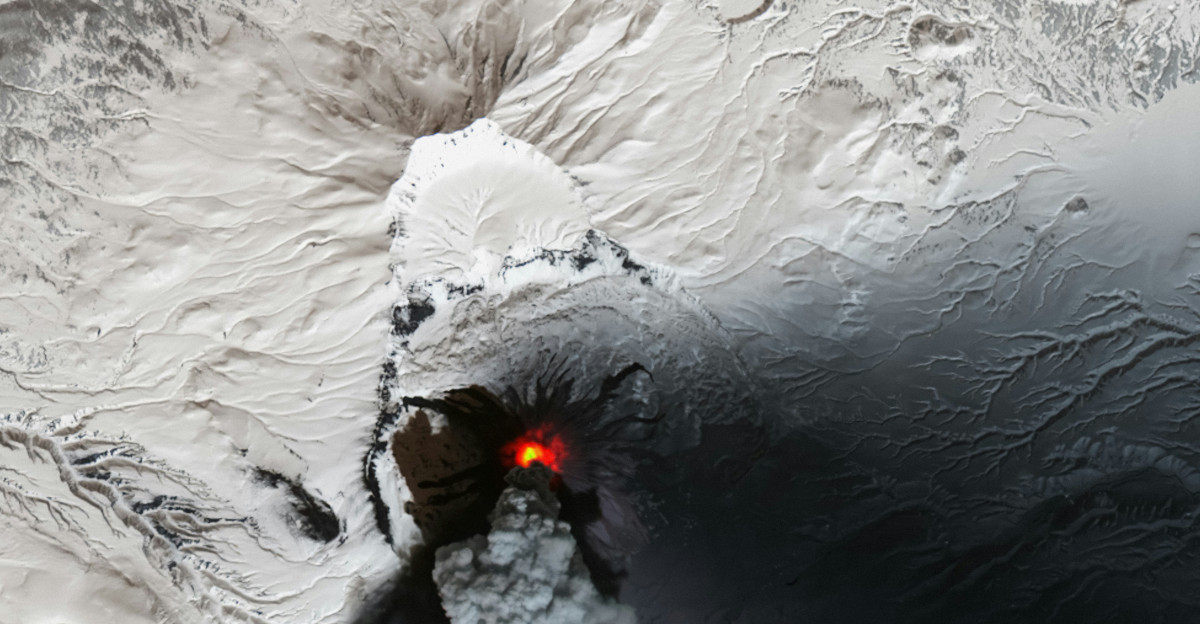

At present, lava remains confined to the summit crater, minimizing immediate threats to communities. Scientists caution that vent expansion could redirect flows, potentially threatening towns or infrastructure. Monitoring focuses on tilt, seismicity, and gas flux to detect changes in the eruption trajectory.
Authorities advise residents to review evacuation plans and remain aware of shifting hazard zones. Even contained eruptions demonstrate the delicate balance between nature’s spectacle and community safety, emphasizing the importance of vigilance as conditions change.
Lava Fountains Reach Hundreds of Feet in Stunning Surges

Recent eruptions have sent lava jets soaring 30 to over 1,000 feet, with rare surges exceeding 300 meters. Height depends on vent shape, magma pressure, and composition, all of which can shift rapidly. Even experienced volcanologists are surprised by sudden bursts, highlighting Kilauea’s unpredictable energy.
Studying these fountains helps scientists understand vent stability and eruption mechanics while informing public safety measures. The extraordinary scale offers both a scientific window and a dramatic display that few landscapes on Earth can rival.
Underground Pressure Signals Volcano’s Potential Fury
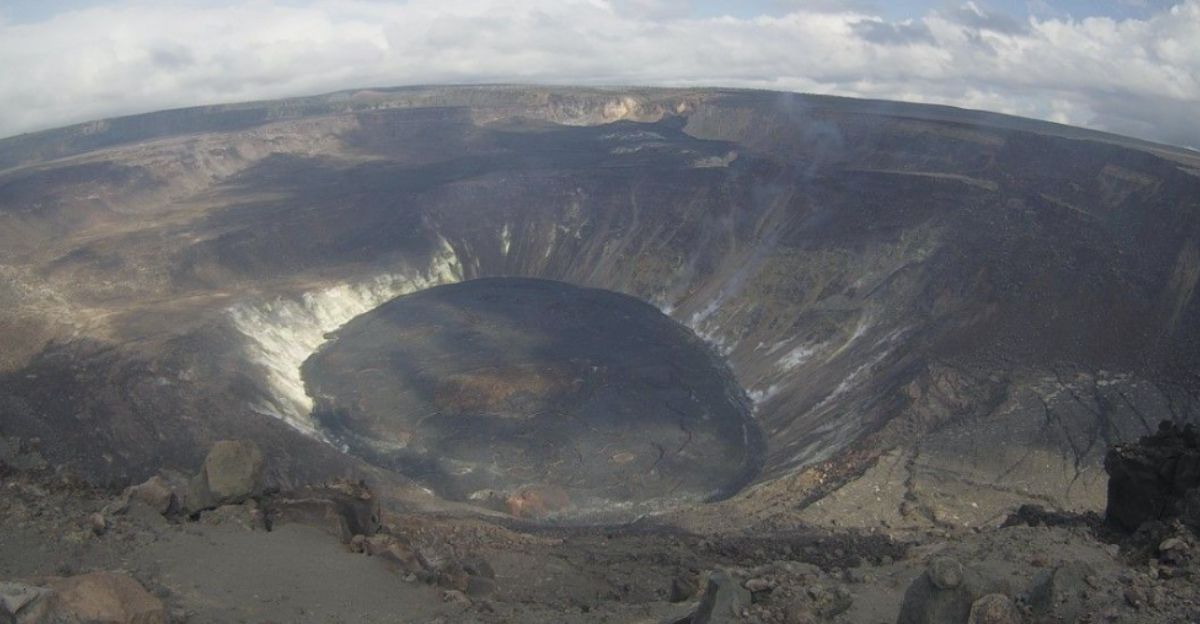

Seismic activity and inflation show magma accumulating beneath the summit. Low-frequency tremors coincide with periodic gas bursts, classic signs that the volcano is nearing a critical threshold. These subtle readings, combined with visual observations, provide an early glimpse into potential eruption intensity and duration.
Experts say this buildup illustrates the enormous subterranean forces shaping Kilauea, reminding observers that even the quietest periods can mask immense geological energy ready to emerge.
Sulfur Dioxide Plumes Add Danger to the Air
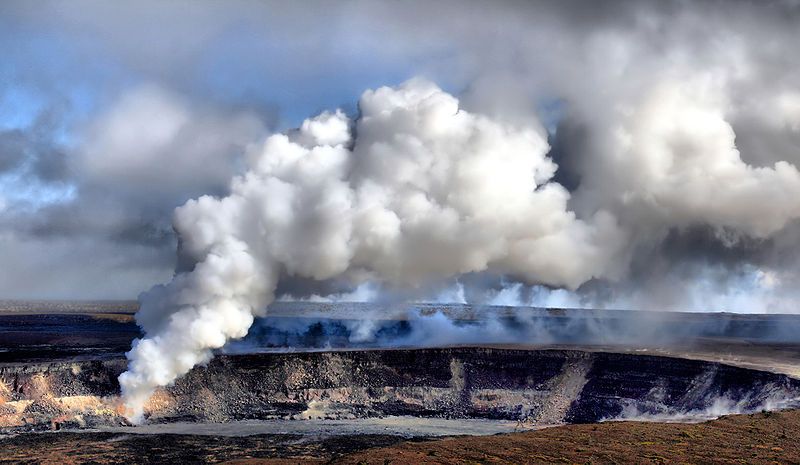

Sulfur dioxide emissions have surged, forming plumes that reduce air quality around the summit. Levels fluctuate with lava pulses and gas-piston activity. Officials warn that exposure can irritate eyes and lungs, particularly for visitors with respiratory conditions. Observatories issue real-time alerts when concentrations exceed safe limits.
While visually striking, these emissions highlight how volcanic hazards extend beyond molten rock, reinforcing the need for caution and preparedness even in areas that appear physically safe from lava flows.
Episode 33 Could Be the Longest, Largest Yet
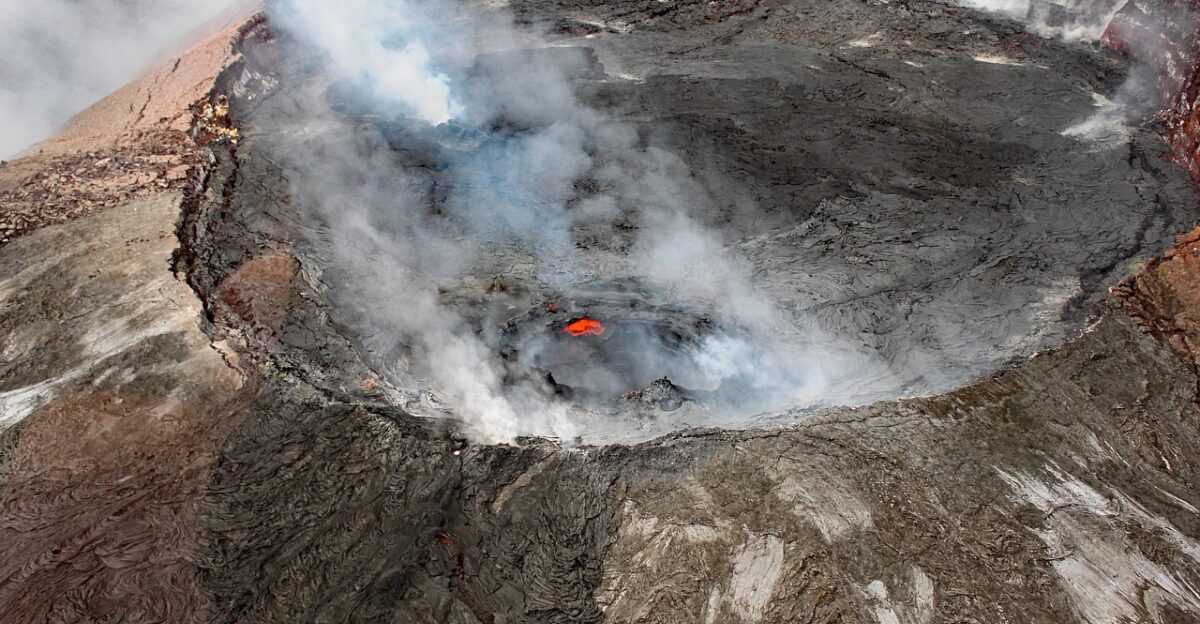

Kilauea’s eruption cycle began in December 2024 and produced more than 30 episodes by September 2025. Each follows a predictable rhythm: inflation, lava fountaining, and relative calm. Scientists warn Episode 33 may break records for both duration and lava volume. Local officials urge residents and visitors to remain alert, noting that conditions can shift suddenly.
The unfolding sequence offers scientists an unprecedented opportunity to study volcanic behavior while the public witnesses a rare, potentially historic chapter in Hawaii’s geologic story.
How Lava Bursts Across the Summit
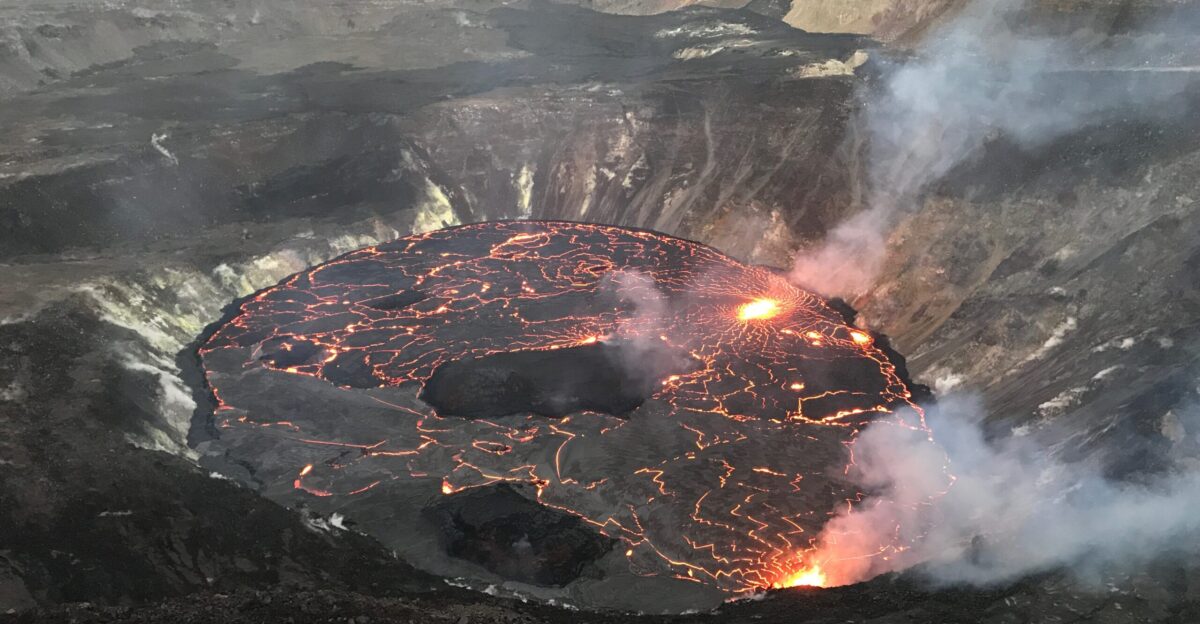

The Halemaʻumaʻu crater has evolved dramatically. Vent geometry now influences lava fountain height and trajectory, sometimes creating spectacular arches of molten rock visible for miles. Geologists note that subtle changes in cone structure or vent widening can redirect flows, shaping both the immediate landscape and hazard zones.
Continuous observation allows scientists to track how subterranean pressure interacts with surface features, offering insight into eruption patterns while illustrating the dynamic nature of Hawaii’s volcanic terrain.
Authorities Monitor Closely as Risk Evolves
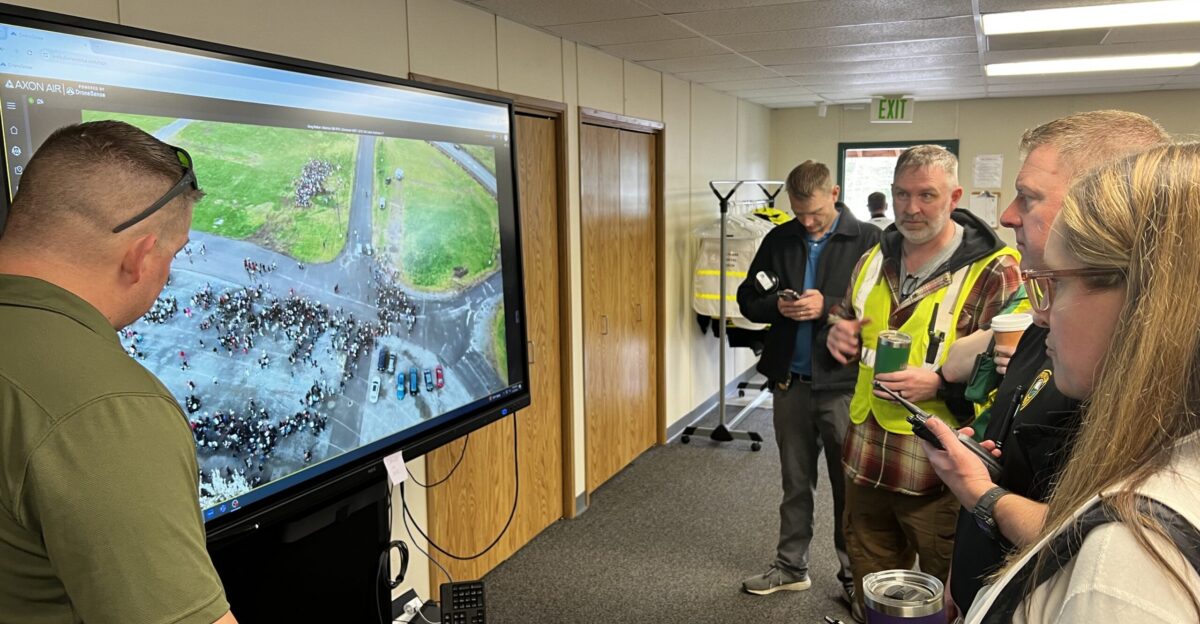

Officials remain on high alert, coordinating with emergency services and local agencies. No evacuations have been ordered, but monitoring informs risk planning, tracking ground deformation, gas emissions, and seismicity.
Response teams are ready to act when lava paths shift or vent activity intensifies. This proactive approach combines science, policy, and public awareness, ensuring residents can observe nature’s power safely while agencies maintain readiness for rapid changes in the volcano’s behavior.
Curiosity Draws Visitors Despite Official Warnings
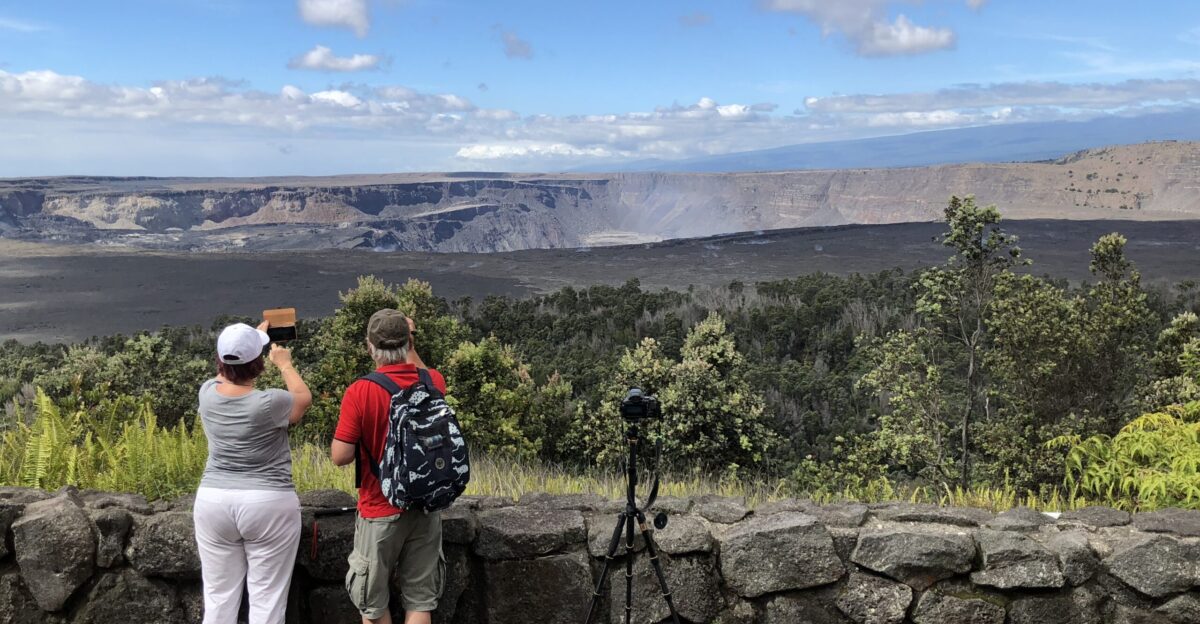

Despite repeated alerts, some residents and tourists approach the crater to witness its dramatic activity. Officials stress adherence to park closures and designated observation zones, as proximity to vents can be deadly. Scientists note the human fascination with extreme natural events, describing it as a mix of curiosity and reverence.
Safe viewing areas allow observers to experience the spectacle without compromising safety, balancing the allure of unprecedented geological displays with the practical need for caution.
Scientists Brace for the Moment Lava Might Explode

As of September 19, 2025, Episode 33 could begin at any moment. Scientists monitor every tremor, gas burst, and lava overflow, knowing that the next hours could unleash Hawaii’s largest fountaining in 39 years. The summit’s energy offers both awe and risk, transforming landscapes and reminding residents that the island’s volcanic origins are ever-present.
Observers—from locals to volcanologists—watch with anticipation, aware that the unfolding eruption could become one of Kilauea’s most remarkable events in nearly four decades.