
By lowering methane emissions and increasing feed efficiency, scientists have created revolutionary cattle feed that will radically alter how cows behave. These feeds frequently use cutting-edge additives like seaweed extracts, flaxseed, and pea protein to change the microbial activity in the cow’s rumen, which is where methane is created during digestion.
According to preliminary studies, these feeds can increase milk production and nutrient absorption while lowering methane emissions by 30 to 80%. Beyond nutrition, this development has ramifications for global greenhouse gas mitigation, agricultural economics, and environmental sustainability. A new era in livestock management is marked by improved protein utilization and gut microbiome modulation, which further enhance animal health and productivity.
The Historical Background of Innovation in Feed

Early in the 20th century, developments like pelleting revolutionized feed handling and nutrition, marking the beginning of the development of animal feed technology. These early developments gradually integrated scientific understanding of the effects of nutrients on animal performance while also improving feed palatability and storage. Compound feeds evolved over decades from grains and byproducts to complex formulations that catered to particular dietary requirements.
Environmental effects, particularly methane emissions, have only lately come into sharp focus, signaling a change from feed design for basic sustenance to feed design for climate change. The development of agriculture from subsistence methods to integrated ecological stewardship is highlighted by this historical trajectory.
The Problem of Methane Emissions in Cattle
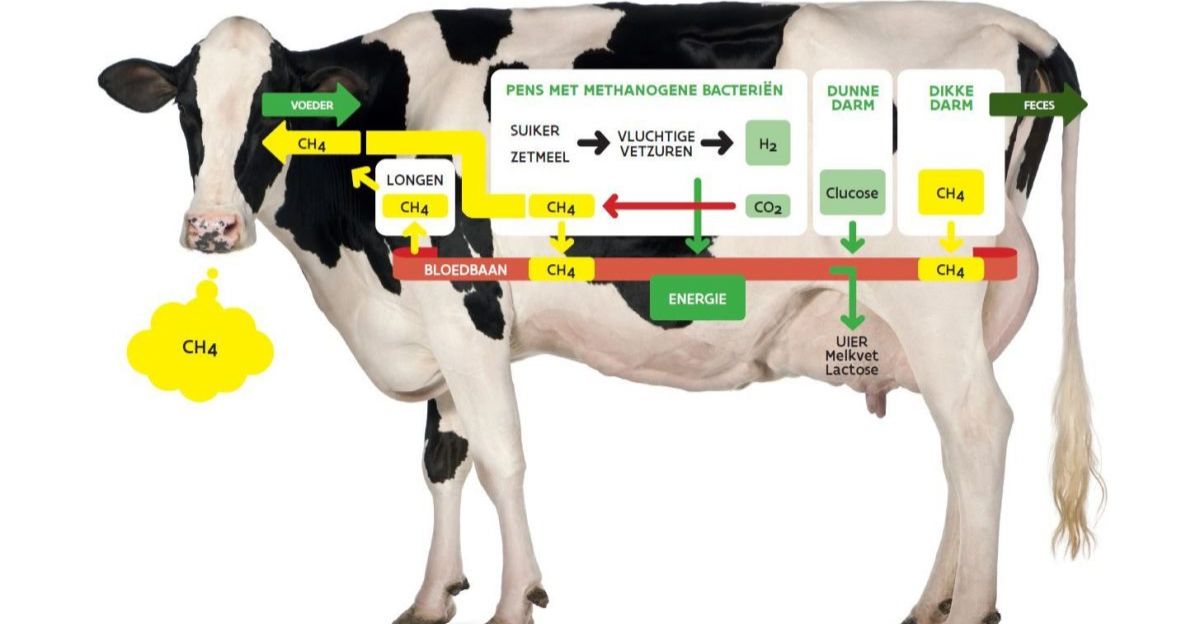
One of the leading greenhouse gases causing climate change is methane from ruminants, which is produced in the rumen by microbes fermenting fibrous feed. The main way that cows expel methane is through belching, which is a byproductbyproduct of breaking down high-fiber roughage like silage and grass. Cattle contribute significantly to agricultural emissions because of this inevitable biological process.
Reducing emissions without impairing digestion or health is a difficult task because traditional feeding techniques do not directly address methane output. Research into innovative feed formulations that inhibit methanogenic microbes while preserving nutritional balance is driven by the pressing need to reduce methane production in cattle.
Methane-Reducing Feed Additives as Modern Solutions

Feed additives that lower methane by blocking enzymes involved in methane biosynthesis or altering microbial fermentation pathways are recent innovations. Seaweed supplements like Asparagopsis taxiformis, synthetic additives like Bovaer®, and garlic and citrus extracts (Mootral) are a few examples. Based on the product and type of cattle, these can lower methane emissions by 30% to more than 80%.
These additives frequently increase feed conversion efficiency, producing more milk or meat per feed unit, in addition to having positive environmental effects. They offer a workable approach to livestock management that balances ecological and financial objectives.
Effects on the Production and Metabolism of Cows

New feeds increase nutrient absorption and digestive efficiency, which boosts cow metabolism. Supplements with enzymes increase the rumen’s volatile fatty acids, which increases the amount of energy available for development and production. Research shows that better body condition is associated with increased growth rates and milk yields.
Precision-tailored feeding also maximizes energy use and minimizes nutrient waste. Both farmers and ecosystems stand to gain from this reinterpretation of feed efficiency, which promises to increase livestock productivity while lowering environmental inputs and expenses.
The Function of AI and Precision Feeding

Precision feeding is made possible by technological advancements, whereby sensors, artificial intelligence, and real-time monitoring tailor each cow’s diet according to her age, health, and stage of production. This maximizes the performance of each individual animal while minimizing nutrient waste.
AI dynamically optimizes feed formulations to reduce nitrogen and phosphorus emissions into the environment. These technologies bring livestock nutrition into a data-driven, highly efficient era by combining personalized nutrition with cutting-edge feed additives, improving sustainability and farm profitability.
Engineering the Microbiome and Gut Health
With over a quadrillion microorganisms, cows’ rumen microbiomes are essential for digestion and methane production. Through the use of probiotics, prebiotics, and antimicrobial peptides, new feeds alter this ecosystem, inhibiting methane-producing microorganisms and encouraging species that absorb nutrients.
By enhancing immune responses, this microbiome engineering lessens the need for antibiotics. By using microbiology to transform livestock science, developments in microbiota manipulation signal a new era where environmental and digestive health outcomes are optimized together.
Field Trials and Case Studies
New feed efficacy is demonstrated by a number of case studies. In lab settings, research from the University of Florida suggests that flaxseed and pea protein supplements reduce methane and increase milk efficiency; larger trials are now underway.
Seaweed additives for beef cattle reduce methane by over 80%, while Mootral’s garlic-citrus supplement reduces methane by up to 38%. These show observable advantages, but they also highlight problems like cost, scalability, and adoption barriers. Translating lab success into broad commercial use requires cooperative outreach with farmers.
Economic and Environmental Trends Fueling Innovation

Feed innovation is fueled by a combination of environmental regulations aimed at reducing livestock emissions, consumer demand for sustainable products, and growing feed prices. It is acknowledged that lowering methane is essential to achieving climate goals.
In the meantime, farmers are looking for more economical and environmentally friendly feeds. These factors spur investment in precision nutrition and next-generation feeds, which have the potential to transform the livestock industry by combining environmental responsibility with profitability.
Unexpectedly Beneficial Effects

Besides cutting methane, new feeds may reduce overall feed requirements, easing pressure on agricultural land. Improved nitrogen use protects biodiversity by reducing soil acidification and ammonia emissions. Antibiotic resistance risks are reduced when healthier cows use fewer antibiotics.
Reducing waste and promoting circular agriculture are two benefits of using byproducts and alternative proteins, such as insect and algae biomass. These systemic advantages show how creative cattle feed can promote economic and environmental resilience in addition to its primary objectives.
Risks and Skepticism
Skeptics warn against making hasty claims. Widespread efficacy has not been established, and much of the methane reduction data is based on small trials. Exorbitant additive costs could hurt small farms and drive up prices for consumers.
If feed additives are given too much attention, systemic changes that are necessary for long-term effects may be overlooked. Novel compounds with unknown ecological or health effects should also be used with caution. A balanced approach demands rigorous testing, regulation, and integration within comprehensive sustainability frameworks.
Emissions Revolution from Seaweed

Studies have shown that the seaweed Asparagopsis taxiformis can reduce methane emissions by over 80%, making it an exceptional example of methane mitigation. Bioactive substances found in this seaweed directly interfere with the pathways involved in methane synthesis by suppressing the activity of methanogenic archaea in the rumen. Even though the results are remarkable, there are still obstacles to overcome before commercial production can be scaled up in a sustainable and cost-effective manner.
Harvesting techniques, supply chain logistics for farmers, and marine ecosystems must all be taken into account when growing seaweed on a large scale. Protocols for feed formulation and shelf stability are being improved to preserve efficacy during transportation and storage. Seaweed-based feed has the potential to transform livestock emissions globally if these obstacles are removed, providing a practical, natural solution at a scale never seen in livestock methane reduction.
Future and Theoretical Theories
In the future, new scientific theories suggest incorporating synthetic biology into the development of innovative animal feed. In the rumen, engineered microbes may be able to convert methane into valuable products like short-chain fatty acids or even produce enzymes that prevent methane biosynthesis. Precision delivery systems that target particular microbial populations or enzymes for optimal effect without upsetting rumen balance may be made possible by nanotechnology.
Through the use of genetic editing technologies, cows or their microbiomes may be modified to reduce methane production or increase feed conversion efficiency naturally. In addition to metabolism, bioactive substances that alter stress reactions or reproductive function may be incorporated into future feed formulations to increase livestock productivity overall.
Historical Parallel: The Revolution from Horse Feed to Cow Feed

The historical revolution of compound feeds for horses in the 19th century, which allowed for the growth of military and industrial logistics, is comparable to the change taking place in contemporary cattle feed. Unprecedented mobility and operational efficiency were made possible by concentrated, transportable horse feed. Similar to this, the current trend toward climate-conscious, scientifically engineered cattle feed has the potential to change both the environmental impact and agricultural productivity significantly.
This historical comparison demonstrates how feed technology reflects human ingenuity in adjusting animal nutrition to modern demands and is in line with larger socioeconomic shifts. Understanding this background highlights the importance of recent innovations in cattle feed, which are not just minor enhancements but also a crucial stage in the development of agriculture with profound effects on society and the environment.
Consequences for World Food Security

The creation of novel cattle feeds that increase productivity and environmental sustainability directly affects global food security as the world’s population continues to grow and puts strain on limited agricultural resources. Increased milk and meat yield per animal due to improved digestion and nutrient use efficiency enables food production to expand without requiring a corresponding expansion of land or water resources.
This efficiency lowers greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation, two important aspects of sustainable food systems. Additionally, improved feed reduces disease susceptibility and mortality rates, making livestock populations more resilient. Adoption of these feeds therefore promotes fair access to animal protein, especially in areas where livestock are a major source of nutrition and income.
Potential Industry Disruptions

The adoption of advanced feed technologies and precision nutrition platforms is poised to disrupt established livestock supply chains globally. Feed production may shift towards highly specialized biotech companies that develop custom microbial additives and enzyme blends, replacing traditional commodity feed suppliers.
Precision feeding technologies will prompt farmers to adopt new herd management and data analytics skills, integrating real-time health and emission monitoring into daily routines. Rising acceptance of alternative protein sources, like insect and algal meals, will influence feed ingredient markets, reducing reliance on conventional crops such as soy and corn. These disruptions could challenge existing industry players but also foster new business models emphasizing sustainability, technological integration, and value-added nutrition, thereby catalyzing renewed investment and innovation in the agriculture sector.
Social and Psychological Factors in Adoption

Overcoming social norms and psychological obstacles that are common among livestock producers is necessary to alter long-standing feeding practices. Gaining confidence in evidence-based procedures and new technologies requires open communication and measurable results. In order to spread awareness of feed innovations and their advantages for the economy and environment, education and extension services are essential. Pilot projects and success stories can generate social proof and early adopters, hastening broader acceptance.
The use of precision feeding technologies may put farming communities’ traditional roles and routines to the test, necessitating both technical training and cultural adjustments. Carefully navigating these social and psychological factors is necessary to guarantee the equitable and long-term adoption of innovative feed techniques.
Broader Economic and Environmental Impacts

Beyond lowering methane, new feeds’ increased feed efficiency and nutrient utilization significantly contribute to a number of environmental advantages, including decreased runoff of nitrogen and phosphorus, lessened soil acidification, and improved biodiversity conservation. In terms of economics, farmers can stabilize livelihoods in the face of agricultural volatility by maximizing feed conversion and cutting waste, which will lower overall costs and increase profitability.
As livestock sustainably increase production without increasing environmental footprints, these advantages also strengthen rural economies and the resilience of the food system. These effects can be further amplified by policy pathways that offer financial incentives, such as carbon credit mechanisms linked to feed-related emission reductions. This can create positive feedback loops in which producers receive monetary rewards for better environmental stewardship.
Directions for Future Research and Policy

Future studies must concentrate on long-term sustainability, safety, and cost-effective accessibility across various agricultural contexts in order to fully realize the potential of these cutting-edge cattle feeds. To optimize feed formulations and thoroughly assess broader ecosystem impacts, microbiologists, animal nutritionists, environmental scientists, and economists must work closely together across disciplinary boundaries.
Through grants and subsidies, policymakers should promote innovation while guaranteeing fair technology transfer to small-scale and resource-constrained farmers. Consumer and regulatory confidence will be increased by using transparent, standardized techniques for methane emission monitoring associated with feed use. Adoption and alignment with international climate and food security goals can be accelerated through international cooperation and open data sharing.
In Conclusion

Scientists have created innovative technologies for cattle feed that offer a once-in-a-lifetime chance to address livestock production’s environmental and productivity issues at the same time. These feeds take advantage of developments in precision nutrition, enzyme technology, and microbiome science to lower strong greenhouse gas emissions, increase feed efficiency, and support animal health.
Despite obstacles related to farmer adoption, costs, and scaling, the combination of digital tools and scientific innovation holds promise for making livestock agriculture a more climate-friendly and sustainable industry. In order to secure the world’s food supplies and reduce agriculture’s contribution to climate change, a paradigm shift is necessary. A future where cattle farming favorably impacts ecological balance and economic vitality will be shaped by the responsible adoption of these innovations.