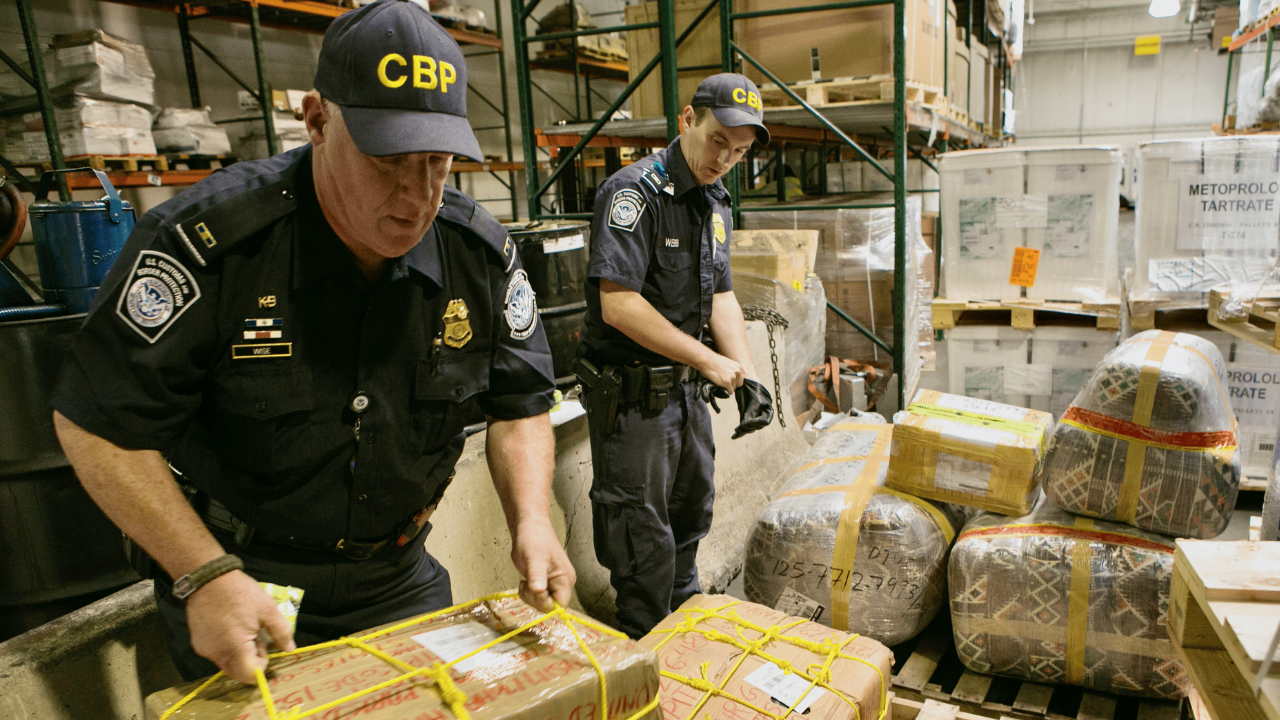

Authorities were shocked when a major smuggling operation was uncovered, involving Nvidia’s elite AI chips, valued at over $160 million. The smuggling ring funneled these high-performance GPUs, which are crucial for powering cutting-edge AI models, to China. The chips, banned for export due to national security risks, were tracked across warehouses in Texas and New York.
The question remains: how did this operation fly under the radar for months?
Escalating Stakes
In 2024, smugglers managed to funnel tens of thousands of Nvidia chips to China, circumventing U.S. export controls. Federal authorities seized over $50 million worth of chips and cash, underscoring the enforcement gaps in the system. With AI hardware becoming an essential tool in global military developments, these illegal operations threaten to erode the U.S.’s technological edge.
What methods did the smugglers use to avoid detection for so long?
The Control Origins
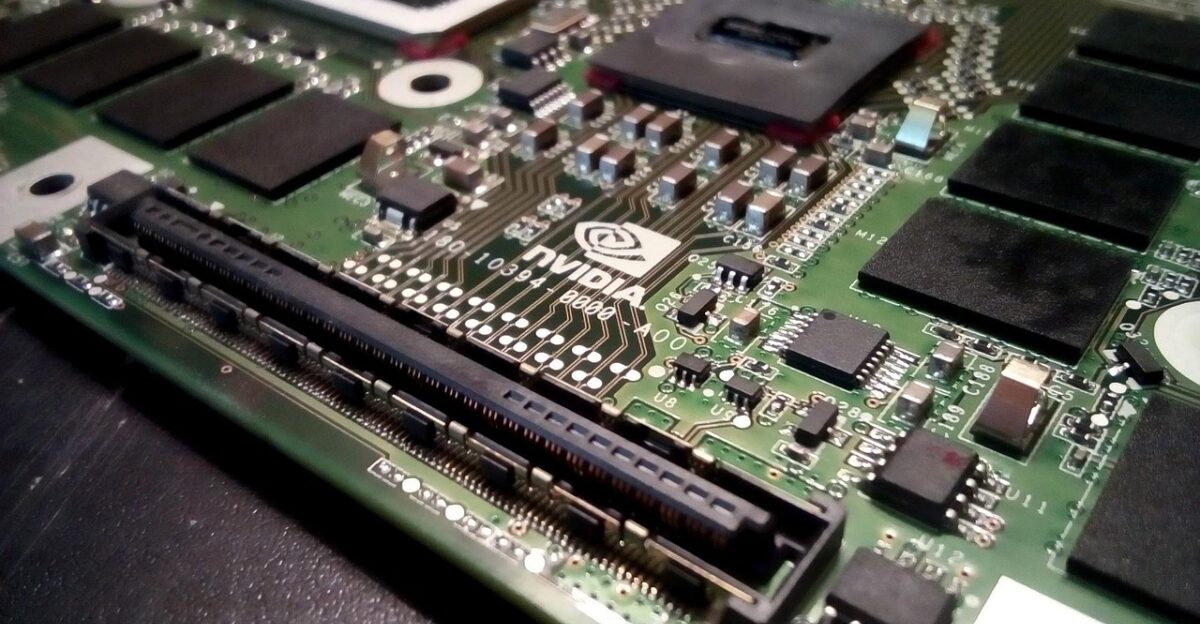

Export restrictions on Nvidia’s H100 and H200 GPUs were implemented in 2022 to curb China’s military AI advancements. These high-end chips, with capabilities like 80GB of HBM3 memory and 3.35 TB/s bandwidth, are essential for AI model training and require a special license to export to China or Hong Kong.
Despite these bans, demand for the chips surged, fueling an underground market.
Tightening the Net
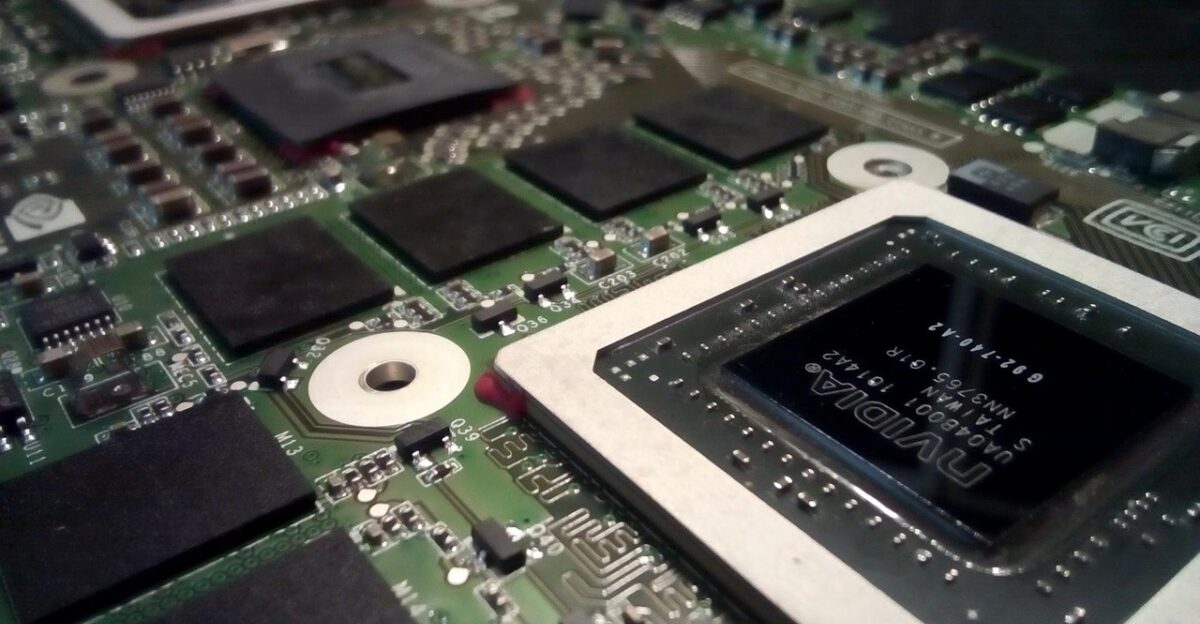

By late 2024, investigations intensified as more cases of diverted Nvidia chips came to light. This growing crisis exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains. With the launch of the Nvidia H200, featuring an upgraded 141GB HBM3e and 4.8 TB/s bandwidth, the stakes grew even higher.
Federal authorities began mounting raids to uncover evidence and halt the increasing flow of smuggled goods.
Ring Busted Wide Open

Texas businessman Alan Hao Hsu, along with his company Hao Global, pleaded guilty to smuggling over $160 million worth of Nvidia H100 and H200 GPUs from U.S. warehouses to China and Hong Kong between 2024 and 2025. Known as Operation Gatekeeper, the investigation revealed a complex web of fraudulent labeling schemes operating out of Brooklyn facilities.
Why resort to such elaborate evasion tactics?
Texas-New York Fallout

Hsu’s operation spanned multiple locations, including Texas and New York. In Houston, chips were acquired through straw buyers, while Brooklyn warehouses carried out relabeling operations. Shipments were rerouted through Hong Kong, bypassing export restrictions, and intended for a Chinese IT firm.
The seizures of assets disrupted the smuggling channels and impacted local economies.
The Faces Behind the Scheme

Alan Hao Hsu, 43, faces sentencing in February 2026. His accomplices, Fanyue Gong, a Chinese national, and Benlin Yuan, a Canadian CEO based in Ontario, could face up to 20 years in prison. U.S. Attorney Nicholas J. Ganjei described the gravity of the offense: “These chips are crucial for AI military applications.”
The families of the defendants now await the final verdicts.
Regulatory Ripples
The Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) highlighted the bust as an example of new smuggling tactics, including physical relabeling of chips to hide their true origins. Nvidia has responded by enhancing tracking systems to detect second-hand smuggling.
Global competitors like AMD are facing similar scrutiny, leading to tighter regulations on AI hardware.
Macro AI Race
The U.S.-China chip conflict continues to drive policy shifts as smuggling rings persist despite export bans. The Nvidia H100/H200 chips, capable of up to 3,958 TFLOPS FP8, are critical for AI training, making them a prized commodity.
With smuggling undermining U.S. controls, global enforcement efforts are increasing to prevent further erosion of technological leadership.
Fake Branding

Under Gong’s direction, workers in U.S. warehouses stripped Nvidia labels off the chips and rebranded them as “SANDKYAN”—a completely fictitious name—allowing them to pass as generic parts. Falsified shipping documents further obscured their true destinations, while Yuan coordinated with inspectors to cover up shipments destined for China.
The smuggling operation was backed by millions in Chinese funds.
Stakeholder Fury

The U.S. Attorney’s Office expressed strong concerns over national security, as the illicit trade of these chips threatens to empower Chinese AI projects, potentially for military use. Nvidia has reaffirmed its commitment to compliance and is working on tightening control over resale channels.
Meanwhile, Chinese funders and AI companies face potential repercussions.
Leadership Shakeup

Hsu’s guilty plea highlights the importance of corporate accountability. Yuan and Gong, however, remain at the center of the investigation, showing the critical role of leadership in smuggling schemes.
While there has been no major leadership shakeup yet, these cases highlight the increasing scrutiny of cross-border operations involved in tech smuggling.
Enforcement Pivot

As Operation Gatekeeper expands, federal authorities are focusing on ramping up warehouse crackdowns. Nvidia is improving traceability on second-hand markets, while seized assets are being reinvested into further investigations.
Preemptive licensing and global partnerships are now being emphasized to address smuggling activities before they can escalate.
Expert Doubts Linger

Despite the high-profile bust, experts remain cautious about the effectiveness of these measures. Analysts point out that while raids like these make an impact, the fundamental issues—such as the ability to divert vetted exports—remain unresolved.
As AI demand grows, the illegal trade in GPUs is expected to continue adapting and evolving.
Future Horizons

With new policies being rolled out, such as the 25% fee on H200 exports to China, U.S. authorities are attempting to curb illicit trade by providing legal channels for sales. However, China’s swift rejection of the approved H200 exports suggests that this strategy may not be effective.
The question remains: can the U.S. secure its AI lead long-term by balancing bans and controlled sales?
Policy Battleground
This bust underscores the Trump administration’s dual strategy: prosecuting smugglers while allowing Nvidia to ship H200 chips to approved customers in China with a cut of the profits. However, China’s rejection of these exports raises doubts about the long-term effectiveness of such a model.
As tensions escalate, the political debate over national security versus economic benefits continues.
Global Echoes
This case has broader implications, involving logistics networks in Hong Kong and AI firms in China. The operation has placed a strain on U.S.-China relations, with Beijing potentially retaliating by accelerating domestic chip production.
Canada, where one of the co-conspirators is based, may also face increased pressure to align with export control regulations.
Legal Reckoning

Gong faces up to 10 years for his role in the smuggling conspiracy, while Yuan faces up to 20 years under the Export Control Reform Act. Fines for Hao Global could total double their illicit gains.
The ongoing case sets a precedent for future smuggling cases involving physical relabeling operations and illegal exports of high-tech materials.
Ethical Tech Shift

The smuggling ring has raised significant ethical concerns about AI development. While some advocate for global access to AI, others stress the importance of securing sensitive technologies.
As generational views shift, debates over whether export restrictions stifle or protect innovation continue to intensify.
What Signals Next

The largest Nvidia bust to date has opened a new frontier in smuggling enforcement, signaling a shift toward hybrid enforcement strategies that combine raids with licensed sales. As new AI chips like the H200 continue to drive demand, the U.S. must adapt its controls to maintain its technological edge.
The next challenge: preventing similar breaches from happening again.
Sources:
U.S. Department of Justice Press Release / Official Statement (December 8, 2025)
CNBC – “Nvidia chips: Plots to send GPUs to China expose $160 million” (December 9, 2025)
Fox 26 Houston – “Feds say Houston-linked ‘Operation Gatekeeper’ broke $160M AI chip smuggling pipeline to China” (December 8, 2025)
Arnold Porter – “DOJ Announces Shutdown of Major China-Linked AI Tech Smuggling Network” (December 14, 2025)
Times of India / Multiple outlets – “Technology company CEOs caught smuggling Nvidia GPUs worth $160 million” (December 9, 2025)