
Astronomers watched the data update in real time as an object tore through the inner solar system at more than 150,000 miles per hour—too fast to be captured by the Sun, too active to ignore. Telescopes began reporting a bright coma forming far beyond Jupiter, where most comets stay frozen and dark.
Within days, it was clear this wasn’t just another comet. This was 3I/ATLAS, and its behavior was already breaking expectations. What scientists uncovered next only deepened the mystery.
Only the Third Interstellar Object Ever Confirmed
Confirmed on July 1, 2025 by the ATLAS survey and the Minor Planet Center, 3I/ATLAS became just the third known interstellar object ever observed, following 1I/’Oumuamua and 2I/Borisov. With a sample size this small, every detail matters.
Rather than reinforcing patterns suggested by earlier visitors, 3I/ATLAS immediately disrupted them, hinting that interstellar objects may be far more diverse—and common—than astronomers first assumed.
A Hyperbolic Escape Route, Not a Solar Capture

Orbital calculations showed 3I/ATLAS moving on a hyperbolic trajectory, confirming it came from another star system and will never return. Its velocity ranged from roughly 58 to 68 kilometers per second, peaking near 152,000 miles per hour around perihelion.
That speed isn’t just dramatic—it forces astronomers to rethink how frequently planetary systems eject icy bodies and how many interstellar objects may be passing unseen through the galaxy.
Bright, Active, and Immediately Cometary

Unlike ‘Oumuamua, which lacked a visible coma, 3I/ATLAS behaved unmistakably like a comet. It developed a bright coma and tail early, well before nearing the Sun. The rapid brightening suggested fresh, volatile-rich ices were being exposed for the first time.
That contrast underscored a key realization: interstellar comets don’t share a single personality. They may span a wide spectrum of activity, composition, and evolutionary history.
Hubble Reveals a Puzzling Size Range

High-resolution observations from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope constrained the comet’s solid nucleus to somewhere between 440 meters and 5.6 kilometers across.
That unusually broad range reflects the challenge of separating a nucleus from a dense, bright coma at extreme distances. The uncertainty isn’t a flaw—it’s a lesson.
Scientists are now refining techniques to estimate sizes more precisely before the next interstellar visitor vanishes just as quickly.
A Safe Distance With Strategic Value
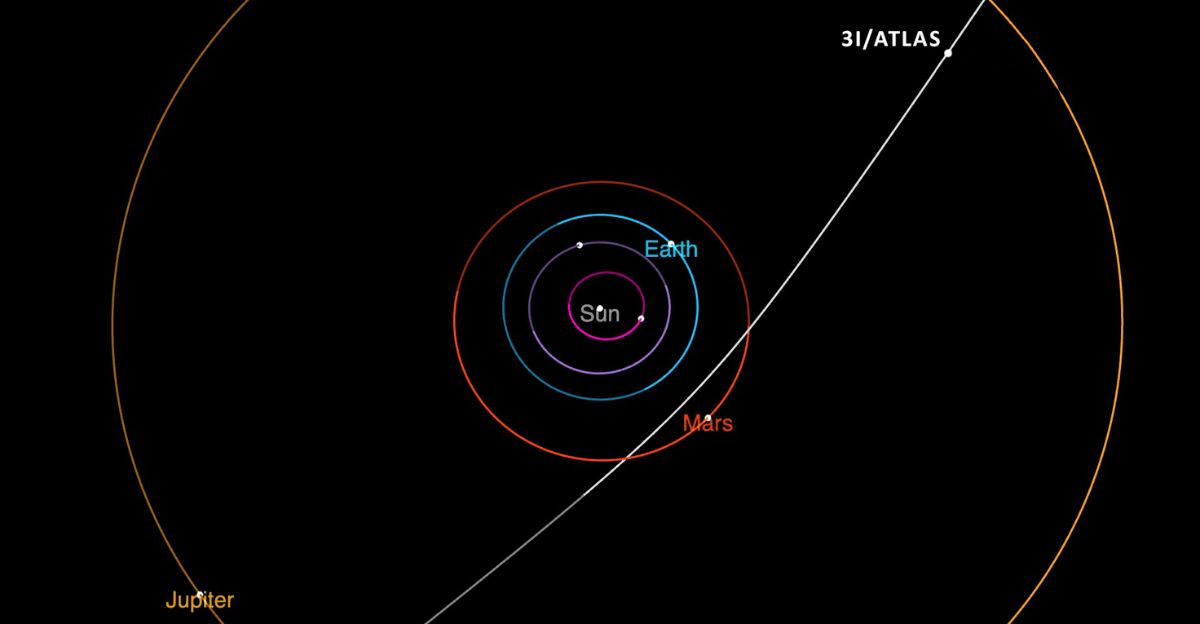
Trajectory models confirmed that 3I/ATLAS never came closer than about 1.8 astronomical units, or 170 million miles, from Earth. There was never any danger. While that distance limited naked-eye viewing, it created an ideal scientific scenario: zero risk, maximum observation time.
Researchers used the opportunity to test how rapidly global observatories could coordinate when faced with a fleeting object from beyond the solar system.
Activity Where Most Comets Stay Frozen

One of the biggest surprises came when 3I/ATLAS developed a coma beyond Jupiter’s orbit, where most comets remain dormant. Scientists linked the activity to highly volatile ices, especially carbon dioxide, which can sublimate far from the Sun.
This behavior challenges thermal models based on solar-system comets and suggests some interstellar bodies may contain ice mixtures unlike anything commonly observed closer to home.
NASA’s Fleet Responds at Record Speed

Within weeks of discovery, more than a dozen NASA assets were observing 3I/ATLAS. These included Hubble, James Webb, SPHEREx, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, spacecraft like Lucy and Psyche, Mars orbiters MAVEN and MRO, the Perseverance rover, and Sun-watching missions STEREO, Parker Solar Probe, SOHO, and PUNCH.
The effort became an unprecedented, multi-wavelength campaign—effectively a rehearsal for how agencies might respond if a future interstellar object presents even rarer or more puzzling characteristics.
Methanol Levels That Shattered Expectations

Spectroscopic studies revealed something extraordinary: methanol made up about 8 percent of the comet’s vapor, roughly four times higher than typical solar-system comets. That translates to approximately 40 kilograms of methanol venting every second.
Methanol is a key organic molecule linked to chemical complexity, and its abundance forces astrochemists to rethink how different planetary systems assemble and preserve carbon-rich materials.
Hydrogen Cyanide Adds a Prebiotic Signal

Alongside methanol, scientists detected hydrogen cyanide (HCN) outgassing from near the nucleus at rates of 250 to 500 grams per second. While toxic to humans, HCN is considered a critical prebiotic molecule in astrochemistry.
The coexistence of HCN and methanol strengthens the idea that interstellar comets could transport life-linked chemistry between star systems, potentially influencing the early chemical environments of young planets.
Possibly the Oldest Comet Ever Observed

Modeling suggests 3I/ATLAS may have spent millions to billions of years drifting through interstellar space before entering the solar system in 2025. If confirmed, it could be among the oldest comets ever studied, preserving chemistry from another star system’s earliest era.
That possibility is driving new research into how radiation, time, and isolation reshape cometary surfaces across galactic timescales.
No Single “Interstellar Chemistry” Blueprint

When scientists compared 3I/ATLAS with 2I/Borisov and native comets, a clear pattern failed to emerge. Instead of uniformity, researchers found striking diversity in methanol, carbon dioxide, and volatile ratios.
The takeaway is sobering: our Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud may not represent a universal standard. Other planetary systems could be producing icy bodies with radically different chemical histories.
A Worldwide Coordination Drill

The global response to 3I/ATLAS became an unplanned rehearsal. Observatories across continents—from optical and infrared telescopes to radio arrays and Mars-orbiting spacecraft—rapidly reallocated time.
Scientists now describe the event as proof that the astronomical community can pivot quickly, track a fast-moving interstellar target, and extract meaningful data before it disappears back into deep space.
From Speculation to Standard Physics
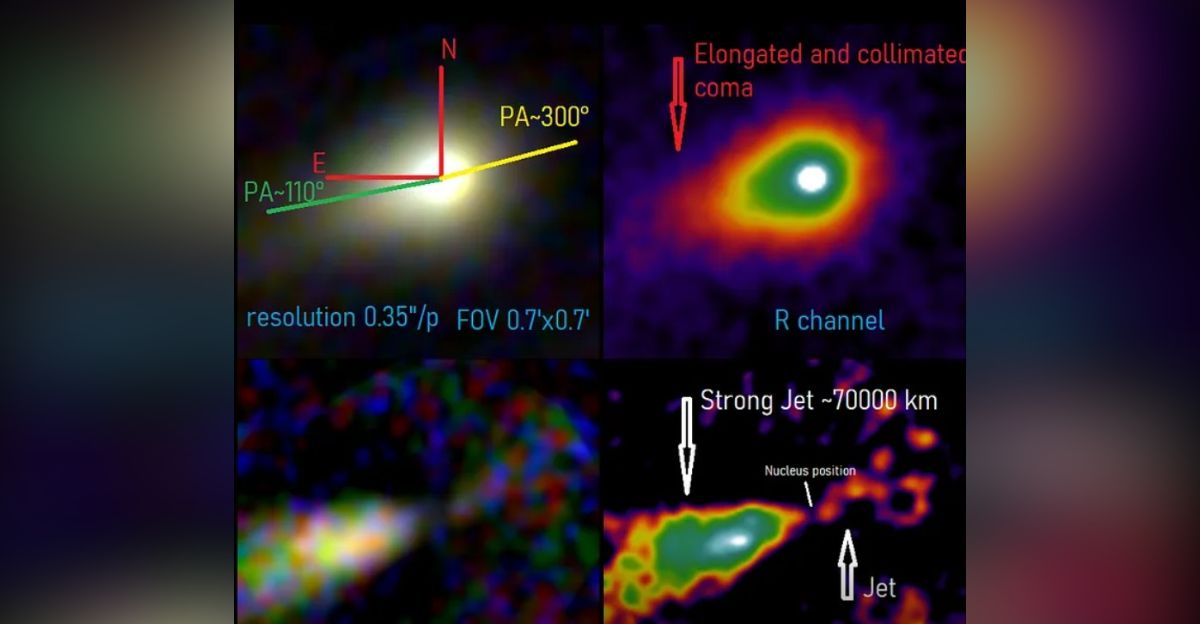
Early brightness and unusual behavior sparked public speculation about artificial origins. Detailed imaging soon revealed a textbook comet: a natural nucleus, classic coma, and volatile-driven outgassing dominated by carbon dioxide.
For researchers, the episode highlighted how unfamiliar phenomena can ignite cultural imagination—even as careful measurements steadily return them to well-understood physical and chemical processes.
A Calm, Methodical SETI Check

Given the attention surrounding interstellar visitors, Breakthrough Listen and partner teams conducted extensive radio searches for technosignatures.
Telescopes including Allen, MeerKAT, Green Bank, and Parkes scanned wide frequency ranges. The result was unambiguous: no artificial signals detected. Every observed emission aligned with expectations for a natural, outgassing comet.
Ruling Out Even Weak Technology

A focused campaign using the Green Bank Telescope pushed sensitivity to remarkable limits. Researchers confirmed they could have detected transmitters emitting less than one-tenth the power of a typical cell phone.
Nothing appeared. While not disproving every exotic scenario, the findings set a new benchmark for how rigorously future interstellar objects can be evaluated using radio astronomy.
A Blueprint for Future Technosignature Searches

The 3I/ATLAS campaign helped formalize a repeatable framework for technosignature investigations. Scientists combined broadband and narrowband scans, cross-checked natural emission models, and coordinated multiple observatories.
Even a null result proved valuable, refining how teams decide which anomalies deserve deeper scrutiny—and which can be explained by physics alone.
Rubin Observatory and What Comes Next

Astronomers expect the Vera C. Rubin Observatory to revolutionize this field. Its decade-long survey could uncover dozens or even hundreds of interstellar objects.
In that future flood of data, 3I/ATLAS will stand as both a baseline and a warning. Its chemistry may be rare—or it may be the first glimpse of a vast, previously invisible population.
A Top Science Story Without an Alien Payoff

Even after confirming its natural origin, major science outlets ranked 3I/ATLAS among 2025’s most significant discoveries. The reason wasn’t spectacle—it was substance.
A visitor from another star system, loaded with complex chemistry, observed in unprecedented detail, reshaped scientific expectations without relying on sensational conclusions.
Why 3I/ATLAS Forces a Scientific Rethink

Taken together—its extreme speed, early carbon-dioxide activity, high methanol content, uncertain size, great age, and null technosignature results—3I/ATLAS doesn’t overturn comet science. It sharpens it.
Models of comet formation, ejection, chemistry, and detection are being revised in real time. When the next interstellar visitor arrives, scientists will be ready—because this one passed through first.
Sources:
“Comet 3I/ATLAS.” NASA Science Solar System Exploration, July 2025.
“CH₃OH and HCN in Interstellar Comet 3I/ATLAS Mapped with the ALMA Atacama Compact Array: Distinct Composition Compared to 2I/Borisov.” arXiv Preprint, November 2025.
“Breakthrough Listen Observations of Interstellar Object 3I/ATLAS.” Breakthrough Listen SETI Research Center, June 2025.
“A newly discovered interstellar object might predate the sun.” Science News, 11 July 2025.